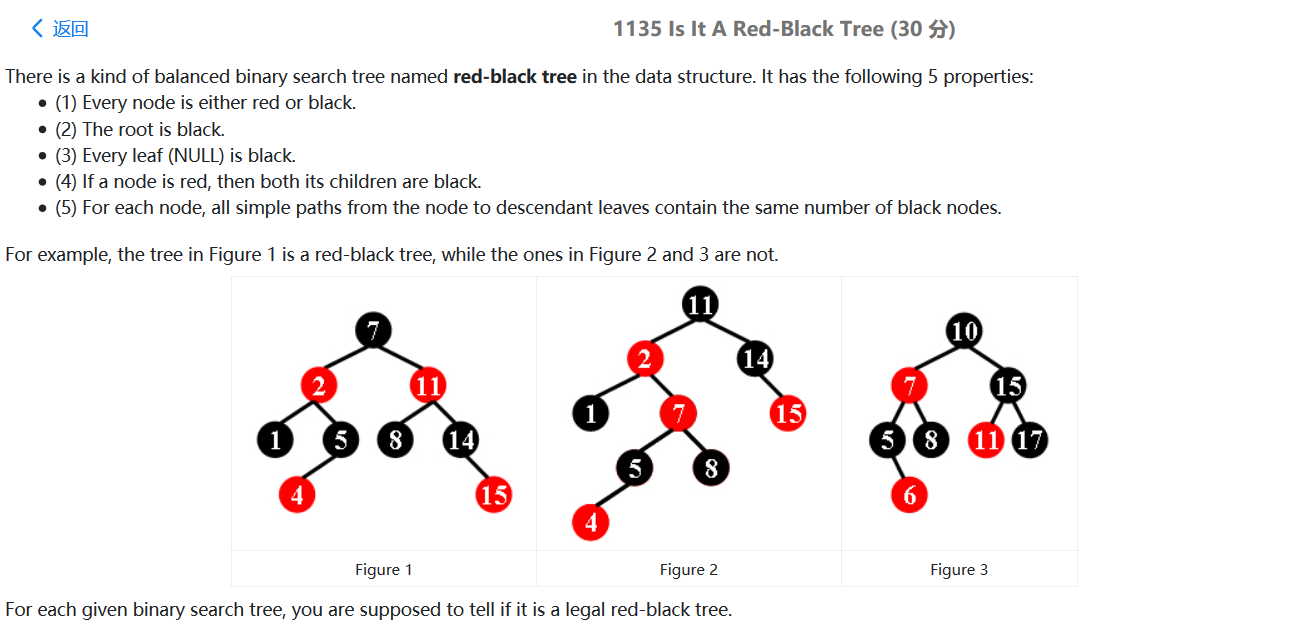
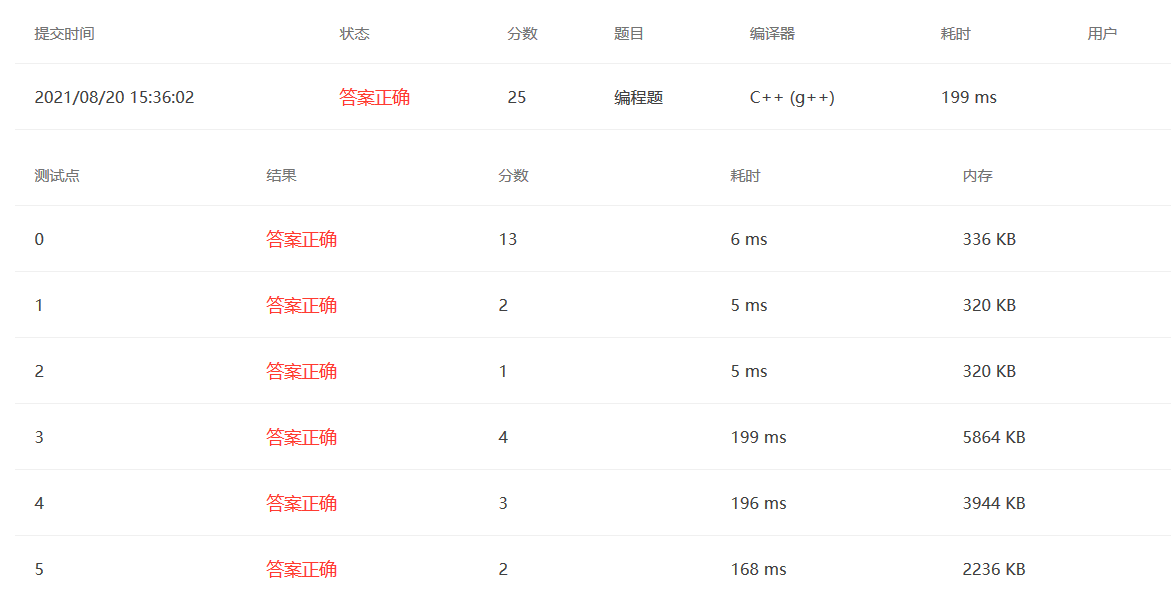
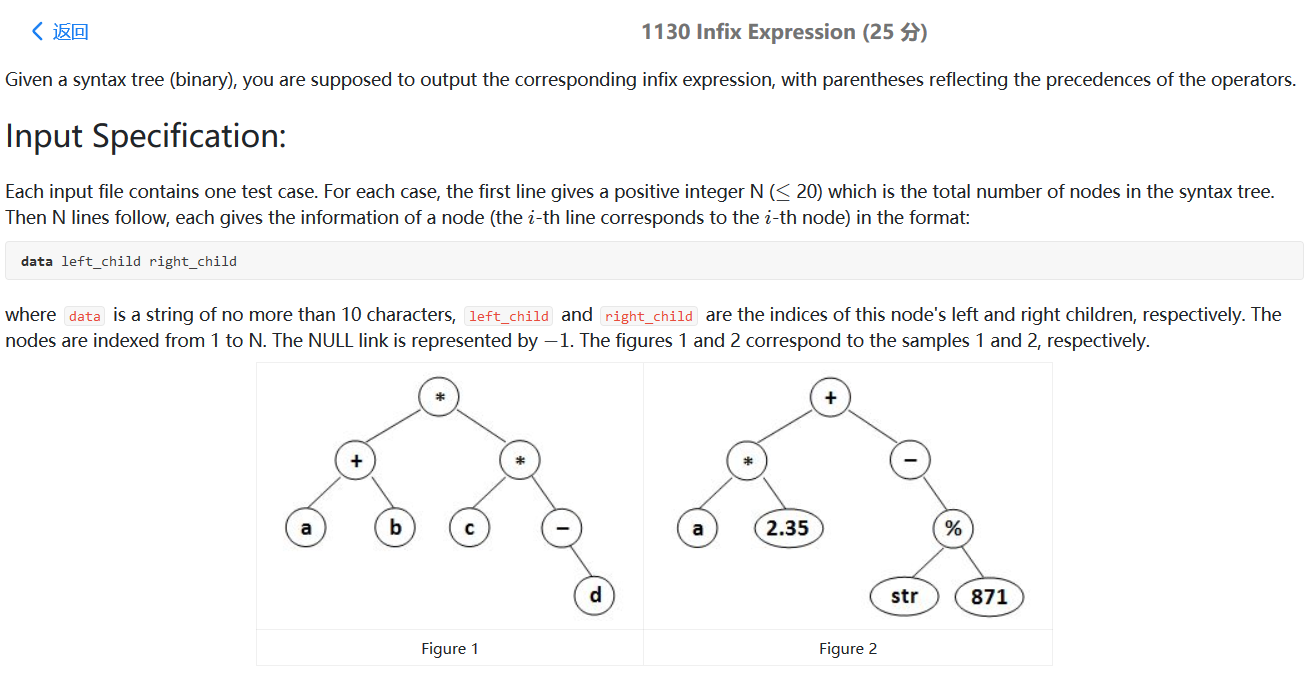
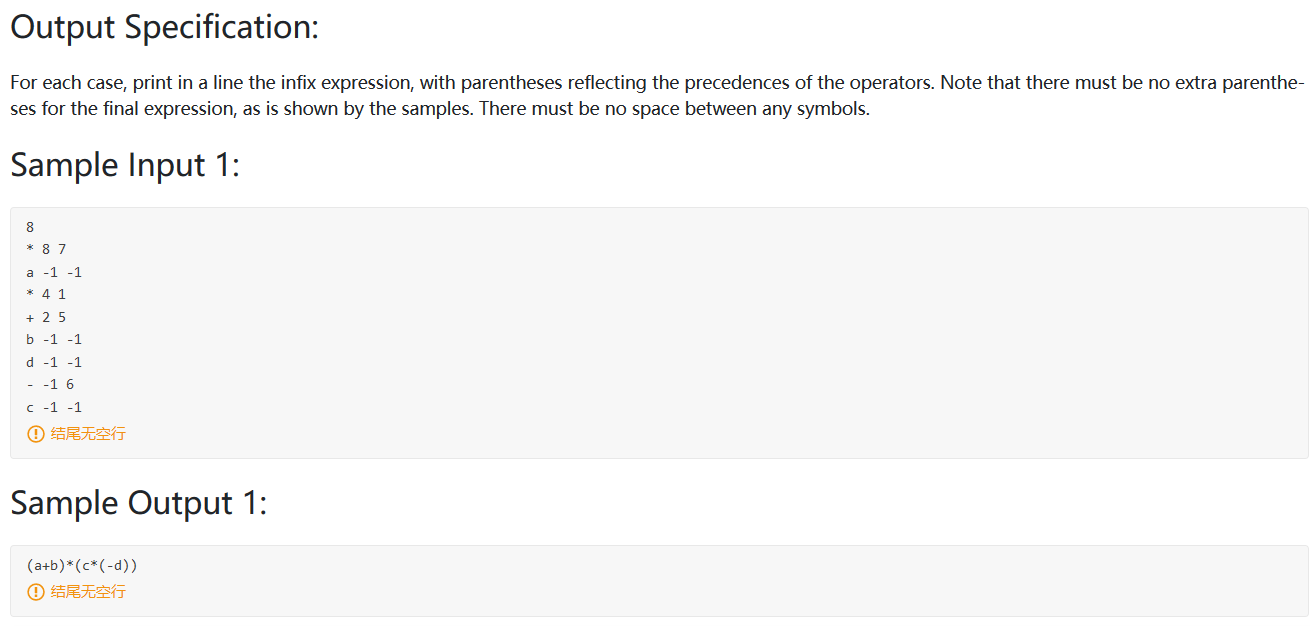
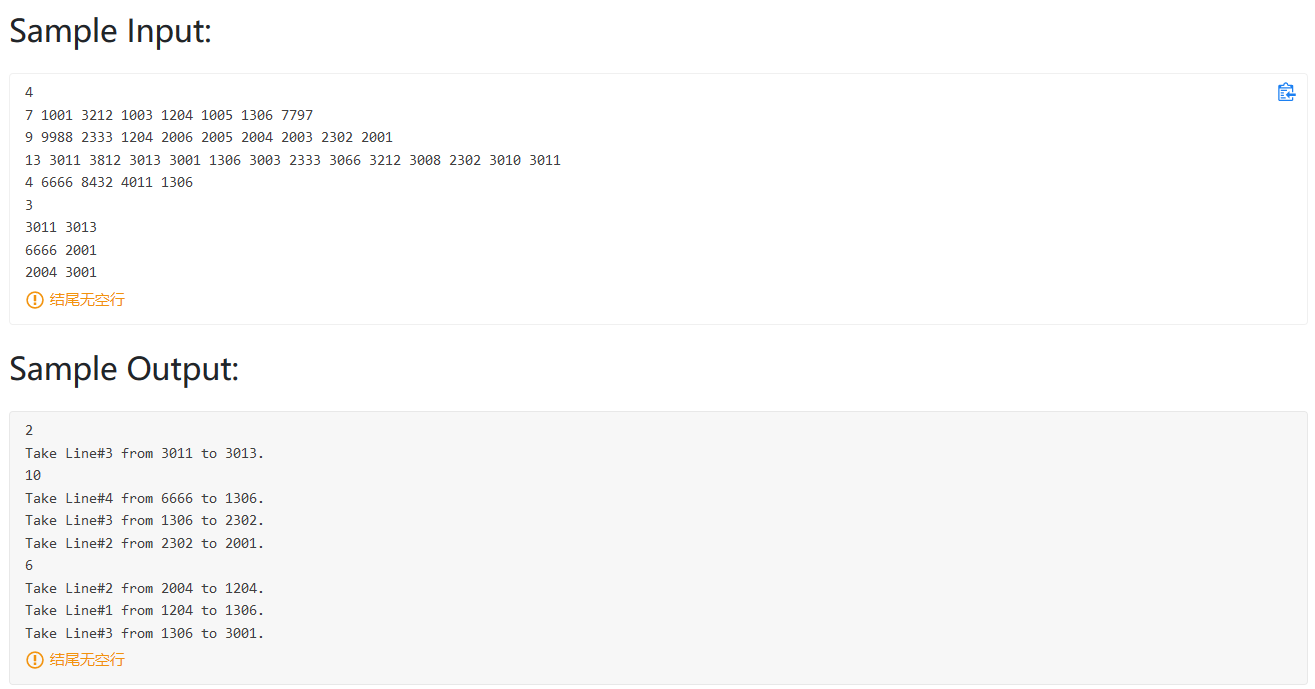
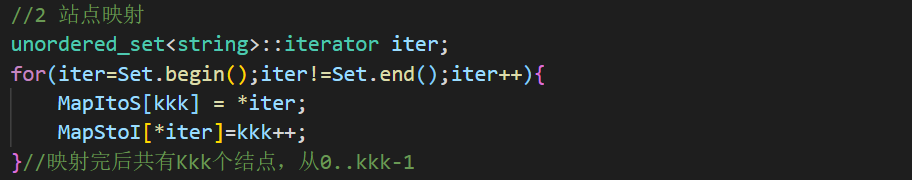
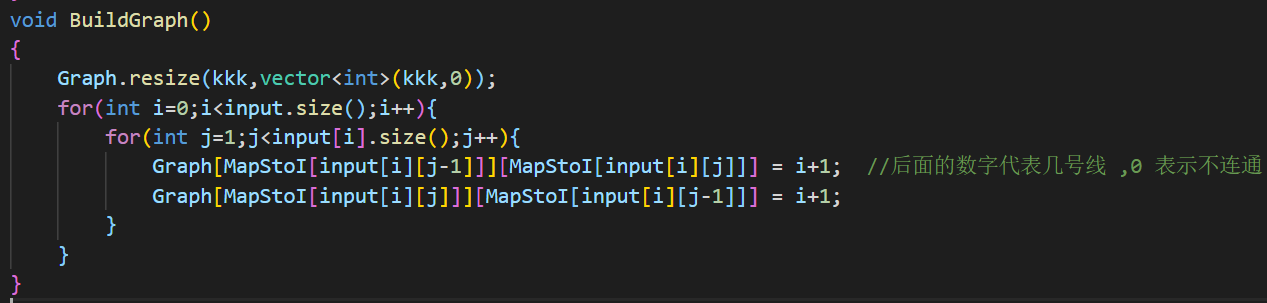
PAT甲级刷题指南 《算法笔记》C++标准模板库(STL)介绍 vector 定义 :变长数组
初始化 :1 2 3 4 5 6 1、vector<int> v(size,0); //初始化为0 2、vector<int> v; v.resize(n,0); //resize一个大小为n,初值为0的可变数组 3、vector<type> v; //不初始化,type可以是一个结构体 4、vector<int> ilist2(v); vector<int> ilist2 = v; //两种方式等价,都是深拷贝 5、vector<int> ilist = {1,2,3.0,4,5,6,7}; //和数组初始化方法一样 6、vector<int> ilist3(ilist.begin()+2,ilist.end()-1); //迭代器初始化
访问 :1 2 3 4 5 6 1、随机访问数组下标访问 v[i] 2、迭代器访问数组 vector<int>::iterator iter; for(iter = vi.begin();iter != vi.end();iter++){ cout<<*iter<<" "; }
常用函数 :1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 1、插入push_back v.push_back(i); 2、删除pop_back v.pop_back(); //删除最后一个元素,回溯的时候常用 3、大小size v.size(); //获取数组大小 4、清空clear v.clear(); //清空数组 5、插入insert //尽量不要频繁使用这个函数,会引起大量数据移动,降低程序效率 v.insert(v.begin(),8);//在最前面插入新元素 v.insert(v.begin()+3,1);//在迭代器中下标为3的元素前插入新元素 v.insert(v.end(),3);//在向量末尾追加新元素 v.insert(v.end(),3,0);//在尾部插入3个0 6、删除erase //erase函数有两种函数原型,一种是给定要删除的位置,另一种是给定删除的区域。 有两种函数原型,c.erase (p),c.erase(b,e);第一个删除迭代器p所指向的元素,第二个删除迭代器b,e所标记的范围内的元素,c为容器对象,返回值都是一个迭代器,该迭代器指向被删除元素后面的元素(这个是重点) 应用一:删除连续数字 //但是这种代码也是存在缺陷的,首先是我们无法连续删除数字3,其次是迭代器在指向vec.end()的时候,还会进行一次++,这就发生了数组越界,所以我们一概这样修改: for(auto iter=vec.begin();iter!=vec.end(); iter++) { if(*iter == 3) iter = veci.erase(iter); } //可以删除连续的数字3 for(auto iter=vec.begin();iter!=vec.end(); ) { if( *iter == 3) iter = veci.erase(iter);//当删除时erase函数自动指向下一个位置,就不需要进行++ else iter ++ ; //当没有进行删除的时候,迭代器++ } //另一种解决无法删除连续的数字的方法 我们先介绍一下remove函数: remove是个stl的通用算法std::remove(first,last,val)移除[first, last)范围内等于val的元素在vector里面用就类似于 iter=std::remove(vec.begin(), vec.end(), val)但这个函数只是把val移到vec的末尾,并不真正删除,真正删除还是要调用一次erase函数 veci.erase(remove(vec.begin(),vec.end(),3),vec.end()); 应用二:删除重复数字,顺序不发生变化 如果不要求顺序的话,我们可以直接调用unique函数进行操作,这里介绍一下unique函数:从头到尾,判断当前元素是否等于上一个元素,将不重复的元素移到前面来(赋值操作),而不是将重复的元素移动到后面去。 vec.erase(unique(vec.begin(),vec.end()),vec.end()) //将重复的区域删除,顺序会改变
常见错误 :
set 定义 :是一个内部自动有序且不含重复元素的容器
unordered_set 无序 其余和set的用法一样,效率更高
初始化: 1 2 3 4 5 set<T> s; set<T> s(b, e); 比如: int arr[]={1,2,3,4,3,2,1}; set<int> iset(arr,arr+sizeof(arr)/sizeof(*arr));
访问 :1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1、迭代器访问 set<int> st; set<int>::iterator it for(it = st.begin();it != st.end();it++){ printf("%d ",*it); } 2、随机访问 在set中查找2,返回其迭代器 set<int>::iterator it = st.find(2); printf("%d ",*it);
常用函数: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 set<int> st; 1、插入 insert() st.insert(3); 2、查找 find() set<int>::iterator it = st.find(2); if(st.find(2)==st.end()) printf("没找到"); 3、删除 erase() st.erase(it) it为需要删除元素的迭代器,复杂度O(1) st.erase(value) value为要删除元素的值,复杂度O(logN) st.erase(st.find(2)); st.erase(2),效果一致,两种用法 4、获取元素个数 size() cout<<<<st.size()<<endl; 5、清空 clear() st.clear(); 6、判空 empty() st.empty()
string 定义: 字符串
初始化: 1 2 3 4 1、string s1; s1为空字符串 2、string s2("ABC"); 用字符串字面值初始化s2 3、string s3(s2); 用s3初始化为s2的一个副本 4、string s4(n,'c'); 将s4初始化为字符'c'的n个副本
访问: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1、通过下标访问 string str = "abcd"; for(int i=0;i < str.length();i++){ printf("%c",str[i]); } 2、通过迭代器访问 cout<<"通过迭代器访问如下:"<<endl; for(string::iterator;it=str.begin();it!=str.end();it++){ printf("%c",*it); }
常用函数: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 1、判空 s.empty() 2、统计字符个数 s.size() / s.length() 3、拼接字符串 += str3 = str1+str2; //拼接后再赋值 str1 += str2; //直接接在后面,效率更高 4、字符串比较大小 == != >=等等 5、插入 insert() insert(pos,string) 在pos位置插入string insert(it,it2,it3) 在it位置插入 [it2,it3)的串,it2,it3为待插字符串的首尾迭代器 str1 = "abcxyz"; str2 = "opq"; //insert(pos,string) str1.insert(3,str2); cout<<"abcxyz字符串第三个位置插入opq字符串后变为:"<<str1<<endl; str1.insert(str1.begin()+3,str2.begin(),str2.end()); //insert(it,it2,it3) cout<<"abcopqxyz字符串第三个位置插入opq字符串后变为:"<<str1<<endl; 6、删除单个元素、区间元素 erase() 删除单个元素 str.erase(it) it为删除元素的迭代器 删除一个区间内的所有元素 str.erase(first,last) [first,last) str.erase(pos,length) pos为开始位置,length为长度 str1 = "abcopqopqxyz"; str1.erase(str1.begin()+3);//str.erase(it)删除4号位o cout<<"abcopqopqxyz字符串删除第四个位置o字符串后变为:"<<str1<<endl; str1.erase(str1.begin()+3,str1.end()-3);//str.erase(first,last) cout<<"abcpqopqxyz字符串删除第4~8位置字符后变为:"<<str1<<endl; str1.erase(3,3);//str.erase(ipos,length) cout<<"abcxyz字符串删除从第4位置开始的3个字符后变为:"<<str1<<endl; 7、清空 clear() str1.clear(); 8、子串 substr() substr(pos,len) 返回从pos号开始,长度为len子串 str1 = "abcxyz"; cout<<"abcxyz字符串从下标2开始长度为3的子串为:"<<str1.substr(2,3)<<endl; 9、查找 find() str.find(str2) 当str2是str的子串时,返回其在str中第一次出现的位置,如果str2不是str的子串,返回string::npos(常数) str.find(str2,pos) 从str的pos号位置开始匹配str2,返回指相同 str1 = "abcxyz",str2="xyz"; cout<<"xyz子串在abcxyz中第一次出现的位置为:"<<str1.find(str2)<<endl; position = s.find("jk"); if (position != s.npos) printf("position is : %d\n" ,position); //查找成功 else printf("Not found the flag\n"); //查找失败 10、替换 replace() str.replace(pos,len,str2) 把str从pos号开始,长度为len的子串替换为str2 str.replace(it1,it2,str) 把str的迭代器[it1,it2)返回的子串替换为str2 str1 = "Maybe you will turn around."; str2 = "will not";str3 = "surely"; cout<<"Maybe you will turn around.字符串从第10位开始的4位替换为str2后为:"; cout<<str1.replace(10,4,str2)<<endl; cout<<"Maybe you will not turn around.字符串从起始位开始的5位替换为str3后为:"; cout<<str1.replace(str1.begin(),str1.begin()+5,str3)<<endl;
string和char[]的转换 1 2 3 4 5 1、string转char* printf("%s",str.c_str()); 2、char* 转string char* p = "abc"; string s = p;
string和int等类型的转换 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 转string: string to_string (int val); string to_string (long val); string to_string (long long val); string to_string (unsigned val); string to_string (unsigned long val); string to_string (unsigned long long val); string to_string (float val); string to_string (double val); string to_string (long double val); 转Int stoi(str1); //int stof(str1); //float stoll(str1); //long long
大小写转换 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 #include <string> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; int main() { string strA = "yasaken@126.com"; string strB = "LURY@LENOVO.com"; printf("Before transform:\n"); printf("strA:%s \n", strA.c_str()); printf("strB:%s \n\n", strB.c_str()); transform(strA.begin(), strA.end(), strA.begin(), ::toupper); transform(strB.begin(), strB.end(), strB.begin(), ::toupper); printf("After transform to toupper:\n"); printf("strA:%s \n", strA.c_str()); printf("strB:%s \n\n", strB.c_str()); transform(strA.begin(), strA.end(), strA.begin(), ::tolower); transform(strB.begin(), strB.end(), strB.begin(), ::tolower); printf("After transform to lower:\n"); printf("strA:%s \n", strA.c_str()); printf("strB:%s \n\n", strB.c_str()); return 0; }
map 定义: map即映射,是常用的STL容器,它可以将任何基本类型(包括STL容器)映射到任何基本类型(包括STL容器)。
uordered_map无序容器,效率更高
初始化: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1、直接赋值 map<string, int> m1; m1[string("abc")] ++; //如果“abc"已经存在,会在原来的基础上++,如果不存在,则会创建一个hash_key 2、用insert添加 map<string, int> m2; m2.insert({ string("abc"), 1 }); m2.insert(make_pair(string("defg"), 2)); m2.insert(pair<string, int>(string("hijk"), 3));
访问: map会以键从小到大的顺序自动排序,unordered_map则不会排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 1、通过key访问value map<char,int> mp; //通过下标访问 mp['c'] = 20; mp['c'] = 30;//20被覆盖 printf("%d\n",mp['c']);//输出30 2、通过迭代器访问 for(map<char,int>::iterator it = mp.begin();it != mp.end();it++){ //it->first是当前映射的键;it->second是当前映射的值 printf("%c %d\n",it->first,it->second); }
常用函数: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 1、查找 find() if(M.find(exponent)!=M.end()){ printf("%d",M[exponent]); }else{ printf("没找到"); } map<char,int>::iterator it = mp.find('b'); printf("%c %d\n",it->first,it->second); 2、删除 erase mp.erase(key); key为想要删除的键 mp.erase(first,last); 删除一个区间内的元素,first,last为迭代器 it = mp.find('m'); mp.erase(it);//删除b 2 mp.erase('r');//删除b 2 3、获取大小 size() cout<<"此时map的长度为:"<<mp.size(); 4、清空 clear() mp.clear();
multimap: multimap 和 map 很相似,但是 multimap 允许重复的元素。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 multimap<int, string> multi_map; // 可实现多重映射 multimap.insert({ 520, "huameng" }); multimap.insert({ 520, "huameng1" }); multimap.insert({ 520, "huameng2" }); for (auto& i: multi_map) { cout << i.first << " " << i.second << endl; } 520 huameng 520 huameng1 520 huameng2
queue 定义: Queue翻译为队列,理解为一个先进先出的容器
queue初始化: 1 queue<int> first; // empty queue
访问: 1 2 3 访问队首元素:如q.front() 访问队尾元素,如q.back(); printf("%d %d\n",q.front(),q.back());
常用函数: 1 2 3 4 size()-容器大小 empty()-容器判空 push()尾部增加元素 pop()删除尾部元素
priority_queue: 在< queue>头文件中,还定义了一个非常有用的模版类priority_queue(优先队列),优先队列与队列的差别在于优先队列不是按照入队的顺序出队,而是按照队列中元素的优先权顺序出队(默认为大者优先,也可以通过指定算子来指定自己的优先顺序)。
priority_queue模版类有三个模版参数,元素类型,容器类型,比较算子。其中后两个都可以省略,默认容器为vector,默认算子为less,即小的往前排,大的往后排(出队时序列尾的元素出队)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 定义priority_queue对象 priority_queue<int >q1; priority_queue<pair<int,int> >q2; priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >q3;//定义小的先出队 //其中第二个参数( vector ),是来承载底层数据结构堆的容器,第三个参数( less ),则是一个比较类, //less 表示数字大的优先级高,而 greater 表示数字小的优先级高
priority_queue的基本操作均与queue相同,优先队列没有back()操作
1 2 3 4 5 q.size();//返回q里元素个数 q.empty();//返回q是否为空,空则返回1,否则返回0 q.push(k);//在q的末尾插入k q.pop();//删掉q的第一个元素 q.top();//返回q的第一个元素
操作示例1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 #include <iostream> #include <queue> using namespace std;int main () priority_queue<int > q; q.push (3 ); q.push (4 ); q.push (1 ); cout<<"优先队列341的队首为:" ; printf ("%d\n" ,q.top ()); q.pop (); cout<<"弹出队首元素后优先队列的队首为:" ; printf ("%d\n" ,q.top ()); cout<<"此时队列为空吗?" <<endl; if (q.empty () == true )printf ("Empty\n" ); else printf ("Not Empty\n" ); cout<<"此时队列大小为:" <<q.size ()<<endl; return 0 ; }
优先级操作示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 #include <iostream> #include <queue> using namespace std;int main () priority_queue<int ,vector<int >,less<int > > q; q.push (3 ); q.push (4 ); q.push (1 ); printf ("%d\n" ,q.top ()); return 0 ; }
结构体优先级的设置:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 #include <iostream> #include <queue> using namespace std;struct fruit { string name; int price; friend bool operator < (fruit f1,fruit f2){ return f1.price < f2.price; } }f1,f2,f3; int main () priority_queue<fruit> q; f1.name = "桃子" ; f1.price = 3 ; f2.name = "梨子" ; f2.price = 4 ; f3.name = "苹果" ; f3.price = 1 ; q.push (f1); q.push (f2); q.push (f3); cout<<q.top ().name<<" " <<q.top ().price<<endl; return 0 ; }
也可以类似Cmp写在外面
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 #include <iostream> #include <queue> using namespace std;struct fruit { string name; int price; friend bool operator < (fruit f1,fruit f2){ return f1.price < f2.price; } }f1,f2,f3; struct cmp { bool operator () (fruit f1,fruit f2) return f1.price > f2.price; } }; int main () priority_queue<fruit> q; f1.name = "桃子" ; f1.price = 3 ; f2.name = "梨子" ; f2.price = 4 ; f3.name = "苹果" ; f3.price = 1 ; q.push (f1); q.push (f2); q.push (f3); cout<<q.top ().name<<" " <<q.top ().price<<endl; priority_queue<fruit,vector<fruit>,cmp> qq; f1.name = "桃子" ; f1.price = 3 ; f2.name = "梨子" ; f2.price = 4 ; f3.name = "苹果" ; f3.price = 1 ; qq.push (f1); qq.push (f2); qq.push (f3); cout<<qq.top ().name<<" " <<qq.top ().price<<endl; return 0 ; }
stack 定义: stack即栈,是一种先进后出的容器,区别于queue;
初始化: 访问: 常用函数: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 push() 压栈 top() 取栈顶元素 pop() 出栈 empty() 判空 size() 获取大小 //---1、2、3---push()、top()、pop() for(int i = 1;i <= 5;i++){ st.push(i);//将i压入栈 } cout<<"入栈12345的栈顶为:"; cout<<st.top()<<endl; for(int i = 1;i <= 3;i++){ st.pop(); } cout<<"出栈3个元素后栈顶为:"; printf("%d\n",st.top()); //---4---empty() cout<<"此时栈为空吗?"<<endl; if(st.empty() == true) printf("Empty\n"); else printf("Not Empty\n"); //---5---size() cout<<"此时队列大小为:"<<st.size()<<endl;
pair 定义: Pair可以看作一个内部有两个元素的结构体,且这两个元素的类型可以指定
初始化: 1 2 3 pair<int, double> p1; //使用默认构造函数 pair<int, double> p2(1, 2.4); //用给定值初始化 pair<int, double> p3(p2); //拷贝构造函数
访问: 1 2 3 4 pair<int, double> p1; //使用默认构造函数 p1.first = 1; p1.second = 2.5; cout << p1.first << ' ' << p1.second << endl;
常用函数: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 1、比较操作数 <.>,<=,== //比较规则是先比较first,再比较second int main(){ pair<int,int> p1(5,10); pair<int,int> p2(5,15); pair<int,int> p3(10,5); if(p1 < p3) printf("p1 < p3\n"); if(p1 <= p3) printf("p1 <= p3\n"); if(p1 < p2) printf("p1 < p2\n"); return 0; } 2、make_pair 赋值 pair <string,double> product1 ("tomatoes",3.25); pair <string,double> product2; pair <string,double> product3; product2.first ="lightbulbs"; // type of first is string product2.second =0.99; // type of second is double product3 = make_pair ("shoes",20.0);
常用于作为map的键值对进行插入: 1 2 3 4 map<string,int> mp; //pair作为map键值对进行插入 mp.insert(make_pair("heihei",5)); mp.insert(pair<string,int>("haha",10));
algorithm常用函数 max()、min()、abs() 最大值、最小值、绝对值
1 2 3 int x=1,y=-2; printf("%d %d\n",max(x,y),min(x,y)); printf("%d %d\n",abs(x),abs(y));
swap 交换两个元素的值
1 2 3 int x=1,y=2; swap(x,y); printf("%d %d\n",x,y);
reverse() 1.会将区间内的元素全部逆序。常用于数组,字符串,容器等,其本身的函数参数也不复杂。
1 2 3 4 vector<int> v = {5,4,3,2,1}; reverse(v.begin(),v.end());//v的值为1,2,3,4,5 string str="www.mathor.top"; reverse(str.begin(),str.end());//str结果为pot.rohtam.wwww
fill() 1.按照单元赋值,将一个区间的元素都赋同一个值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 int arr[10]; fill(arr, arr + 10, 2); vector<int> v{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}; fill(v.begin(), v.end(), -1); vector<int> myvector (8);// myvector: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 fill (myvector.begin(),myvector.begin()+4,5); // myvector: 5 5 5 5 0 0 0 0 fill (myvector.begin()+3,myvector.end()-2,8); // myvector: 5 5 5 8 8 8 0 0
sort() 1.Sort函数有三个参数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 1、数组排序 int IntValue[5] = {1,4,3,8,5}; sort(IntValue,IntValue+5); for(int i=0;i<5;i++){ cout<<IntValue[i]<<" "; } 2、vector排序 vector<int> v = {2,6,4,9,6,0,3}; sort(v.begin(),v.end()); vector<int>::iterator start; for(start = v.begin();start!=v.end();start++){ cout<<(*start)<<" "; } 3、自定义排序 #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; /* linli1 20 linli2 24 linli6 8 linli3 8 * */ typedef struct stu{ string name; int age; }stu; bool cmp(stu u,stu g){ //<表示升序排序 if(u.age==g.age){ return u.name<g.name; } return u.age<g.age; } int main(){ vector<stu> v; for(int i=0;i<4;i++){ stu c ; cin>>c.name>>c.age; v.push_back(c); } sort(v.begin(),v.end(),cmp); vector<stu>::iterator start; for(start = v.begin();start!=v.end();start++){ cout<<(*start).name<<" "; } }
lower_bound()和upper_bound() lower_bound:
功能:查找非递减序列[first,last) 内第一个大于或等于某个元素的位置。
返回值:如果找到返回找到元素的地址否则返回last的地址。(这样不注意的话会越界,小心)
用法:int t=lower_bound(a+l,a+r,key)-a;(a是数组)。
upper_bound:
功能:查找非递减序列[first,last) 内第一个大于某个元素的位置。
返回值:如果找到返回找到元素的地址否则返回last的地址。(同样这样不注意的话会越界,小心)
用法:int t=upper_bound(a+l,a+r,key)-a;(a是数组)。
1 2 3 int board[5] = {1,2,3,4,5}; int t1 = lower_bound(board,board+5,3)-board; //2 int t2 = upper_bound(board,board+5,3)-board; //3
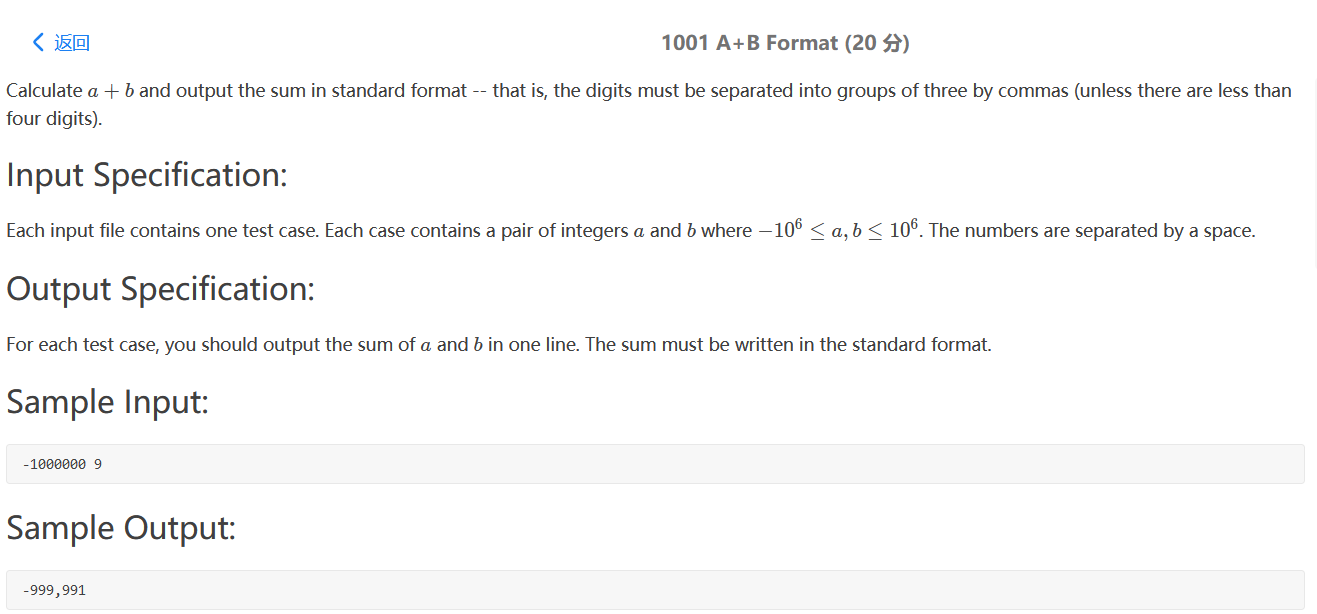
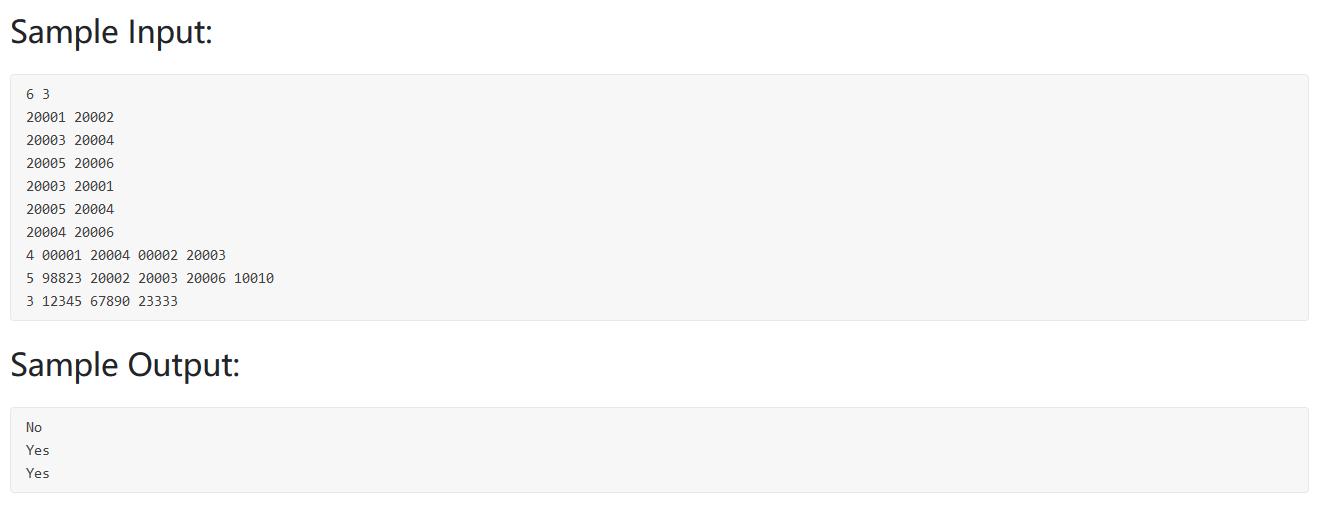
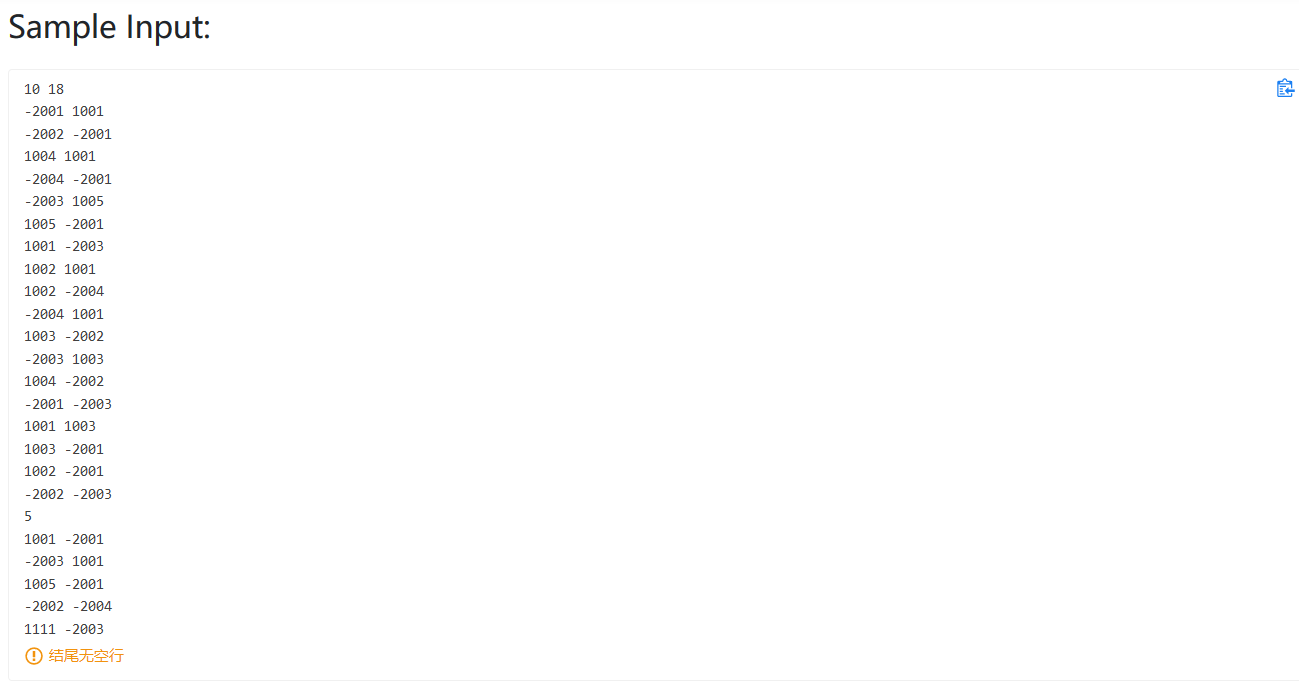
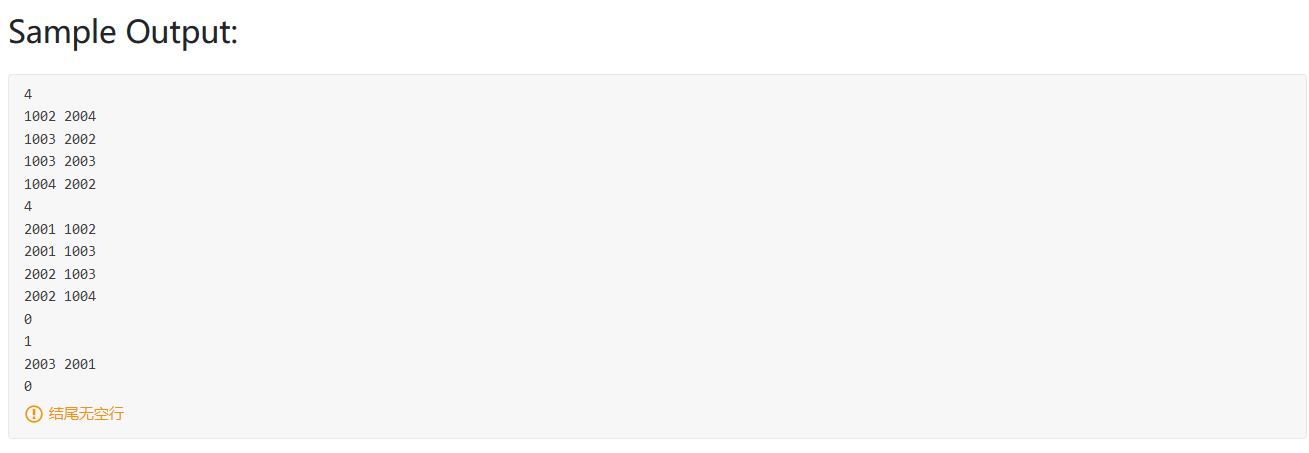
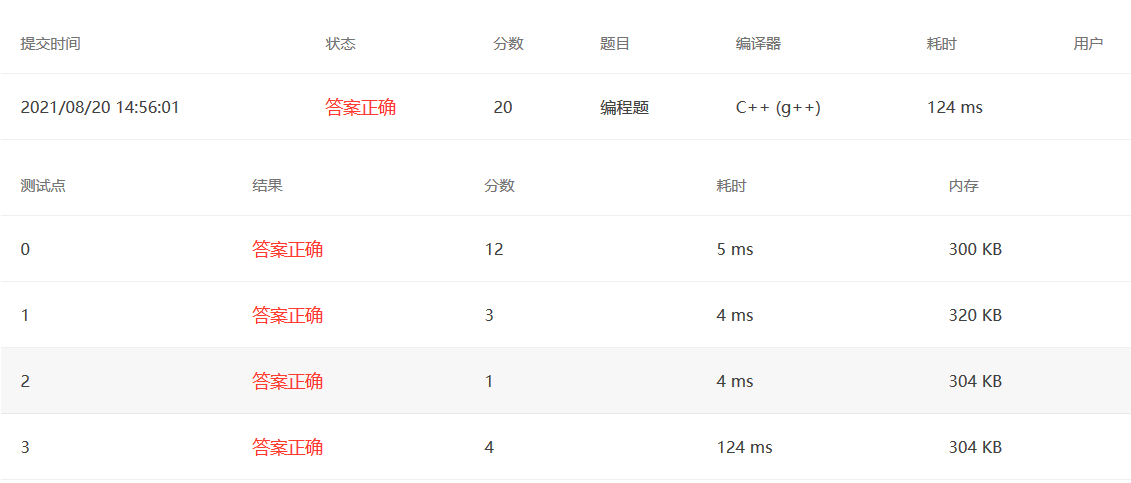
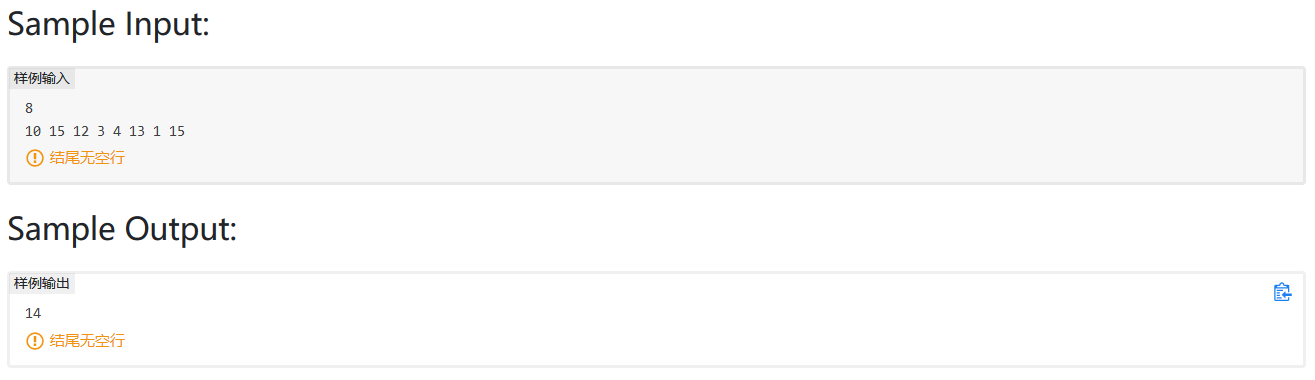
PAT真题模拟 PAT 1001
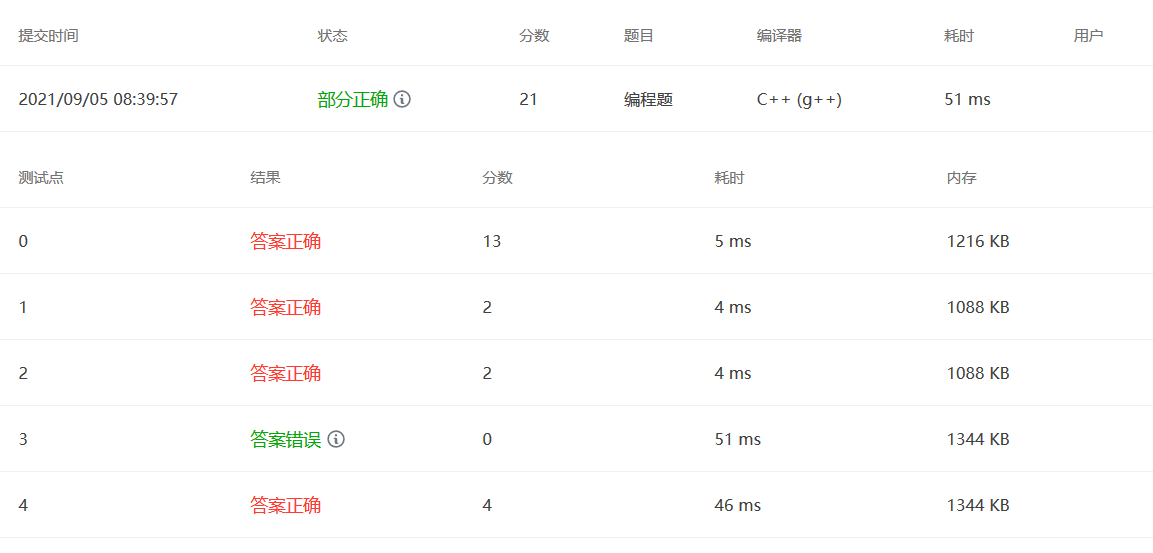
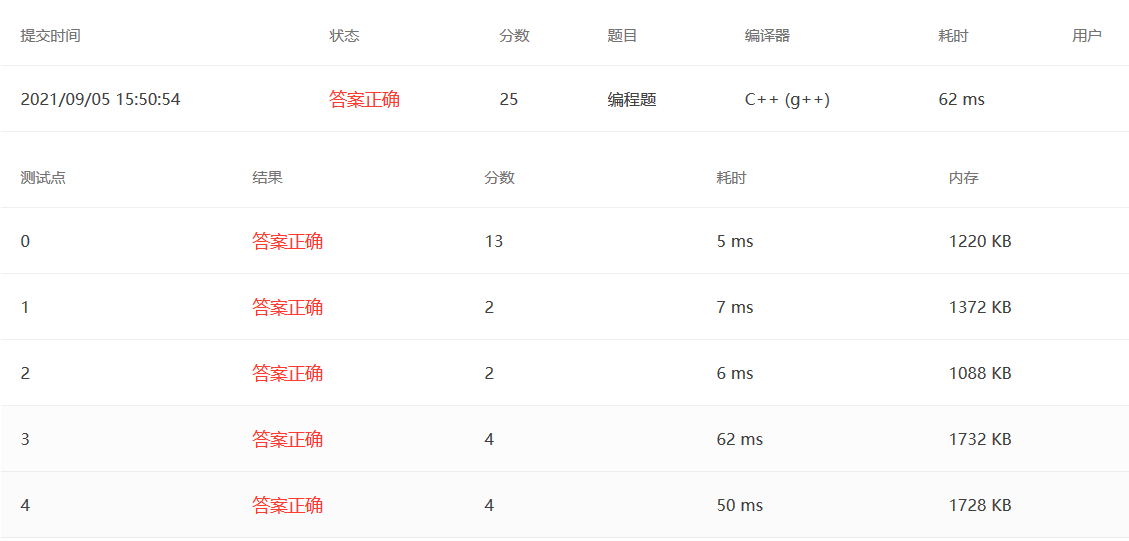
我的做法,难点在于如何3位3位加一个逗号,我用栈来存储。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main () int a, b; cin >> a >> b; int c = a + b; int cishu; string s = to_string (c); stack<char > st; int flag = 0 ; for (int i = s.length () - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { st.push (s[i]); flag++; if (flag == 3 && i != 0 && s[i - 1 ] != '-' ) { st.push (',' ); flag = 0 ; } } while (!st.empty ()) { cout << st.top (); st.pop (); } return 0 ; }
大神的做法见注释,好像比较难想到。
PAT 1002
多项式加法,通过第一个测试点不是很难。
注意点: 系数为0时不进行输出。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main () map<int ,double > M; int n,m; cin>>n; int a; double b; for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++){ cin>>a>>b; M[a] = b; } cin>>m; for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++){ cin>>a>>b; if (M.find (a)!=M.end ()) M[a] += b; else M[a] = b; } map<int ,double >::reverse_iterator iter; int size = 0 ; for (iter = M.rbegin ();iter!=M.rend ();iter++){ if (iter->second!=0 ) size++; } cout<<size; for (iter = M.rbegin ();iter!=M.rend ();iter++){ if (iter->second!=0 ){ cout<<" " <<iter->first<<" " ; printf ("%.1lf" ,iter->second); } } }
具体还有两个未通过也不知道是怎么回事
map的倒叙遍历需要掌握
1 2 3 4 5 6 for (iter = M.rbegin ();iter!=M.rend ();iter++){ if (iter->second!=0 ){ cout<<" " <<iter->first<<" " ; printf ("%.1lf" ,iter->second); } }
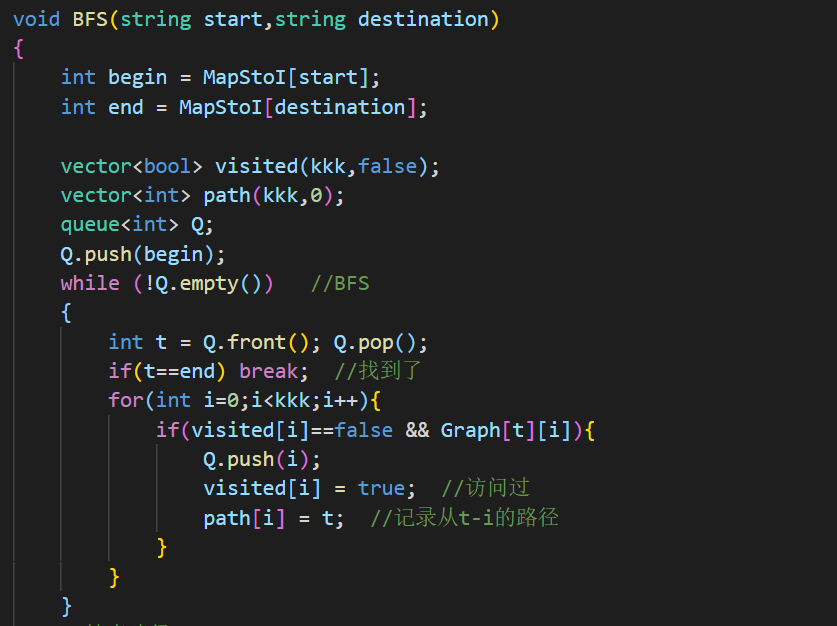
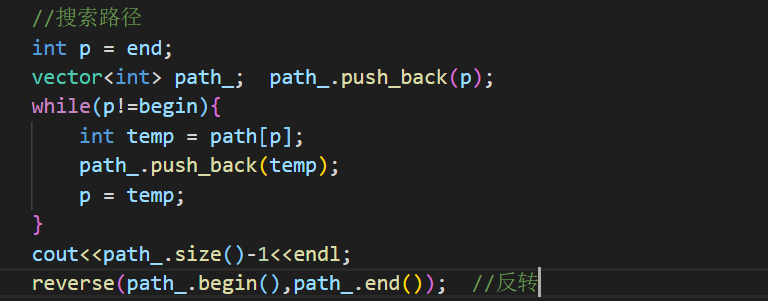
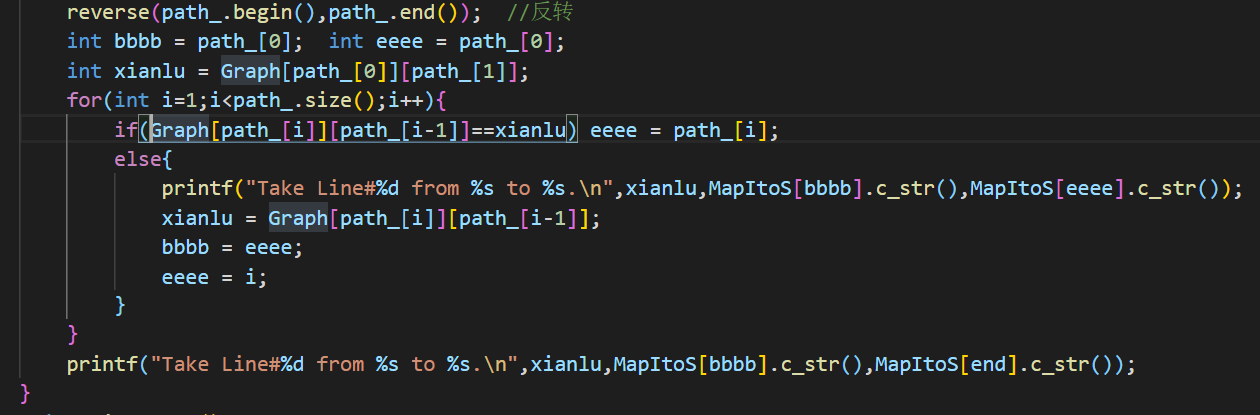
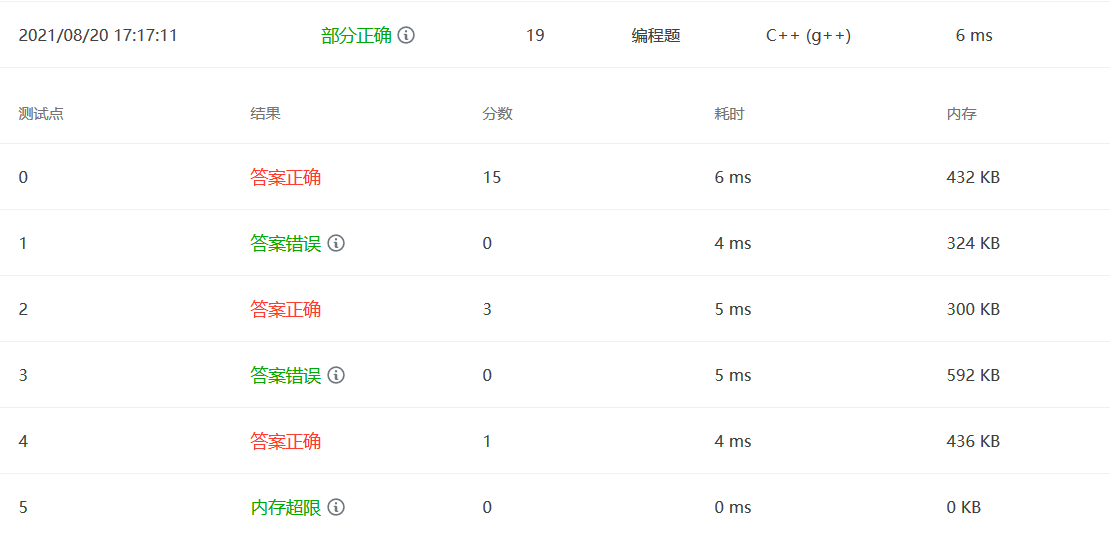
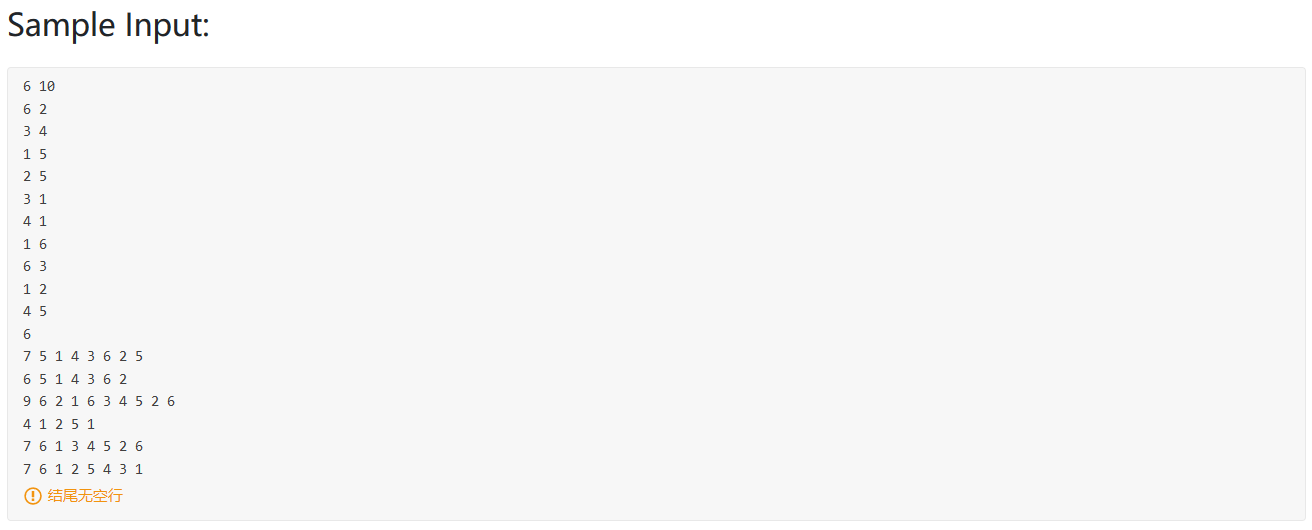
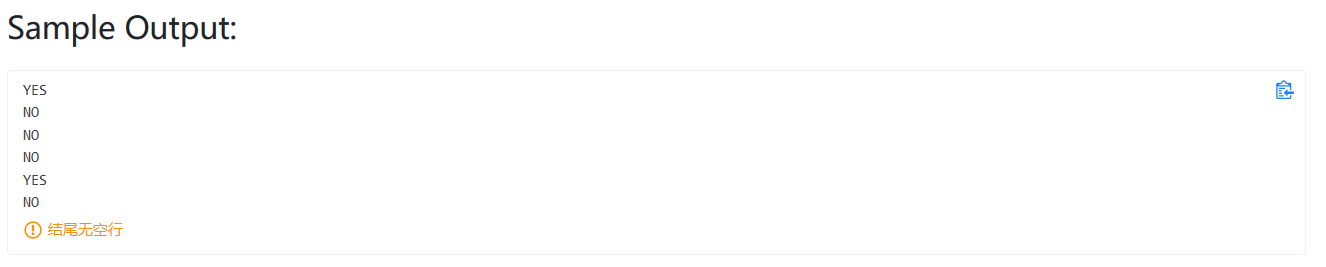
PAT 1003 (dijstra)
题目翻译:
你是一个救援队长,你要救援有危险的城市,你需要尽可能快的到达有危险的城市,并且带尽可能多的人。
输入:
第1行:4个正整数: 城市数量N、 路数量M、你在的城市、你要救援的城市。
第2行:N个整数,第i个数表示第i个城市的救援队数量。
然后M行:每一行表示一条路,三个数字分别是起点、终点、距离。
保证至少有一条路让你去你要救援的城市。
输出:
最短路径条数 可带的最多人数 (我输出理解成了最短路径长度…)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int *dist; int *visited; int *rescue; int **e; int *pre; int *rm; int *num_of_shortest; int N,M,C1,C2;int maxrescue = 0 ; void init () dist = new int [N]; visited = new int [N]; memset (visited,0 ,sizeof (visited)); rescue = new int [N]; pre = new int [N]; memset (pre,-1 ,sizeof (pre)); rm = new int [N]; memset (rm,0 ,sizeof (rm)); num_of_shortest = new int [N]; for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++){ cin>>rescue[i]; } e = new int *[N]; for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++){ e[i] = new int [N]; } for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++) for (int j=0 ;j<N;j++){ if (i==j) e[i][j]=0 ; else e[i][j]=9999 ; } for (int i=0 ;i<M;i++){ int c1,c2,length; cin>>c1>>c2>>length; e[c1][c2] = length; } } void dijstra () visited[C1] = 1 ; num_of_shortest[C1] = 1 ; rm[C1] = rescue[C1]; for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++){ dist[i] = e[C1][i]; if (dist[i]<9999 ){ pre[i]=C1; rm[i] = rescue[C1]+rescue[i]; num_of_shortest[i] = 1 ; } } for (int i=1 ;i<N;i++){ int min = 99999 ,u=-1 ; for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++){ if (!visited[i] && dist[i]<min){ min = dist[i]; u = i; } } if (u==-1 ) return ; visited[u] = 1 ; for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++){ if (!visited[i] && dist[u]+e[u][i]<dist[i]){ dist[i] = dist[u] + e[u][i]; pre[i]=u; rm[i] = rm[u]+rescue[i]; num_of_shortest[i] = num_of_shortest[u]; }else if (!visited[i] && dist[u]+e[u][i]==dist[i]){ if (rm[u]+rescue[i]>rm[i]){ pre[i]=u; rm[i] = rm[u]+rescue[i]; } num_of_shortest[i] += num_of_shortest[u]; } } } } int main () cin>>N>>M>>C1>>C2; init (); dijstra (); cout<<num_of_shortest[C2]<<" " <<rm[C2]; }
dijstra的套路算法,关键是需要增加几个判别的数组,一个是有多少条最短路径num_of_shortest,另一个是当前可以到达的最多救援队数量rm。
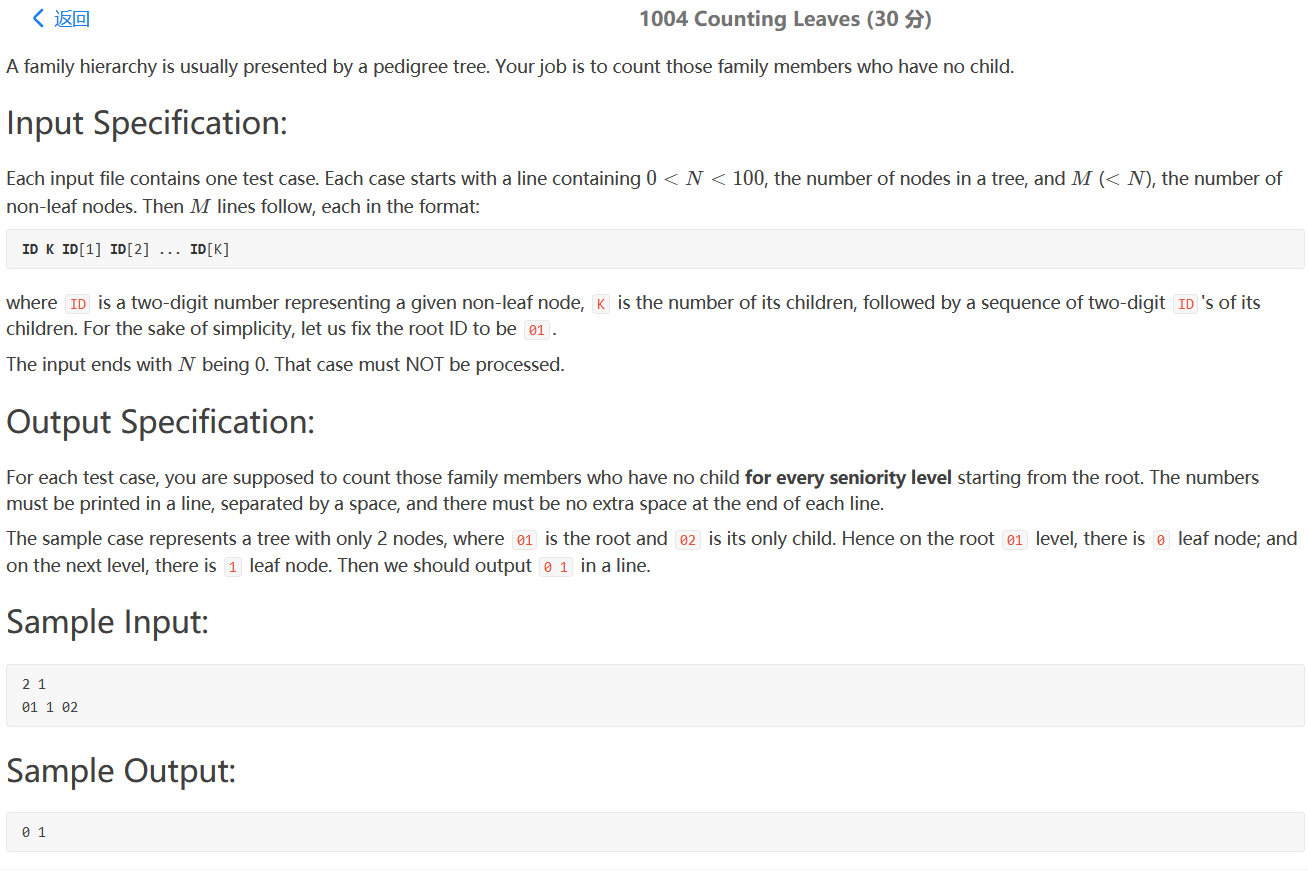
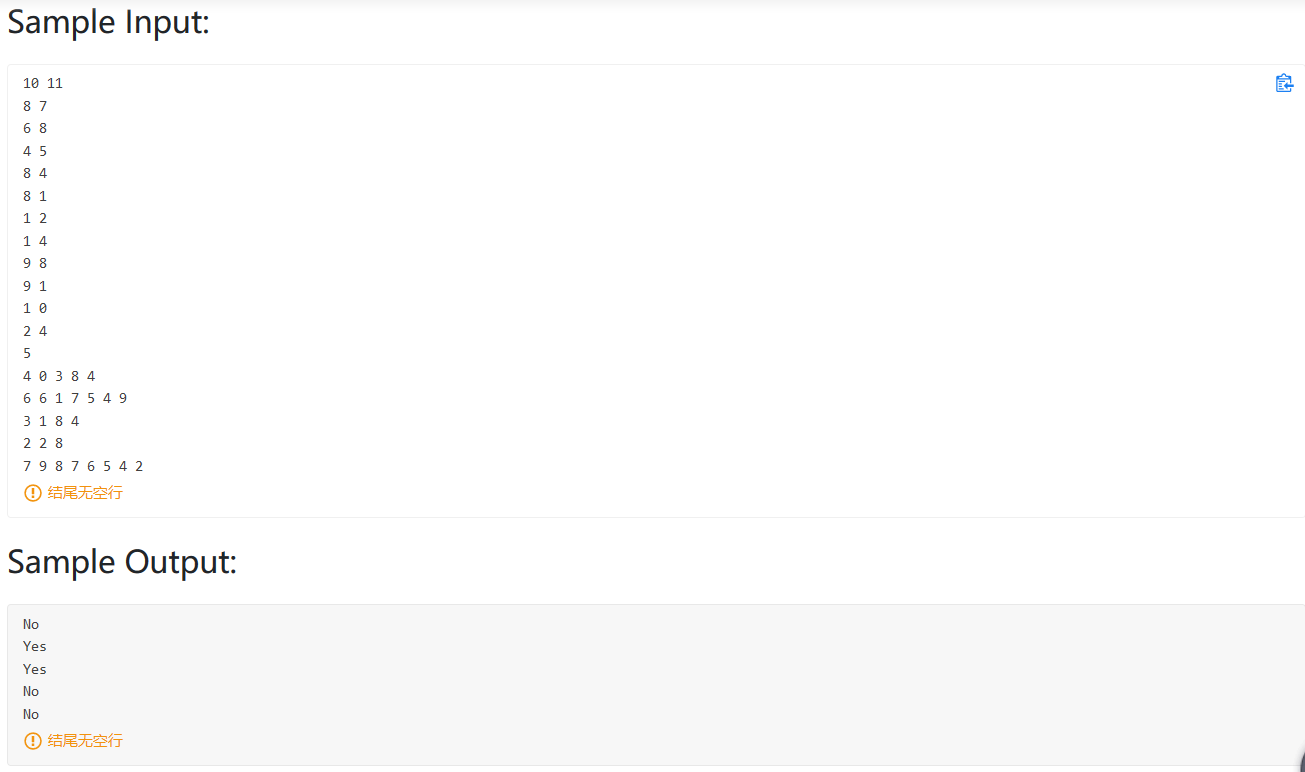
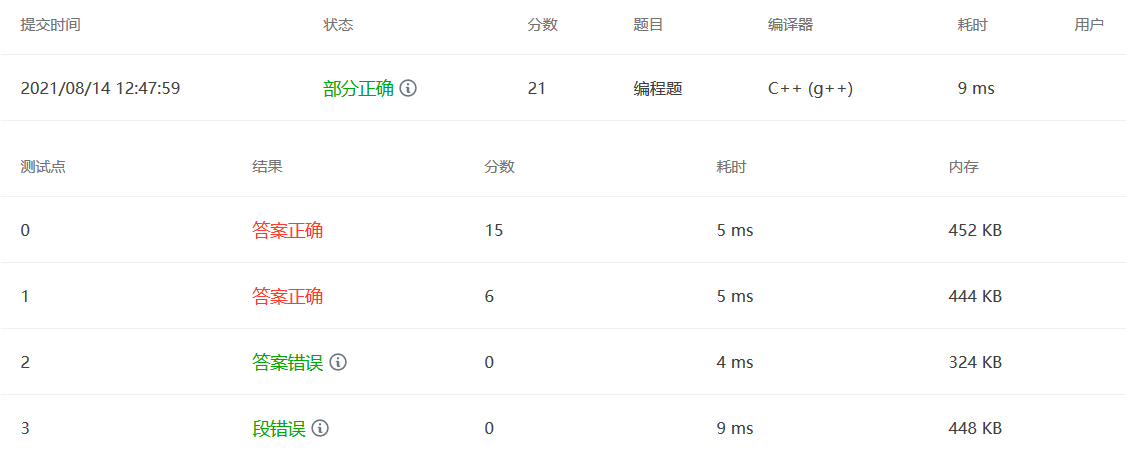
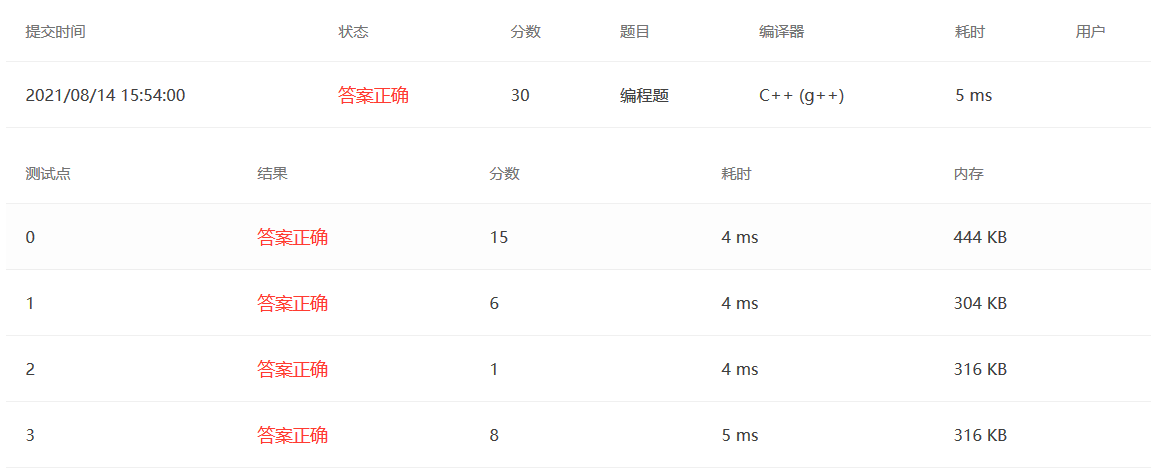
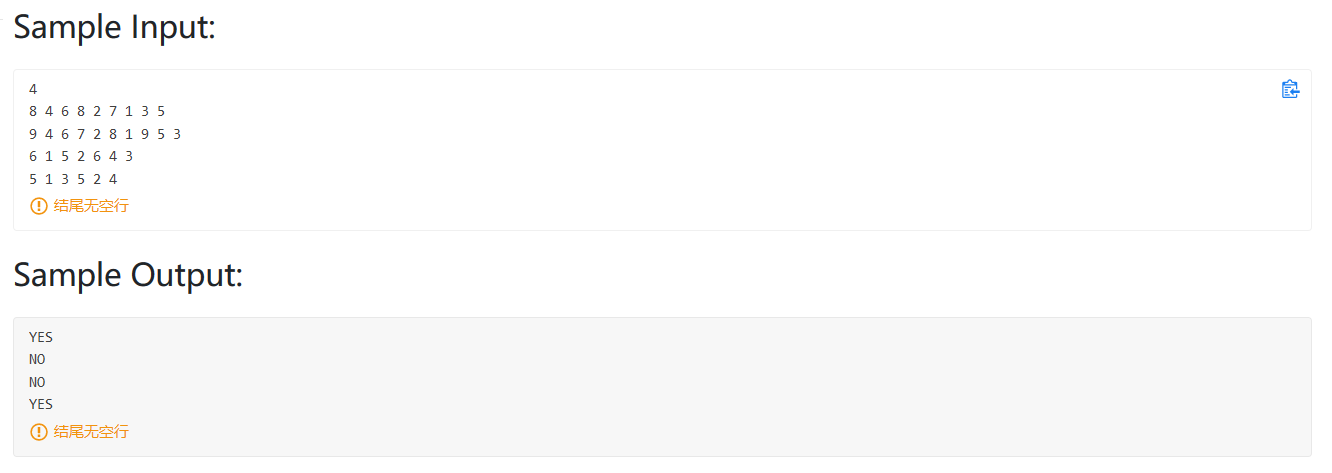
PAT 1004(按层统计树的叶子节点)
题意:按照每一层统计树的叶子节点个数
第一行输入 N=2 树的节点 M=1 非叶子节点个数
下面M行表示非叶子节点所跟的孩子 01 1 02 01表示 01号节点 ,1表示有一个孩子,02表示01的孩子的ID。
题解 :
第一步当然是想数据结构,用什么数据结构来存储这棵树呢?由于树的度不确定,我们很难使用二叉树的链式结构来存储,最初想到的是使用孩子兄弟链表进行存储,但最后发现构造这一棵树并不是太容易,而且我们只是需要统计每一层的非叶子节点数而已。我们不如直接使用结构体数组来存储这棵树,结构体包括ID,节点的孩子vector child ,layer层数,这样我们统计每个节点是否是叶子节点的时候就可以使用child.size()来判断。
1 2 3 4 5 typedef struct Tree_Node { int ID; vector<int > child; int layer; }Tree_Node,*pTree_Node;
其次就是有几个注意点:在分配内存空间的时候需要注意 如果是new,在堆上分配,内存的数据可以是任意的,意味着我们需要额外的初始化。如果使用Tseq[N+1]这种在栈上分配内存的状况,就可以不用初始化,这也导致我几个测试点过不了。
还有一个坑点是,我们统计每一个节点的层数是,利用双亲节点的层数+1,这样有一个问题,要是先输入孩子节点,再输入双亲节点统计就有问题。
1 Tseq[childnum].layer = Tseq[id].layer+1 ;
所以需要对输入的结点ID的大小进行排序,确保上层的节点先被统计进来。这样做法虽然有点蠢,但最后得了27分。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef struct Tree_Node { int ID; vector<int > child; int layer; }Tree_Node,*pTree_Node; typedef struct next_input { int id; vector<int > numvec; }next_input; vector<next_input> input_vector; bool cmp (next_input a,next_input b) return a.id<b.id; } int main () int N,M; cin>>N>>M; if (N==1 ) {cout<<'0' ; return 0 ;} int maxlayer; Tree_Node Tseq[N+1 ]; for (int i=1 ;i<=N;i++) Tseq[i].ID = i; Tseq[1 ].layer = 1 ; for (int i=0 ;i<M;i++){ next_input input; int id,num,child; cin>>id>>num; input.id = id; for (int j=0 ;j<num;j++){ cin>>child; input.numvec.push_back (child); } input_vector.push_back (input); } sort (input_vector.begin (),input_vector.end (),cmp); for (int i=0 ;i<M;i++){ int id,num,childnum; id = input_vector[i].id; num = input_vector[i].numvec.size (); for (int j=0 ;j<num;j++){ childnum = input_vector[i].numvec[j]; Tseq[id].child.push_back (childnum); Tseq[childnum].layer = Tseq[id].layer+1 ; } } for (int i=1 ;i<=N;i++){ maxlayer = max (maxlayer,Tseq[i].layer); } map<int ,int > Map; for (int i=1 ;i<=maxlayer;i++){ Map[i] = 0 ; } for (int i=1 ;i<=N;i++){ if (Tseq[i].child.size ()==0 ){ Map[Tseq[i].layer]++; } } map<int ,int > ::iterator iter; cout<<Map.begin ()->second; iter = Map.begin (); iter++; for (;iter!=Map.end ();iter++){ cout<<" " <<iter->second; } return 0 ; }
最后一个测试点有点懵
如果考虑到只有一个节点的情况,if(N==1){ cout<<”1”<<endl;return 0;} 这句话会根据出现在不同的位置而产生不同的结果。
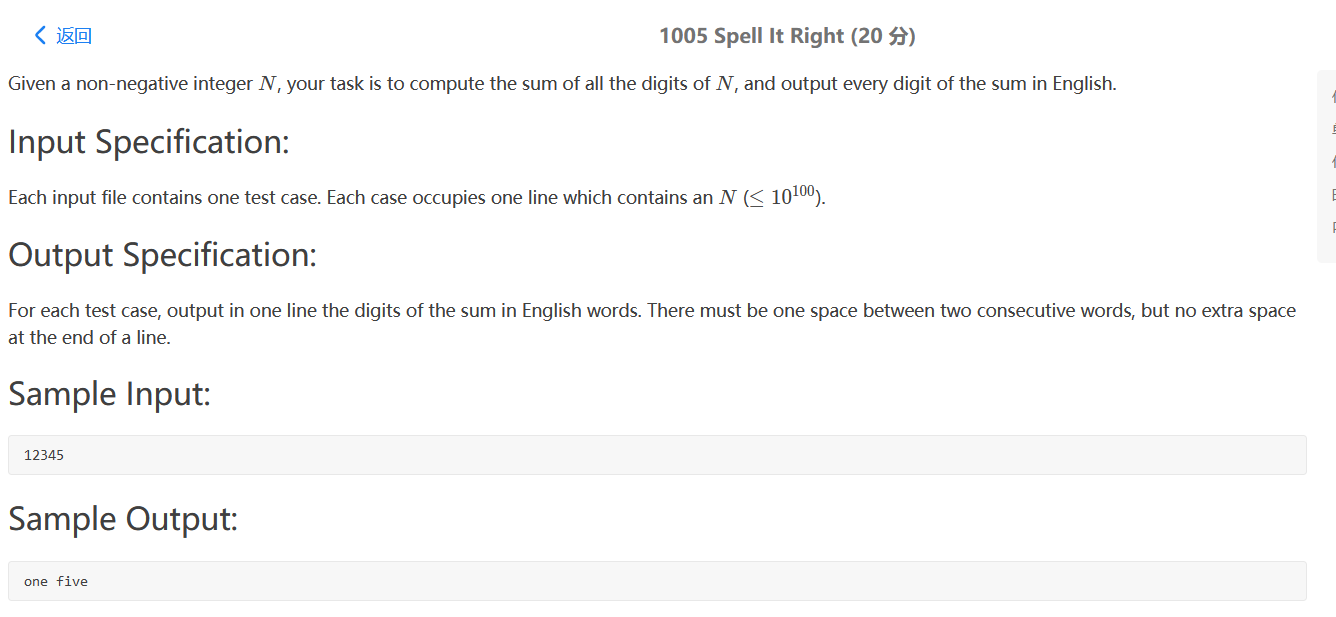
PAT 1005
计算一个数的个位数字之和,英文输出。比较简单,十分钟搞定。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;string Map[] = {"zero" ,"one" ,"two" ,"three" ,"four" ,"five" ,"six" ,"seven" ,"eight" ,"nine" }; int main () int count = 0 ; string s="" ; cin>>s; for (auto i:s){ count += (i-'0' ); } string ss = to_string (count); cout<<Map[ss[0 ]-'0' ]; for (int i=1 ;i<ss.length ();i++){ cout<<" " <<Map[ss[i]-'0' ]; } }
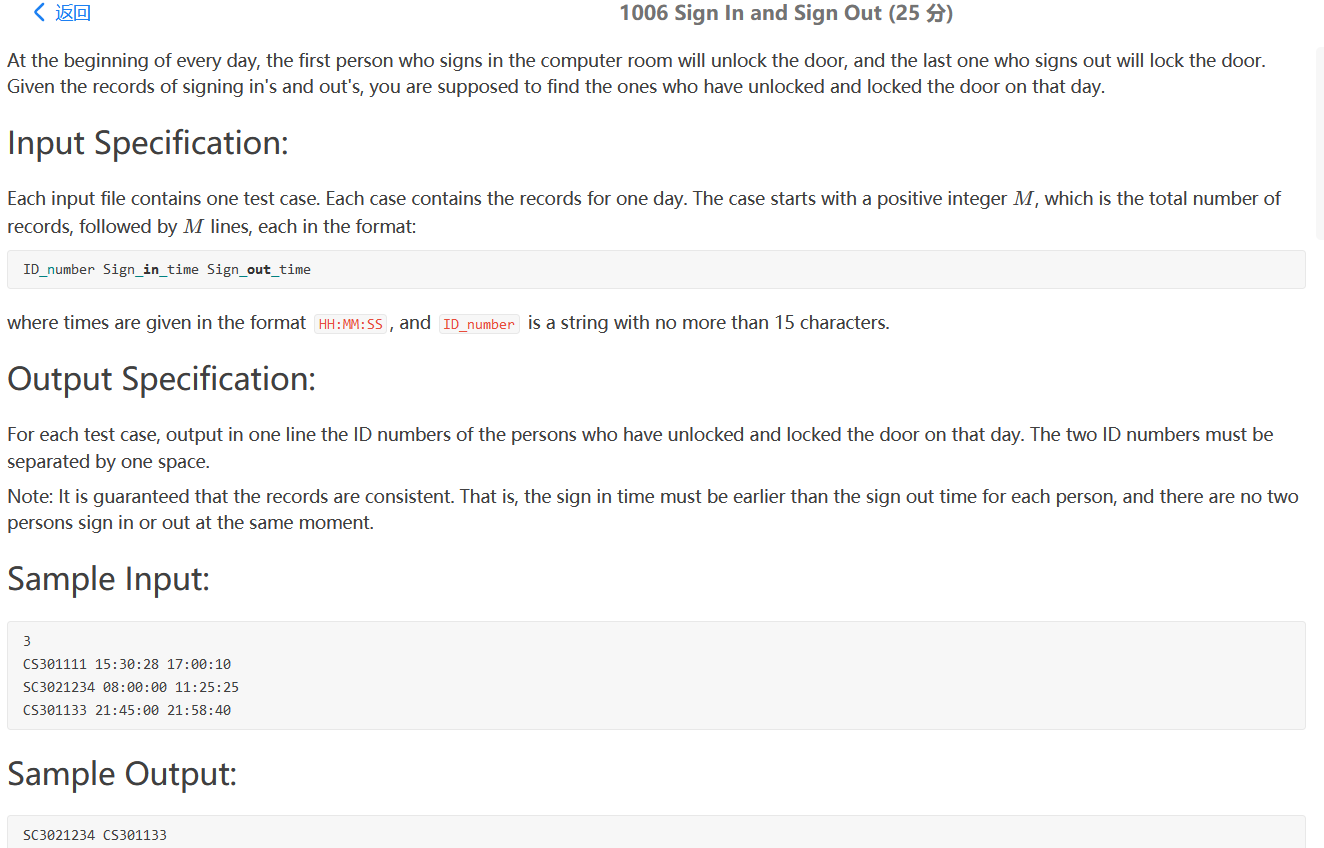
PAT 1006
水题,比较来上班最早的和来上班最晚的,直接写一个结构体比较就好了,二十分钟能搞定。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef struct person { string id; string early; string later; }person; vector<int > sp (string a) vector<int > v; v.push_back (stoi (a.substr (0 ,2 ))); v.push_back (stoi (a.substr (3 ,2 ))); v.push_back (stoi (a.substr (6 ,2 ))); return v; } bool cmpearly (person early,person later) vector<int > a = sp (early.early); vector<int > b = sp (later.early); if (a[0 ]==b[0 ] && a[1 ]==b[1 ]){ return a[2 ]<b[2 ]; }else if (a[0 ]==b[0 ]){ return a[1 ]<b[1 ]; }else { return a[0 ]<b[0 ]; } } bool cmplater (person early,person later) vector<int > a = sp (early.later); vector<int > b = sp (later.later); if (a[0 ]==b[0 ] && a[1 ]==b[1 ]){ return a[2 ]>b[2 ]; }else if (a[0 ]==b[0 ]){ return a[1 ]>b[1 ]; }else { return a[0 ]>b[0 ]; } } int main () vector<person> vec_person; int n; cin>>n; for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++){ person p; cin>>p.id>>p.early>>p.later; vec_person.push_back (p); } sort (vec_person.begin (),vec_person.end (),cmpearly); cout<<vec_person[0 ].id<<" " ; sort (vec_person.begin (),vec_person.end (),cmplater); cout<<vec_person[0 ].id; return 0 ; }
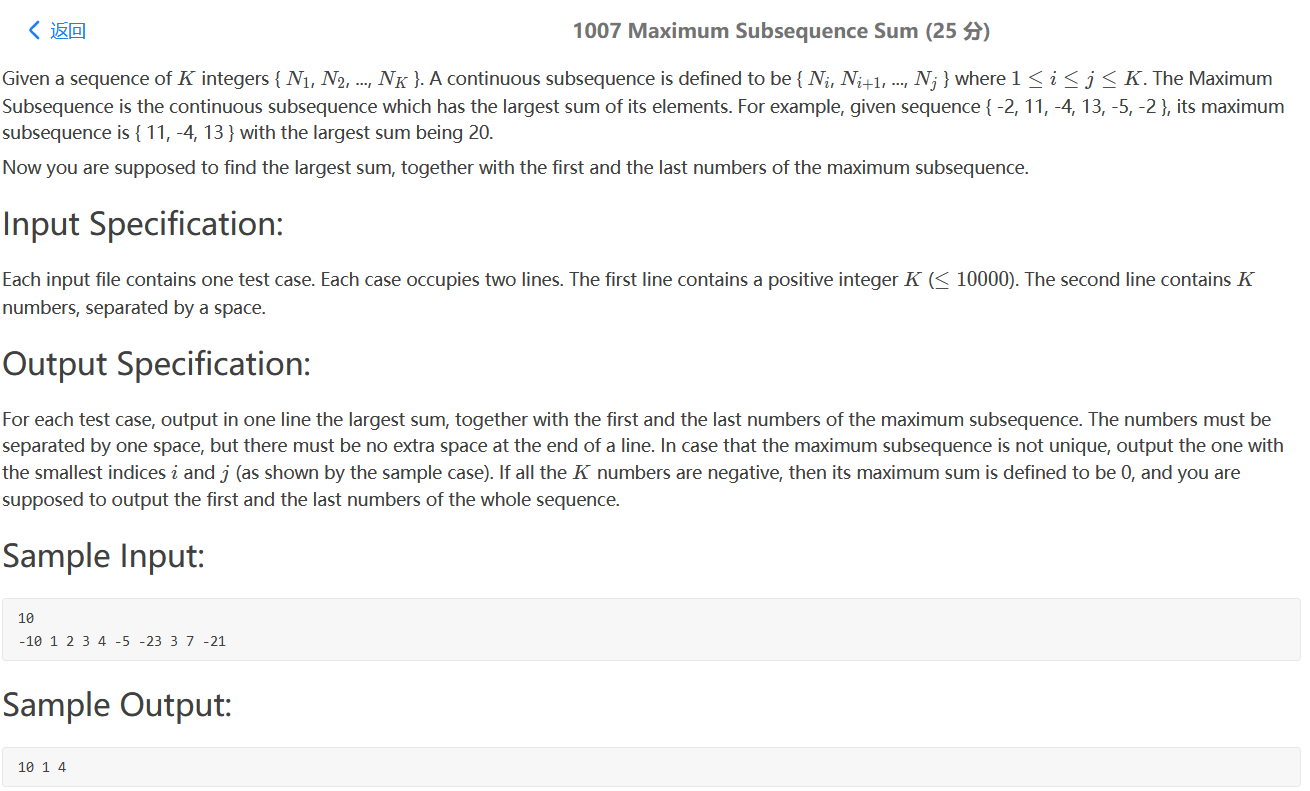
PAT 1007(动态规划)
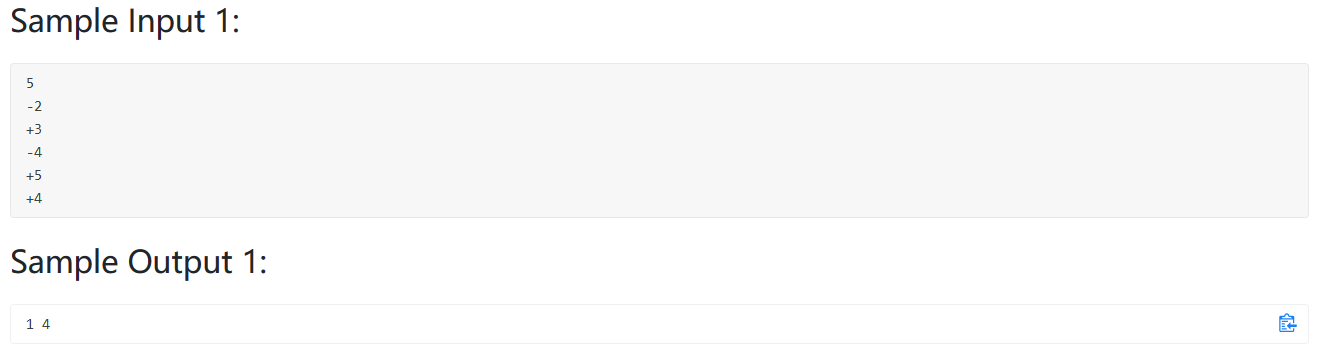
leetcode经典题,最大连续子序列和,一想就知道使用动态规划。
坑点1: output the one with the smallest indices i and j (as shown by the sample case). 这句话的意思是输出开始的数,而不是下标,整了一小时。
坑点2: If all the K numbers are negative, then its maximum sum is defined to be 0, and you are supposed to output the first and the last numbers of the whole sequence. 这句话记得看就好
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main () vector<int > seq; int n; cin>>n; for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++){ int a; cin>>a; seq.push_back (a); } int dp[seq.size ()]; int pre[seq.size ()]; dp[0 ] = seq[0 ]; pre[0 ]=0 ; int maxsub = dp[0 ]; int maxi=0 ,maxj=0 ; for (int i=1 ;i<seq.size ();i++){ if (dp[i-1 ]>0 ){ dp[i] = dp[i-1 ]+seq[i]; pre[i] = pre[i-1 ]; }else { dp[i] = seq[i]; pre[i] = i; } if (dp[i]>maxsub){ maxsub = dp[i]; maxi = pre[i]; maxj = i; } } if (maxsub<0 ){ cout<<'0' <<" " <<seq[0 ]<<" " <<seq[seq.size ()-1 ]; return 0 ; } cout<<maxsub<<" " <<seq[maxi]<<" " <<seq[maxj]; return 0 ; }
我这儿的dp定义的略有不同,不过无伤大雅,dp[i]是指以i结尾的最大连续子序列和。
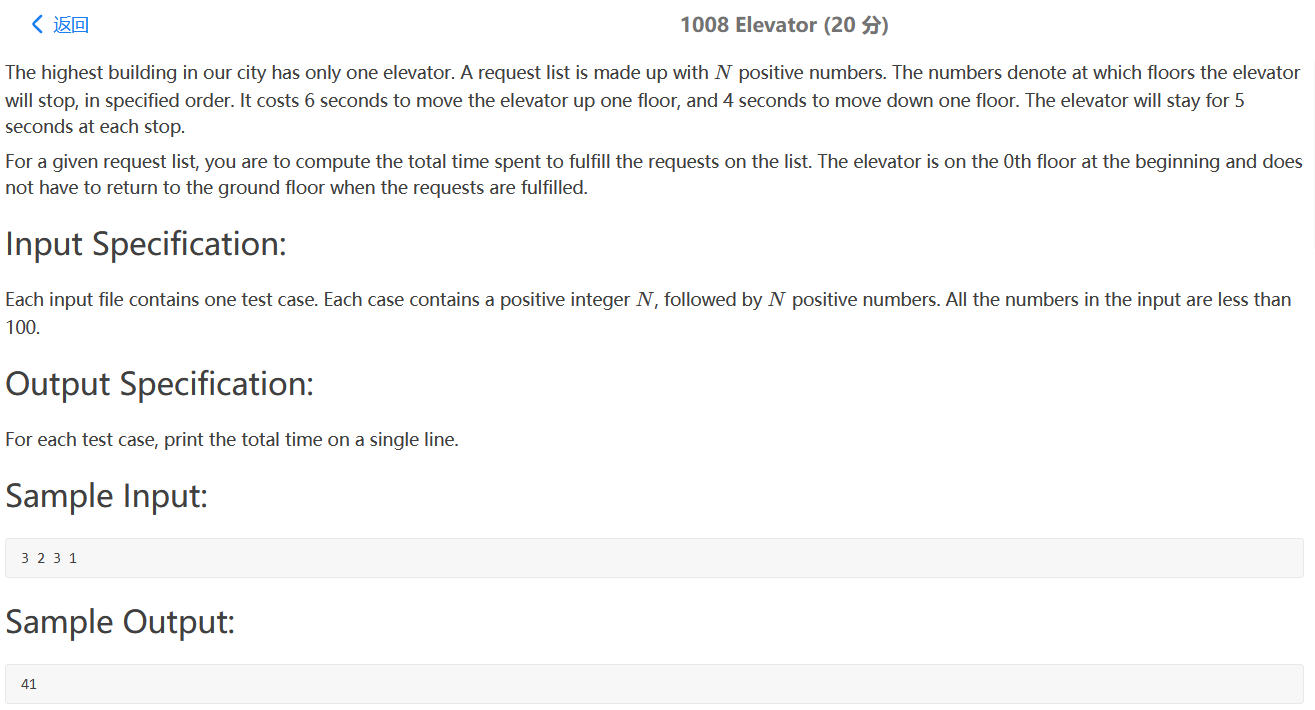
PAT 1008
水题。电梯上升一层6s,下降一层4s,每层有需要停留5s,求电梯所需要时间。十分钟解决。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main () int n; cin>>n; vector<int > v; for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++){ int a; cin>>a; v.push_back (a); } int temp = 0 ; int total_time = 0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<v.size ();i++){ if ((v[i]-temp)>=0 ){ total_time += (v[i]-temp)*6 ; }else { total_time += (temp-v[i])*4 ; } temp = v[i]; total_time += 5 ; } cout<<total_time; return 0 ; }
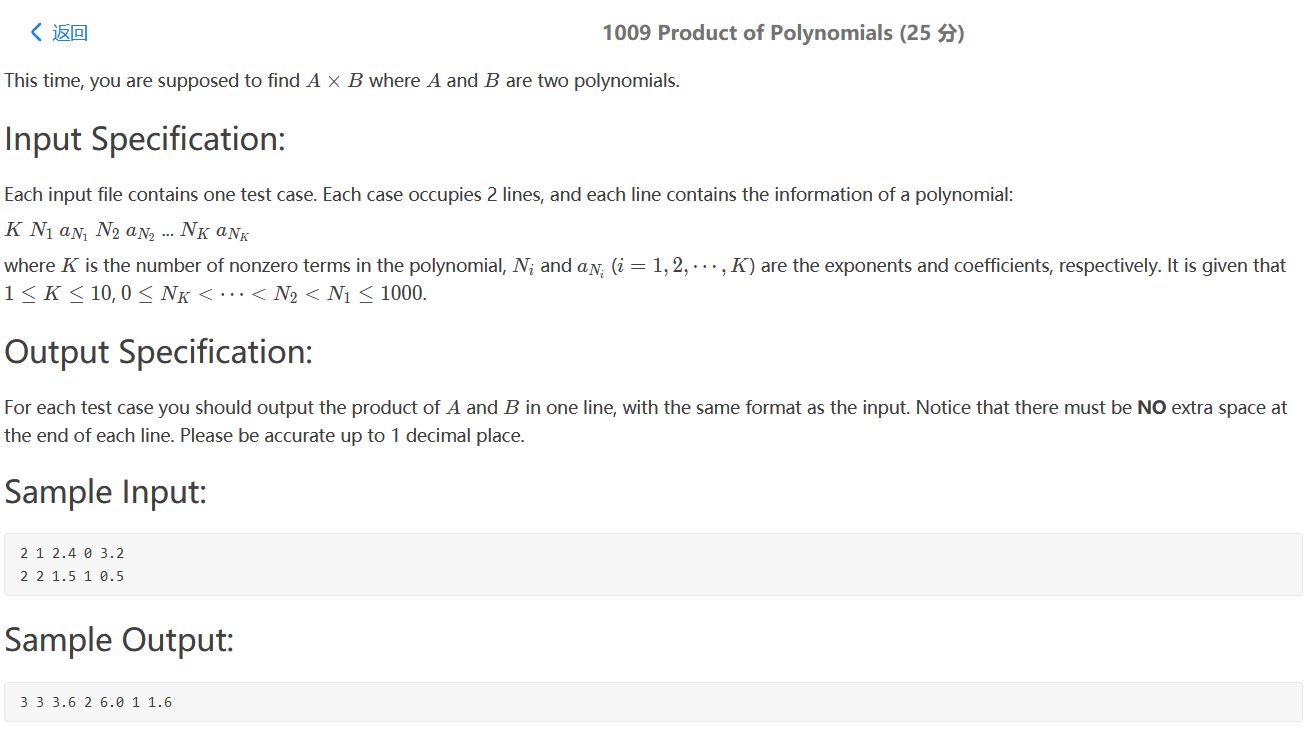
PAT 1009
和pat1002类似,这里做的是乘法A * B,可以采用暴力法二重循环。
注意的是如果系数等于0则不输出。
不能使用cout<<M.size(); 来统计输出的个数,因为会把系数为0的统计进去。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;map<int ,double > M; int main () int n; cin>>n; int a[n]; double b[n]; for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++){ cin>>a[i]>>b[i]; } int k; cin>>k; int ai; double bi; for (int i=0 ;i<k;i++){ cin>>ai>>bi; for (int j=0 ;j<n;j++){ int exponent = ai+a[j]; double coefficient = bi*b[j]; if (M.find (exponent)!=M.end ()){ M[exponent] += coefficient; }else { M[exponent] = coefficient; } } } int count = 0 ; map<int ,double >::reverse_iterator iter; for (iter = M.rbegin ();iter!=M.rend ();iter++){ if (iter->second!=0 ) count++; } cout<<count; for (iter = M.rbegin ();iter!=M.rend ();iter++){ if (iter->second!=0 ){ cout<<" " <<iter->first<<" " ; printf ("%.1lf" ,iter->second); } } }
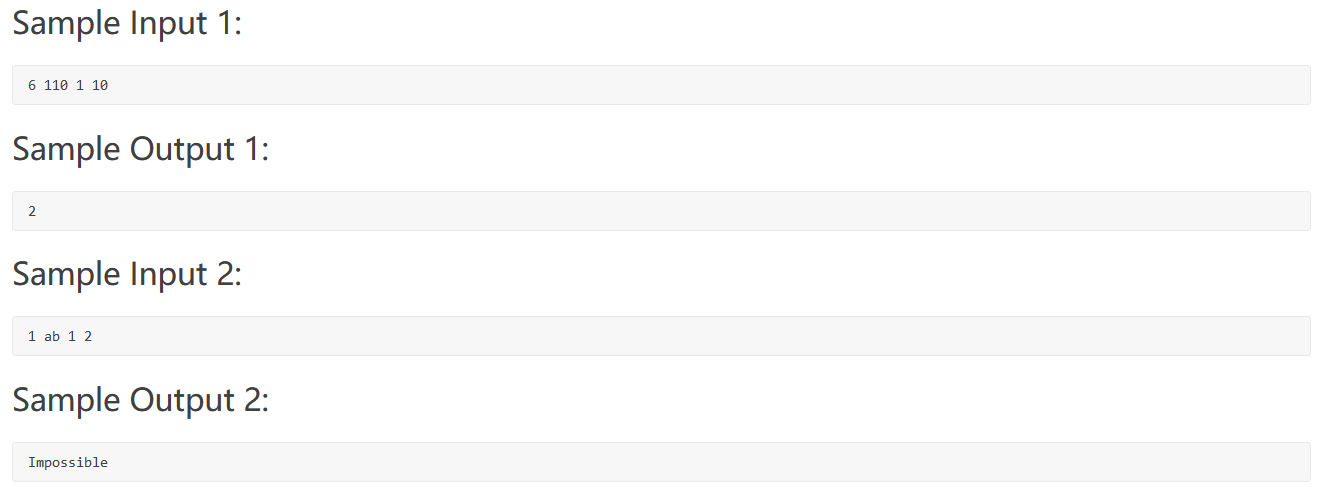
PAT 1010(数学题)
题目大意:N1 N2 tag radix
N1 N2 为两个数,基数未定,范围从[0-9] [a-z],radix表示一个数的基数(tag=1,则表示N1 的基数,tag=2则表示N2的基数)我们要求另一个数的基数,使得N1=N2。若不存在则输出”Impossible”。
最初的想法是把一个数的十进制算出来,另一个数从2 一直往上遍历,遍历到什么时候是个头呢,无从知晓。看了答案之后方才明白。
进制范围的确定 (关键步骤+二分查找)
进制的最小取值为:各个位数最大值+1 如123的最小进制一定大于3, abc的最小进制一定大于12 (这个比较好理解)
现在来讨论进制的上限(max_radix) (这个不好理解)
坑点 :
计算过程中会出现数据溢出。
这一句显得至关重要,有6个测试点来自这。
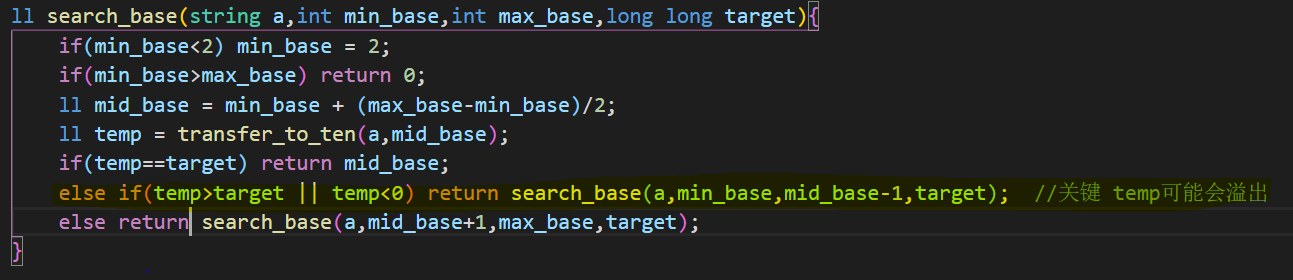
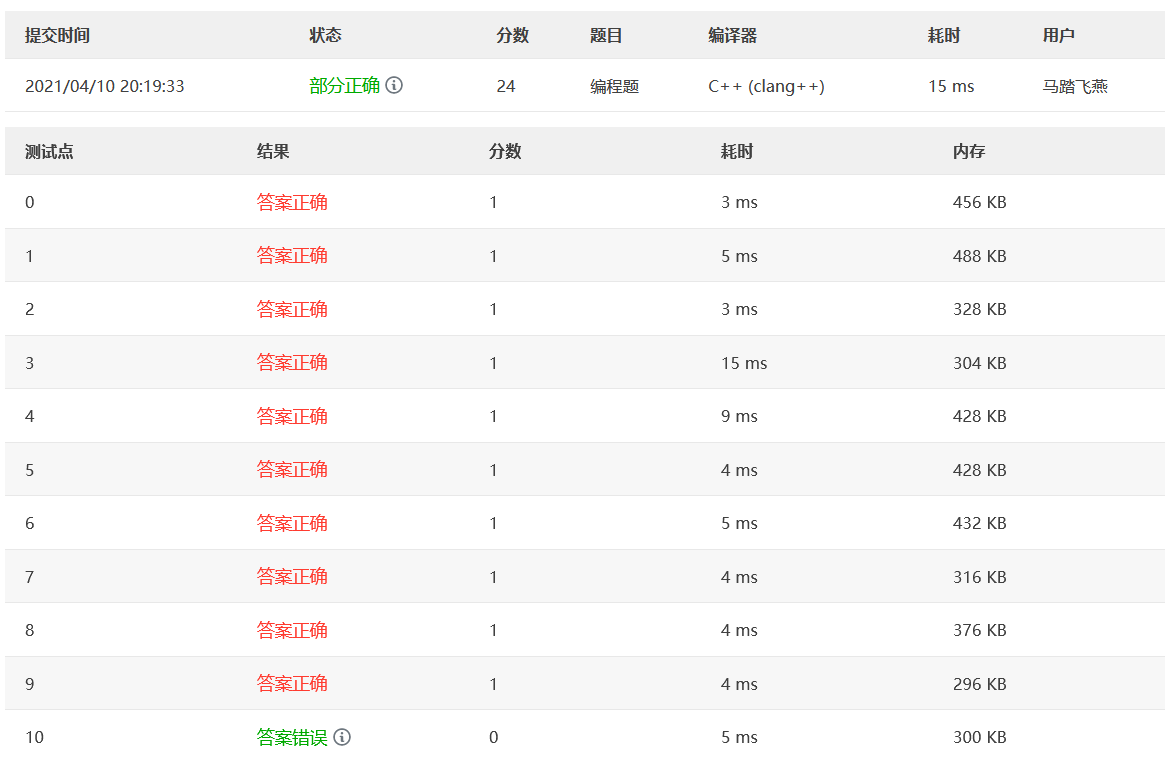
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define ll long long using namespace std;ll transfer_to_ten (string a,int radix) ll total=0 ; ll basement = 1 ; for (int i=a.length ()-1 ;i>=0 ;i--){ if (a[i]<='9' ) total += (a[i]-'0' )*basement; else total += (a[i]-'a' +10 )*basement; basement *= radix; } return total; } int find_min_base (string a) int min_base = 1 ; for (int i=0 ;i<a.length ();i++){ if (a[i]<='9' ) min_base = min_base>(a[i]-'0' +1 ) ? min_base : (a[i]-'0' +1 ); else min_base = min_base>(a[i]-'a' +11 ) ? min_base : (a[i]-'a' +11 ); } return min_base; } ll search_base (string a,int min_base,int max_base,long long target) { if (min_base<2 ) min_base = 2 ; if (min_base>max_base) return 0 ; ll mid_base = min_base + (max_base-min_base)/2 ; ll temp = transfer_to_ten (a,mid_base); if (temp==target) return mid_base; else if (temp>target || temp<0 ) return search_base (a,min_base,mid_base-1 ,target); else return search_base (a,mid_base+1 ,max_base,target); } int main () string a,b; string cc; ll tag,radix; ll target; cin>>a>>b>>tag>>radix; if (tag==1 ){ target = transfer_to_ten (a,radix); cc = b; } else if (tag==2 ){ target = transfer_to_ten (b,radix); cc = a; } ll min_base = find_min_base (cc); ll max_base = target>min_base ? target : min_base; ll mid_base = search_base (cc,min_base,max_base,target); if (mid_base) cout<<mid_base; else cout<<"Impossible" ; return 0 ; }
第10个测试点据说是:10测试点是输入为0
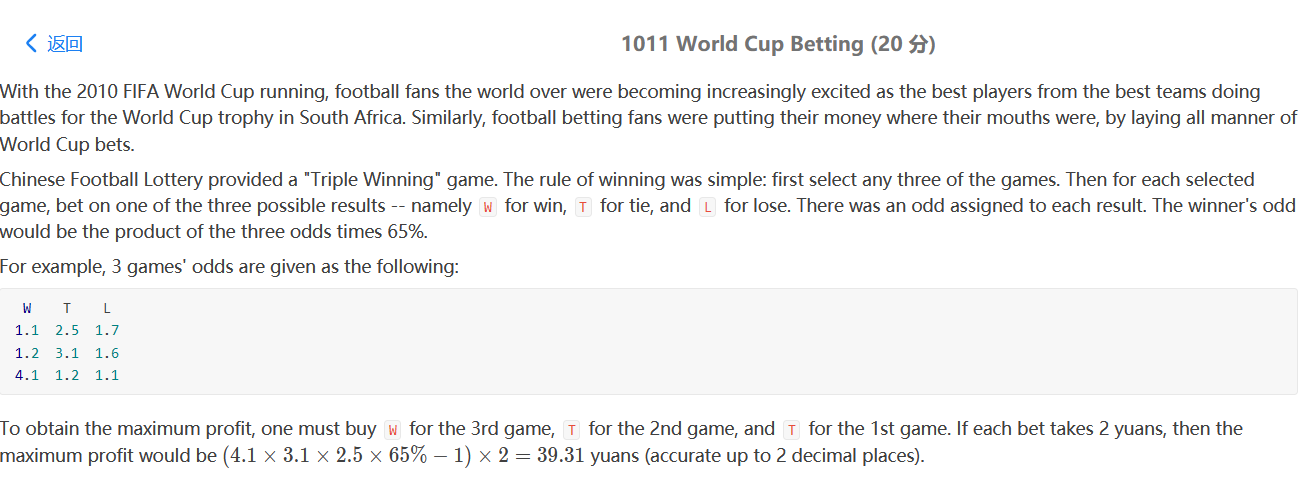
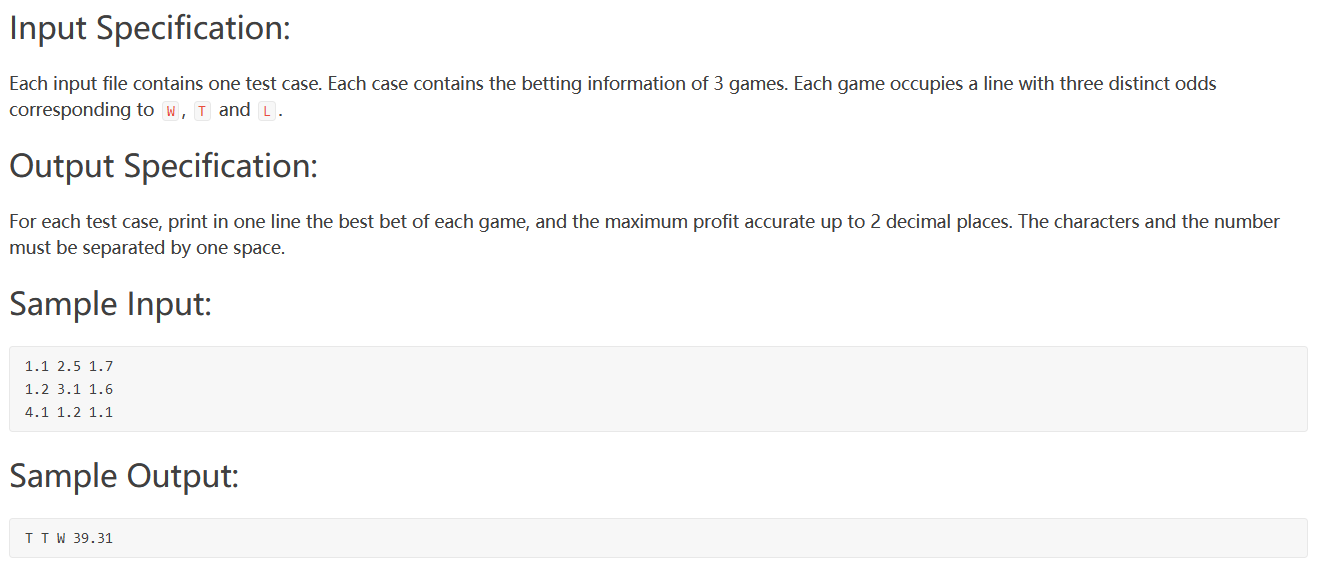
PAT 1011
给定三场比赛和每一场的结果的赔率,问怎么下注使利润最大。每一场都选最大的。无脑题,关键在于读懂题目。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef struct ca { char a; double pro; }ca; bool cmp (ca a,ca b) return a.pro>b.pro; } char a[3 ]={'W' ,'T' ,'L' };double res = 1 ;int main () vector<vector<ca>> v (3 ); for (int i=0 ;i<3 ;i++){ for (int j=0 ;j<3 ;j++){ ca d; cin>>d.pro; d.a = a[j]; v[i].push_back (d); } sort (v[i].begin (),v[i].end (),cmp); } for (int i=0 ;i<3 ;i++){ res *= v[i][0 ].pro; cout<<v[i][0 ].a<<" " ; } res = (res*0.65 -1 )*2 ; printf ("%.2f" ,res); }
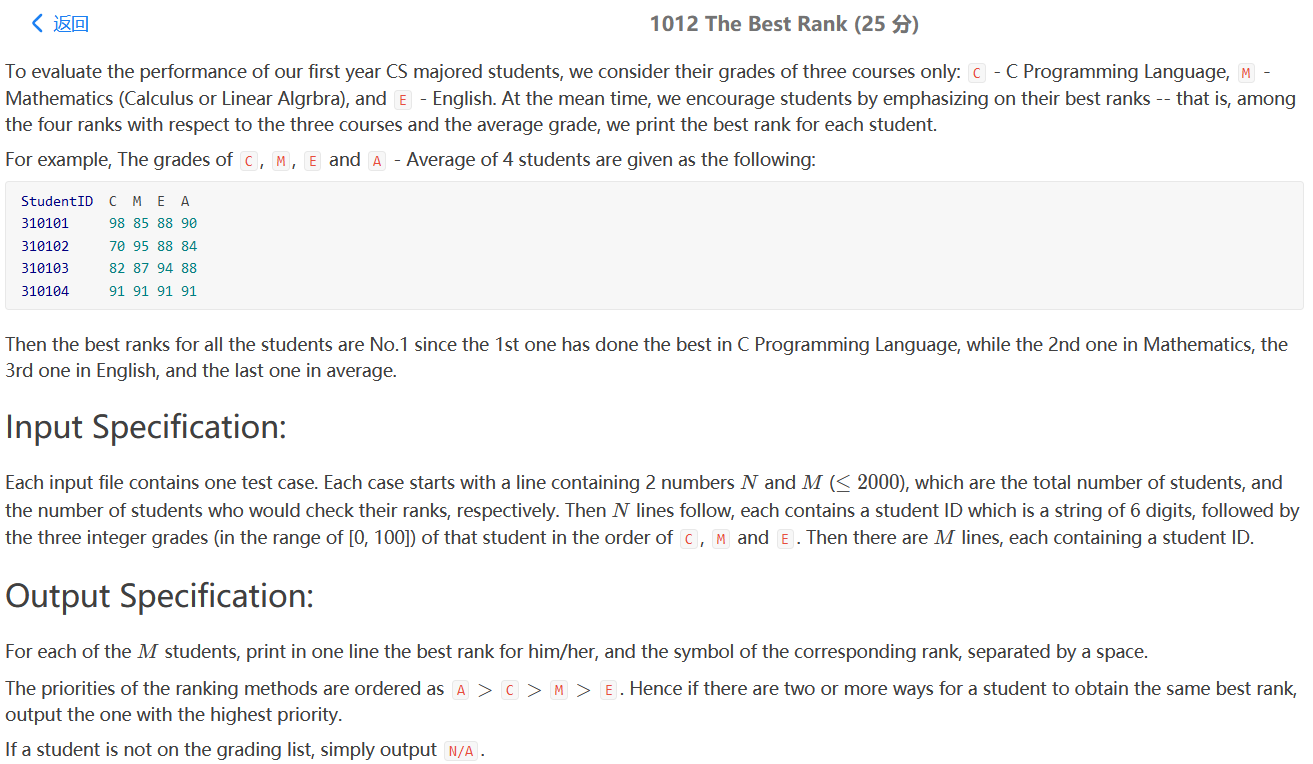
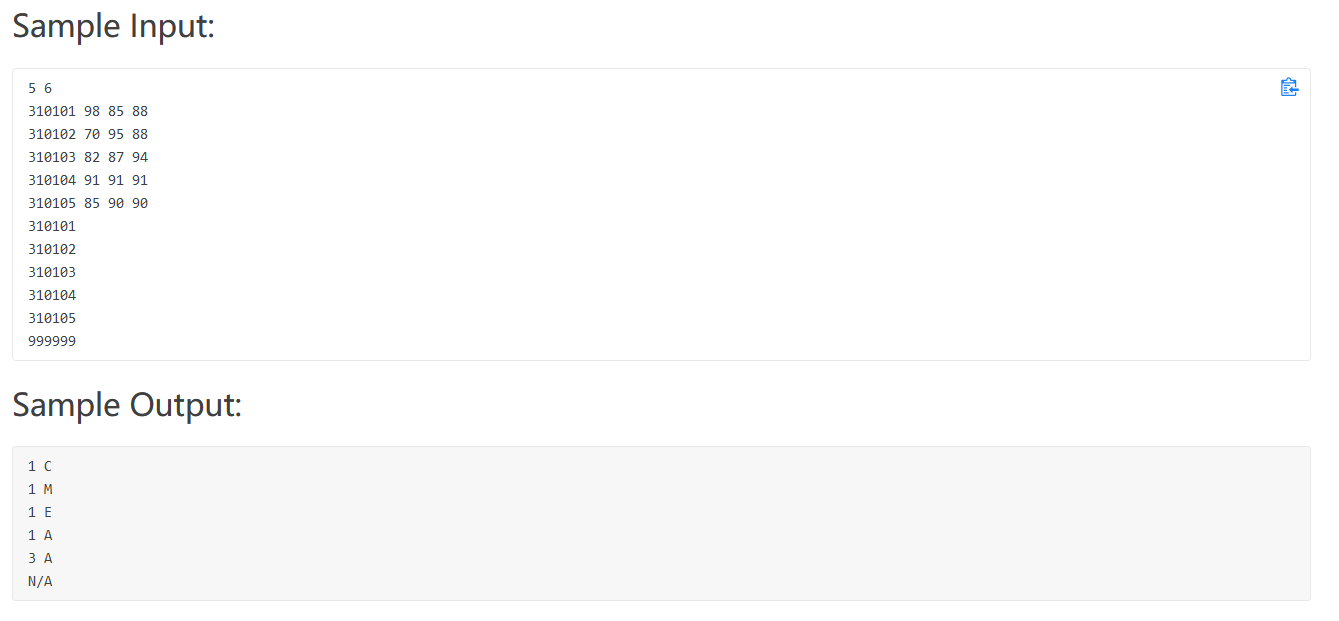
PAT 1012
这一题竟然解决了一个小时。
题目大意:输入学生 以及三门课的成绩,然后每输入一个学生的id就打印最高的排名和对应排名的分类。排名分成三门课的单独排名和平均分的排名。排名也有优先级,A>C>M>E。还算模拟题吧。
我的思路是建立一个学生表Map[string , stu];stu包含学生的信息,包括成绩,排名等等。在第一波输入的时候,我们可以将成绩信息,填入学生表,同时将每科的成绩分门别列进行排序,第二轮遍历学生表Map时我们按照成绩查找对应的排名,本来想用二分查找,(但也必须是改进的二分查找,查找目标==target的最小边界)。然后printinfo函数输出每个学生的信息。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef struct stu { string ID; int C,M,E,A; int rC,rM,rE,rA; }stu; map<string,stu> Map; vector<int > CC; vector<int > MM; vector<int > EE; vector<int > AA; bool cmp (int a,int b) return a>b; } int search (vector<int > A,int target) for (int i=0 ;i<A.size ();i++){ if (A[i]==target) return i+1 ; } } void printstu (stu S) if (S.rA<=min (S.rC,min (S.rE,S.rM))){ cout<<S.rA<<" A" ; return ; } if (S.rC<=min (S.rA,min (S.rE,S.rM))){ cout<<S.rC<<" C" ; return ; } if (S.rM<=min (S.rC,min (S.rE,S.rA))){ cout<<S.rM<<" M" ; return ; } if (S.rE<=min (S.rC,min (S.rA,S.rM))){ cout<<S.rE<<" E" ; return ; } } int main () int N,M; cin>>N>>M; for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++){ string a; int b,c,d; cin>>a>>b>>c>>d; CC.push_back (b); MM.push_back (c); EE.push_back (d); int aver = (int )((double )(b+c+d)/3.0 +0.5 ); AA.push_back (aver); stu temp; temp.ID = a; temp.C=b; temp.M=c; temp.E=d; temp.A=aver; Map[a] = temp; } sort (CC.begin (),CC.end (),cmp); sort (EE.begin (),EE.end (),cmp); sort (MM.begin (),MM.end (),cmp); sort (AA.begin (),AA.end (),cmp); map<string,stu> :: iterator iter; for (iter=Map.begin ();iter!=Map.end ();iter++){ iter->second.rA = search (AA,iter->second.A); iter->second.rC = search (CC,iter->second.C); iter->second.rE = search (EE,iter->second.E); iter->second.rM = search (MM,iter->second.M); } for (int i=0 ;i<M;i++){ string s; cin>>s; if (Map.find (s)!=Map.end ()){ printstu (Map[s]); }else { cout<<"N/A" ; } if (i!=M-1 ) cout<<endl; } }
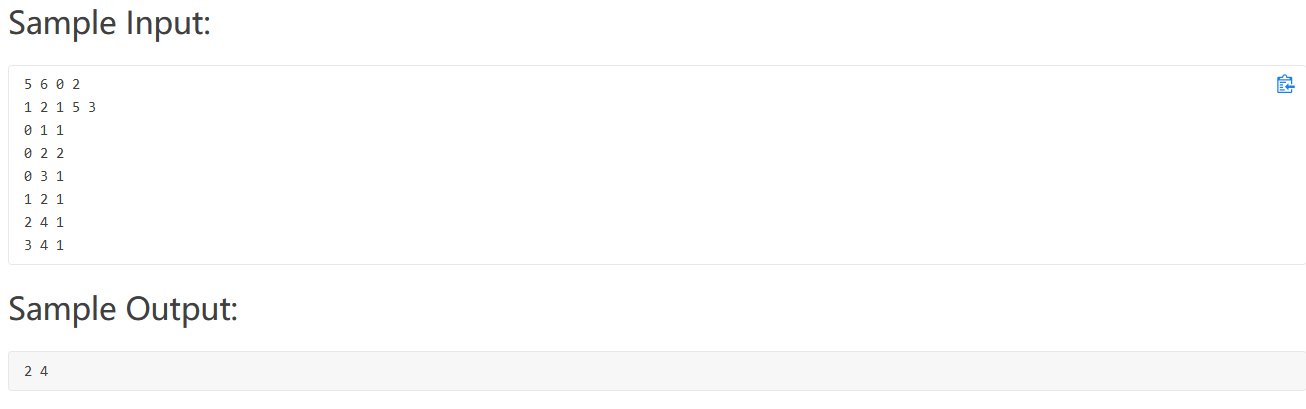
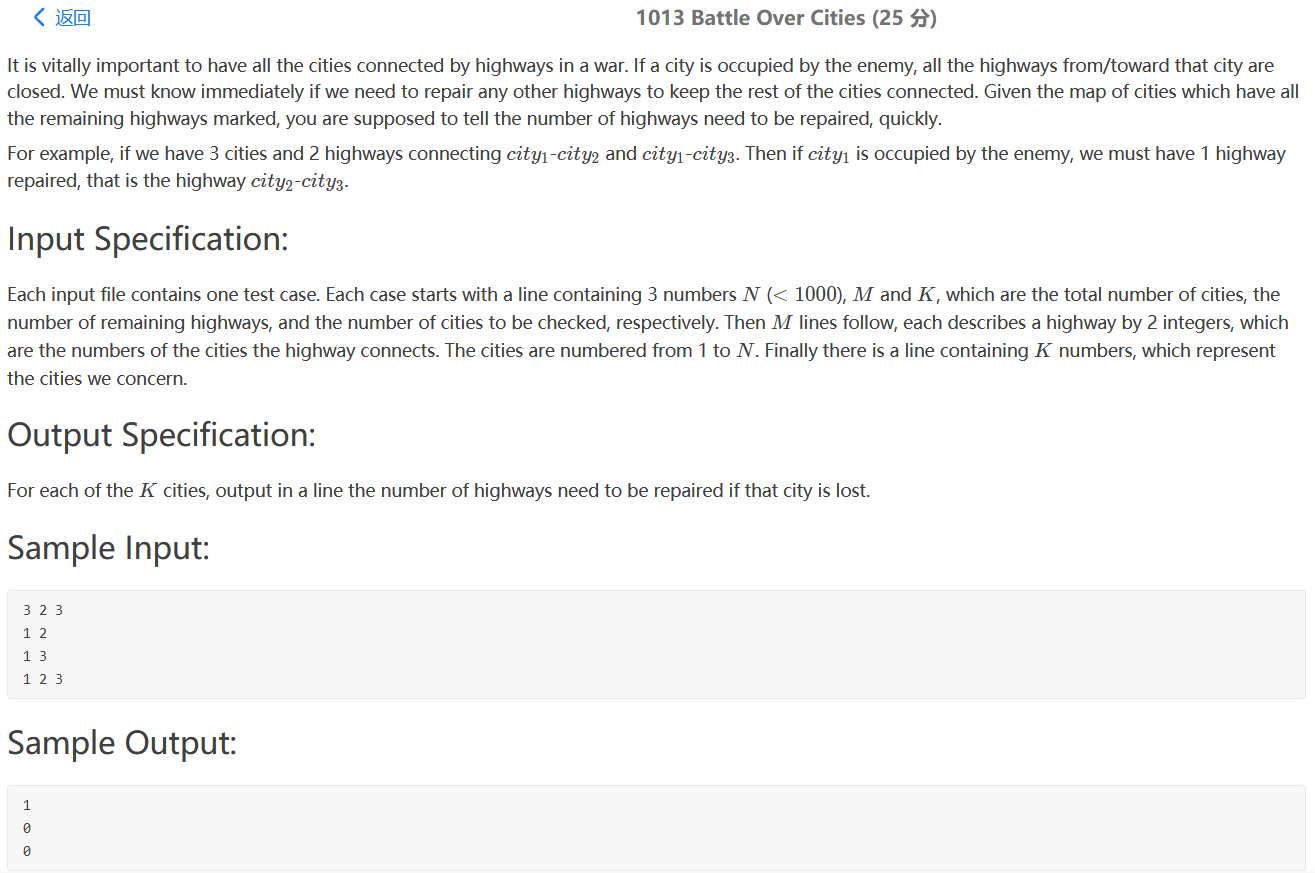
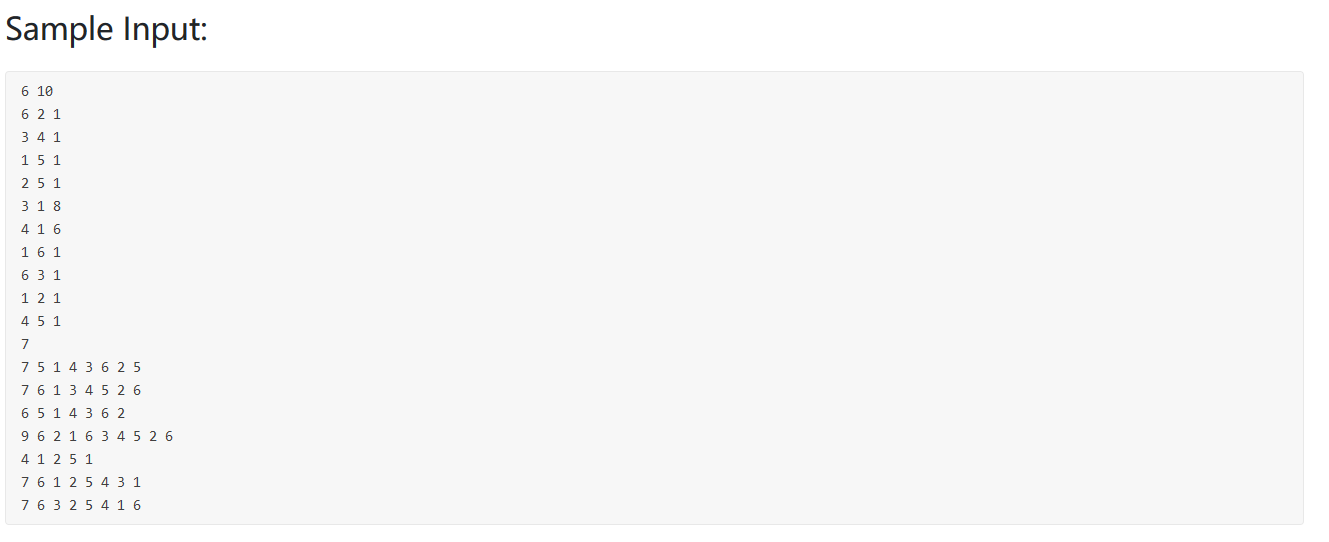
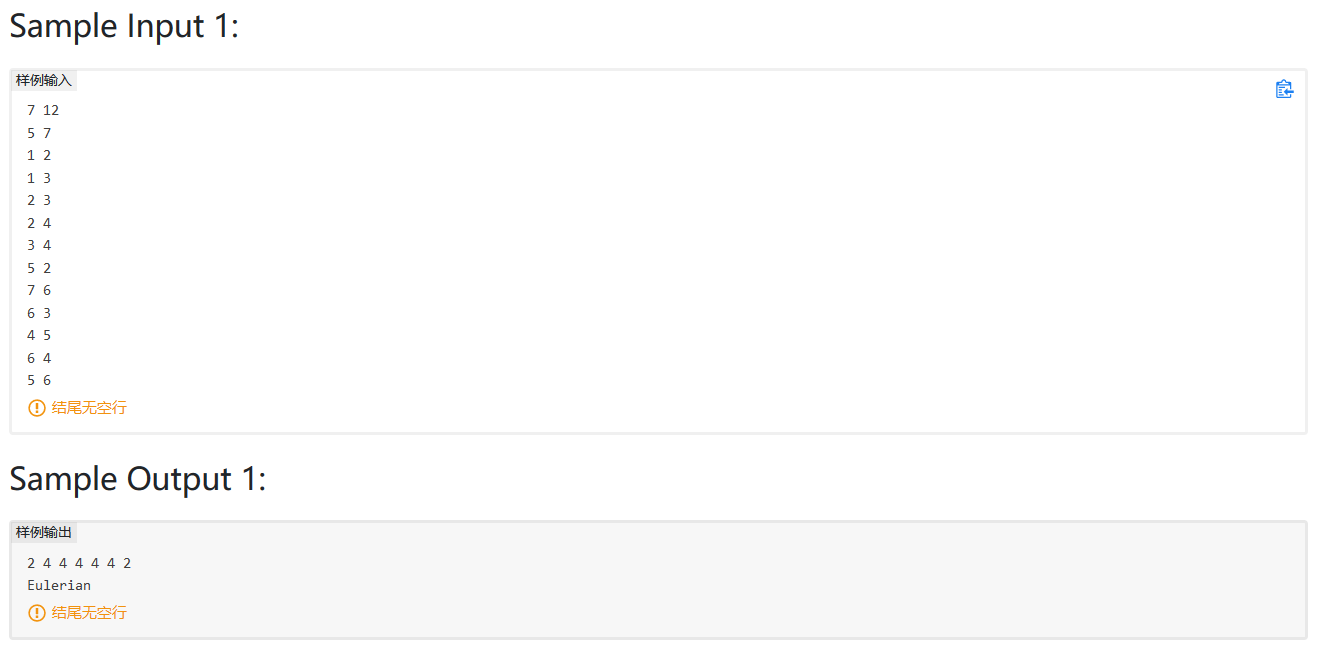
PAT 1013(连通分量)
题意:给出城市个数为N,连接城市间的道路的条数为M,以及询问次数为K
然后输入这M条道路连接的两个端点城市的编号A和B
然后是K次询问,每次询问的方法是:给出一个编号为Q城市,然后将这个城市和与其相连的道路从网络中删除,要求让你求出添加多少条道路,才能使得被删除了编号为Q的城市的网络仍然联通
转化成求连通分量个数。即图的遍历,我这里使用广度优先搜索遍历图,求连通分量k。
bfs(int node);除去node结点的连通分量,从1..N遍历结点,设置一个visited数组表示该结点是否访问过。如果访问过则记作1.k++,然后是用一个栈广度优先搜索该连通分量中可以到达的结点。
最后需要增加的路径=连通分量个数-1
注意:每一次考虑新的结点的时候visited必须复位。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int *visited; int N,M,K;int k; int **Graph; void bfs (int node) for (int i=1 ;i<=N;i++){ if (i==node) continue ; if (visited[i]) continue ; stack<int > S; visited[i]=1 ; k++; S.push (i); while (!S.empty ()){ int top = S.top (); S.pop (); for (int j=1 ;j<=N;j++){ if (j==node) continue ; if (Graph[top][j] && !visited[j]) { visited[j]=1 ; S.push (j); } } } } } int main () cin>>N>>M>>K; visited = new int [N+1 ]; memset (visited,0 ,sizeof (visited)); Graph = new int *[N+1 ]; for (int i=0 ;i<=N;i++){ Graph[i] = new int [N+1 ]; memset (Graph[i],0 ,sizeof (Graph[i])); } for (int i=0 ;i<M;i++){ int a,b; cin>>a>>b; Graph[a][b] = 1 ; Graph[b][a] = 1 ; } for (int i=0 ;i<K;i++){ int a; cin>>a; k = 0 ; for (int i=1 ;i<=N;i++) visited[i]=0 ; bfs (a); cout<<k-1 ; if (i!=K-1 ) cout<<endl; } }
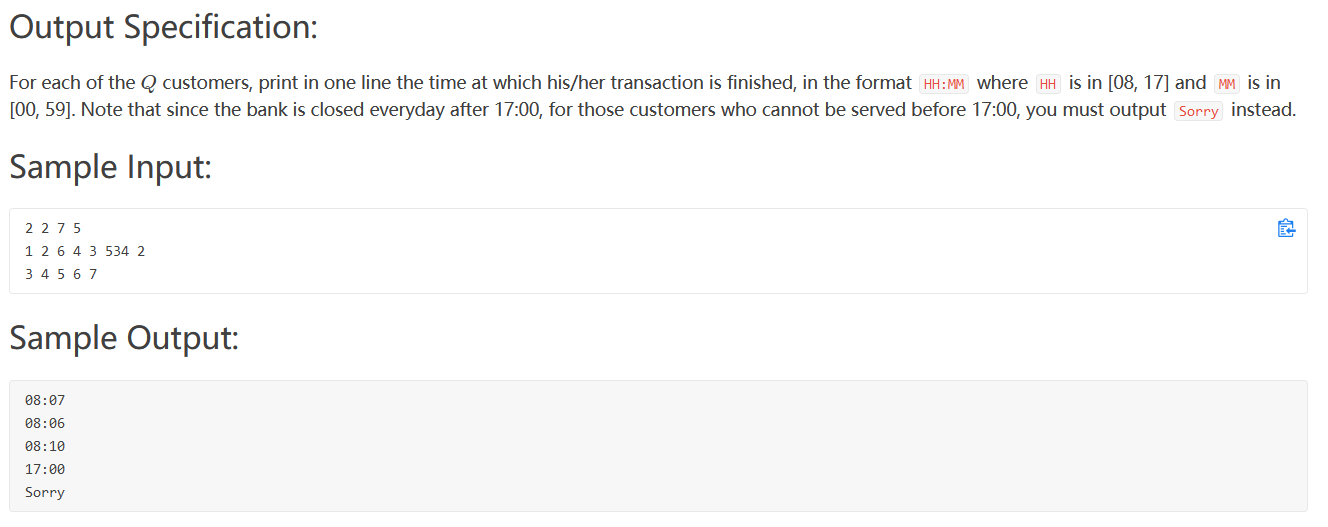
PAT 1014 (队列模拟)
题目大意 :银行有N个窗口,每个窗口划分成两部分,黄线内的和黄线外的
顾客排队有以下几个要求:
1、每个窗口黄线内可以站M个人,第(MN+1)个人得排在黄线外
2、每个顾客选择最短的队伍,(队伍长度相同选择序号小的)
3、顾客i将花费 Ti 的时间处理问题
3、每个窗口的第一位顾客将于8:00被服务
给定每个顾客的处理问题的时间,求每位顾客解决问题的时间点。
输入:第一行 N(窗口)、M(黄线内的人数)、K(顾客人数)、Q(要求的顾客完成时间) 五点之前下班
思路 :用一个vector表示一个窗口,窗口里是一个queue表示窗口队列,首先初始化窗口,之后模拟每一次完成(查找所有窗口剩余时间最少的出队,如果还有人在黄线外等候则加入该窗口的队列,然后更新每个窗口front元素的剩余时间)。持续下去直到所有窗口都为空。 用一个变量nowtime记录当前时间,也即每个顾客的完成时间。
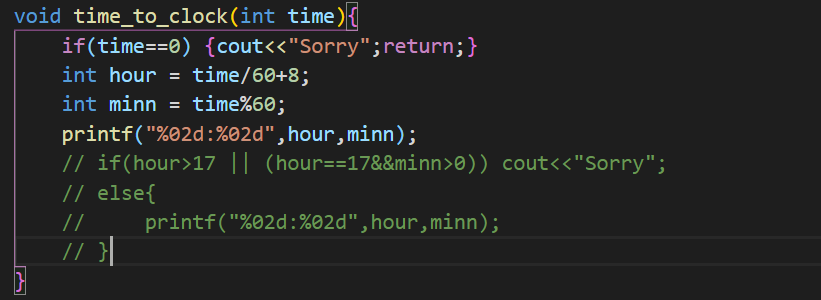
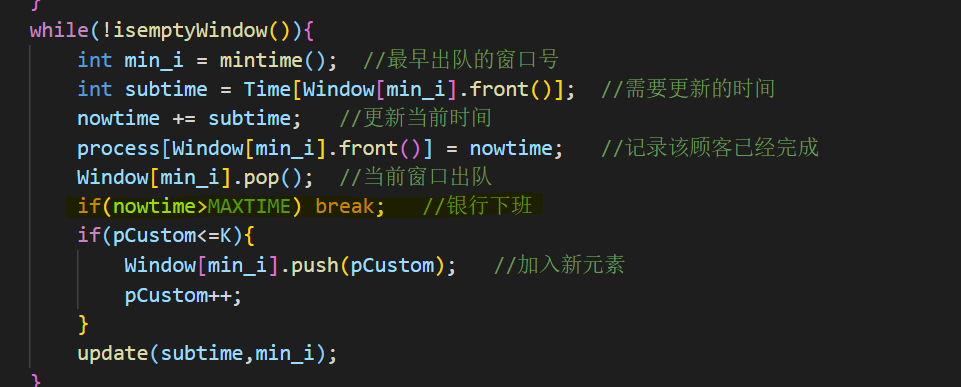
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int N,M,K,Q; int Time[1001 ]; int process[1001 ]; queue<int > Custom; vector<queue<int >> Window; int nowtime = 0 ;bool isemptyWindow () for (int i=0 ;i<Window.size ();i++){ if (!Window[i].empty ()) return false ; } return true ; } int mintime () int min_time = 9999 ; int min_i = -1 ; for (int i=0 ;i<Window.size ();i++){ if (!Window[i].empty () && Time[Window[i].front ()]<min_time){ min_time = Time[Window[i].front ()]; min_i = i; } } return min_i; } void update (int subtime,int t) for (int i=0 ;i<Window.size ();i++){ if (i!=t && !Window[i].empty ()){ Time[Window[i].front ()] -= subtime; } } } void time_to_clock (int time) int hour = time/60 +8 ; int minn = time%60 ; if (hour>17 || (hour==17 &&minn>0 )) cout<<"Sorry" ; else { printf ("%02d:%02d" ,hour,minn); } } int main () int pCustom = 1 ; cin>>N>>M>>K>>Q; for (int i=1 ;i<=K;i++){ cin>>Time[i]; } for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++){ queue<int > q; Window.push_back (q); } while (pCustom<=N*M && pCustom<=K){ Window[(pCustom+1 )%M].push (pCustom); pCustom++; } while (!isemptyWindow ()){ int min_i = mintime (); int subtime = Time[Window[min_i].front ()]; nowtime += subtime; process[Window[min_i].front ()] = nowtime; Window[min_i].pop (); if (pCustom<=K){ Window[min_i].push (pCustom); pCustom++; } update (subtime,min_i); } for (int i=0 ;i<Q;i++){ int a; cin>>a; time_to_clock (process[a]); if (i!=Q-1 ) cout<<endl; } }
看答案发现五点前还没处理完的不可能赶人家走吧,所以修改了一下代码
参考了网上的AC代码,还是没看出来自己为什么错
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main () int win_num, win_len, n, k; scanf ("%d %d %d %d" , &win_num, &win_len, &n, &k); vector<vector<int >> times (win_num); vector<int > data (n) , start_time (n) ; for (int i=0 ; i<n; i++) scanf ("%d" , &data[i]); for (int i=0 ; i<n&&i<win_num*win_len; i++){ int t = i%win_num; start_time[i] = i<win_num?0 :times[t][i/win_num-1 ]; times[t].push_back (start_time[i]+data[i]); } for (int i=win_num*win_len; i<n; i++){ int mint=540 , w=-1 ; for (int j=0 ; j<win_num; j++){ int st = times[j][times[j].size ()-win_len]; if (st<mint){ mint = st; w = j; } } if (w==-1 ) start_time[i] = 540 ; else { start_time[i] = times[w][times[w].size ()-1 ]; times[w].push_back (start_time[i]+data[i]); } } for (int i=0 ; i<k; i++){ int x; scanf ("%d" , &x); x--; if (start_time[x]>=540 ) printf ("Sorry\n" ); else printf ("%02d:%02d\n" , (start_time[x]+data[x])/60 +8 , (start_time[x]+data[x])%60 ); } return 0 ; }
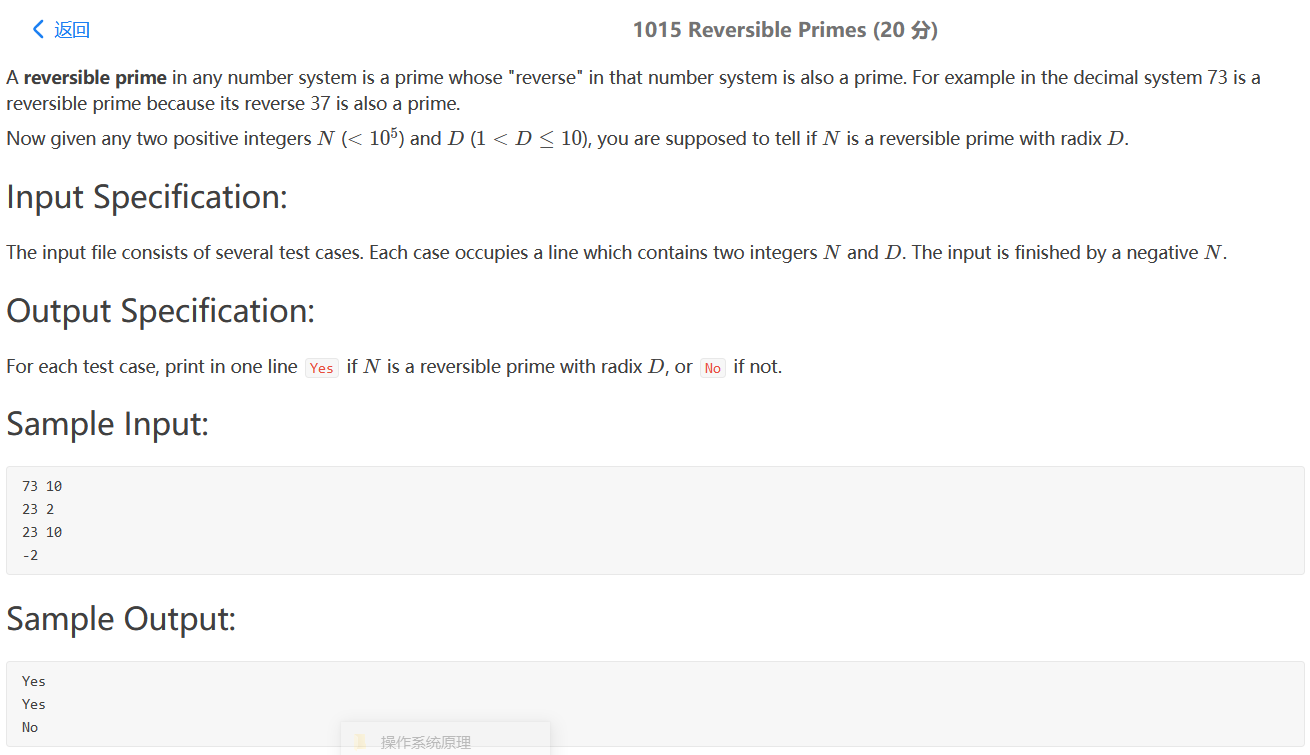
PAT 1015
最初这题题目没看懂
题目大意:给出一个素数,判断在d进制下反转后在十进制下是否是素数,如果是,则输出”Yes”,否,则输出”No”。
Sample input:
73 在十进制下反转 37
23(10111) 在2进制下反转(11101) 29 是质数
23在10进制下反转32不是质数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int z[101 ];bool isPrime (int n) if (n <= 1 ) return false ; int sqr = (int ) sqrt (1.0 * n); for (int i = 2 ; i <= sqr; ++i) { if (n % i == 0 ) return false ; } return true ; } void Check (int n, int d) int zNum = 0 ; do { z[zNum++] = n % d; n /=d; }while (n != 0 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < zNum; ++i) { n = n * d + z[i]; } if (isPrime (n) == true ){ printf ("Yes\n" ); }else { printf ("No\n" ); } } int main (int argc, char const *argv[]) int n, d; while (scanf ("%d" , &n) != EOF){ if (n < 0 ){ break ; } scanf ("%d" , &d); if (isPrime (n) == false ){ printf ("No\n" ); }else { Check (n, d); } } return 0 ; }
PAT 1016 题目大意: 打长途电话每分钟要花一定的费用,这取决于一天中打电话的时间。当客户开始连接长途电话时,时间会被记录下来,客户挂断电话的时间也会被记录下来。每个日历月,每一分钟都会向客户发送一张账单(按一天中的时间确定的费率)。你的工作是准备每个月的账单,给你一套电话记录。
PAT 1039
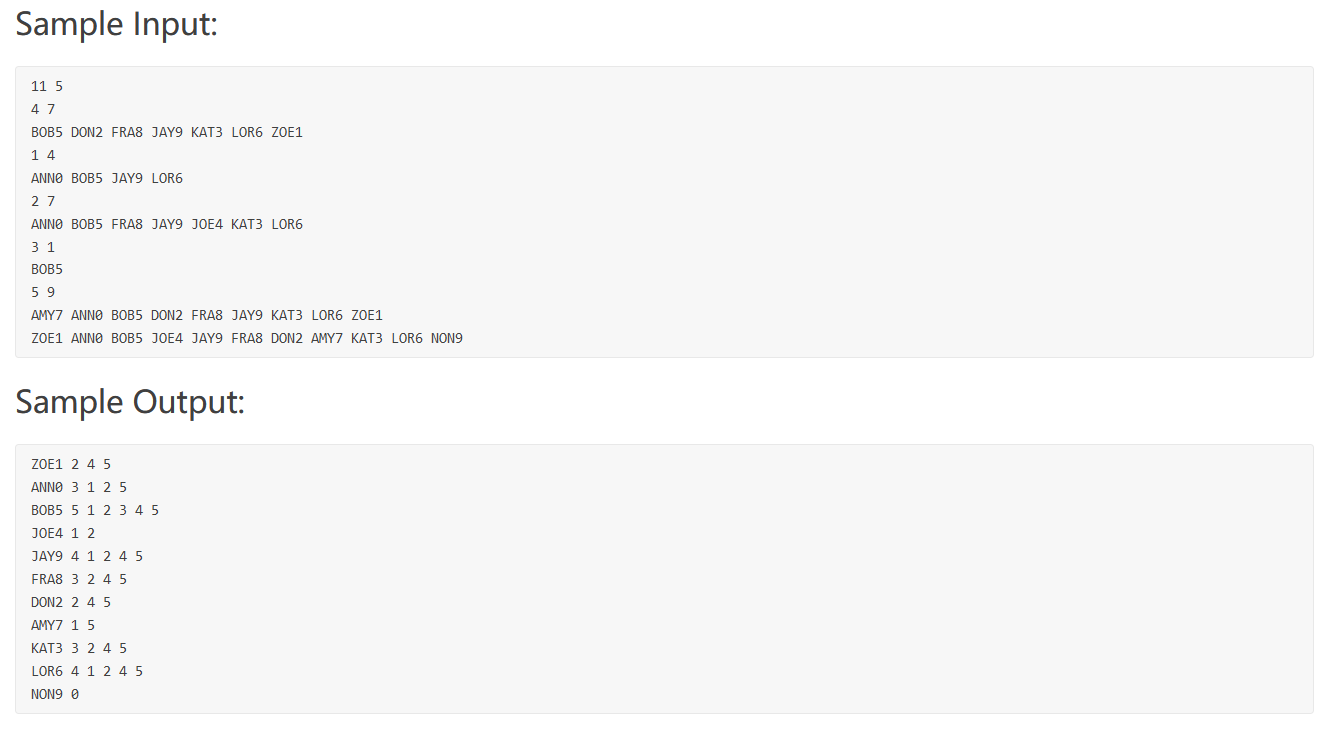
题目大意:有一个表保存了学生的选课信息,根据学生姓名来查询信息,输出该名学生选课情况。
样例解释,有11个学生,共5门课,接下来10行表示每门课的选课情况,例如2,3行,第4门课(4是课程号),7个人选,选课名单BOB5…
最后一行按顺序输出学生的名单。结果输出每个学生的名字,选课门数和课程号。
思路比较清楚,我定义的数据结构还算比较复杂
Query_List 代表学生的选课列表(索引就代表学号),Course_List代表课程的学生列表。
我们先把数据读入课程列表中,再用一个Map将学生的名字和学号一一对应。然后遍历Course_List,查到Course_List的学生选的哪门课就往Query_List中添加。最后将Query_List中的list排序,输出。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 typedef struct Query_List { string name="" ; vector<int > list; }Query_List; typedef struct Course_List { int cno; vector<string> name; }Course_List;
坑点:最后一个测试数据比较大,据说要用scanf和printf,或者用char
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef struct Query_List { string name="" ; vector<int > list; }Query_List; typedef struct Course_List { int cno; vector<string> name; }Course_List; int main () int N,K; cin>>N>>K; vector<Course_List> CList; vector<Query_List> QList; map<string,int > M; for (int i=1 ;i<=K;i++){ int i1,i2; string i3; cin>>i1>>i2; Course_List C; C.cno = i1; for (int i=0 ;i<i2;i++){ cin>>i3; C.name.push_back (i3); } CList.push_back (C); } for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++){ string name; cin>>name; M[name] = i; Query_List Q; Q.name = name; QList.push_back (Q); } for (int i=0 ;i<CList.size ();i++){ for (int j=0 ;j<CList[i].name.size ();j++){ QList[M[CList[i].name[j]]].list.push_back (CList[i].cno); } } for (int i=0 ;i<QList.size ();i++){ sort (QList[i].list.begin (),QList[i].list.end ()); cout<<QList[i].name<<" " <<QList[i].list.size (); for (int k=0 ;k<QList[i].list.size ();k++){ cout<<" " <<QList[i].list[k]; } if (i!=QList.size ()-1 ) cout<<endl; } }
PAT 1040(dp)
题目大意:查询长度最长的对称串
动态规划,dp[i] [j] 表示从 i 开始到 j 结束的对称串。( i<=j )
dp[i] [i] = 1;
dp [i] [i+1] = (s[i] == s[i+1])
dp[i] [i+k] = (s[i] == s[i+k] && dp[i+1] [i+k-1] )
i,j的状态取决于 i+1,j-1是不是对称串
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main () string s; getline (cin,s); int length = s.length (); bool dp[length][length]; for (int i=0 ;i<length;i++) memset (dp[i],false ,sizeof (dp[i])); int maxlength = 1 ; for (int i=0 ;i<length;i++) dp[i][i]=true ; for (int i=0 ;i<length-1 ;i++){ if (s[i]==s[i+1 ]) {dp[i][i+1 ]=true ; maxlength=2 ;} } for (int k=2 ;k<length;k++){ for (int i=0 ;i<length && i+k<length ; i++){ if (s[i]==s[i+k] && dp[i+1 ][i+k-1 ]==true ){ dp[i][i+k]=true ; maxlength=k+1 ; } } } cout<<maxlength; }
PAT 1041
题目大意,找到最近的一个不重复的数,如果找不到输出none。
直接一个map存放出现的次数,之后再从前往后遍历。无脑题。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main () vector<int > A; int N; cin>>N; bool unique = false ; int unicode; int Map[50000 ]; memset (Map,0 ,sizeof (Map)); for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++){ int a ;cin>>a; A.push_back (a); Map[a]++; } int j; while (!unique && j<A.size ()){ if (Map[A[j]]==1 ){ unique = true ; unicode = A[j]; break ; } j++; } if (unique) cout<<unicode; else cout<<"None" ; }
PAT 1081
简单题,模拟分数乘法操作。
注意点:题目准确说明数的范围是Long ing型,第四个测试点出现浮点错误,需要判断一下分母为0的情况。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;long long gcd (long long a, long long b) return b == 0 ? a:gcd (b, a%b); } int main () int N; cin>>N; long long fenzi[N]; long long fenmu[N]; for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++){ scanf ("%lld/%lld" ,&fenzi[i],&fenmu[i]); } long long denominator = 1 ; long long numerator = 0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++) denominator *= fenmu[i]; for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++) numerator += denominator/fenmu[i]*fenzi[i]; if (denominator==0 ){ printf ("0" ); return 0 ; } long long interger = numerator/denominator; if (interger) cout<<interger; long long re_numerator = numerator - interger*denominator; if (re_numerator){ if (interger) cout<<" " ; long long g = gcd (re_numerator,denominator); re_numerator /= g; denominator/= g; printf ("%lld/%lld" ,re_numerator,denominator); } }
2021.7.10 PAT 1152
题目大意:给定一个N位的数,寻找第一次出现的m位素数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #include <math.h> using namespace std;#define LL long long bool issushu (LL t) if (t==2 ) return true ; for (LL s = 2 ; s<sqrt (t) ;s++ ){ if (t%s==0 ) return false ; } return true ; } int main () int m,n; string s="" ; cin>>m>>n; cin>>s; string res = "" ; bool flag = false ; for (int i=0 ;i+n<=m;i++){ res = s.substr (i,n); if (issushu (stoi (res))){ cout<<res; flag = true ; break ; } } if (flag==false ) cout<<"404" ; }
PAT 1153
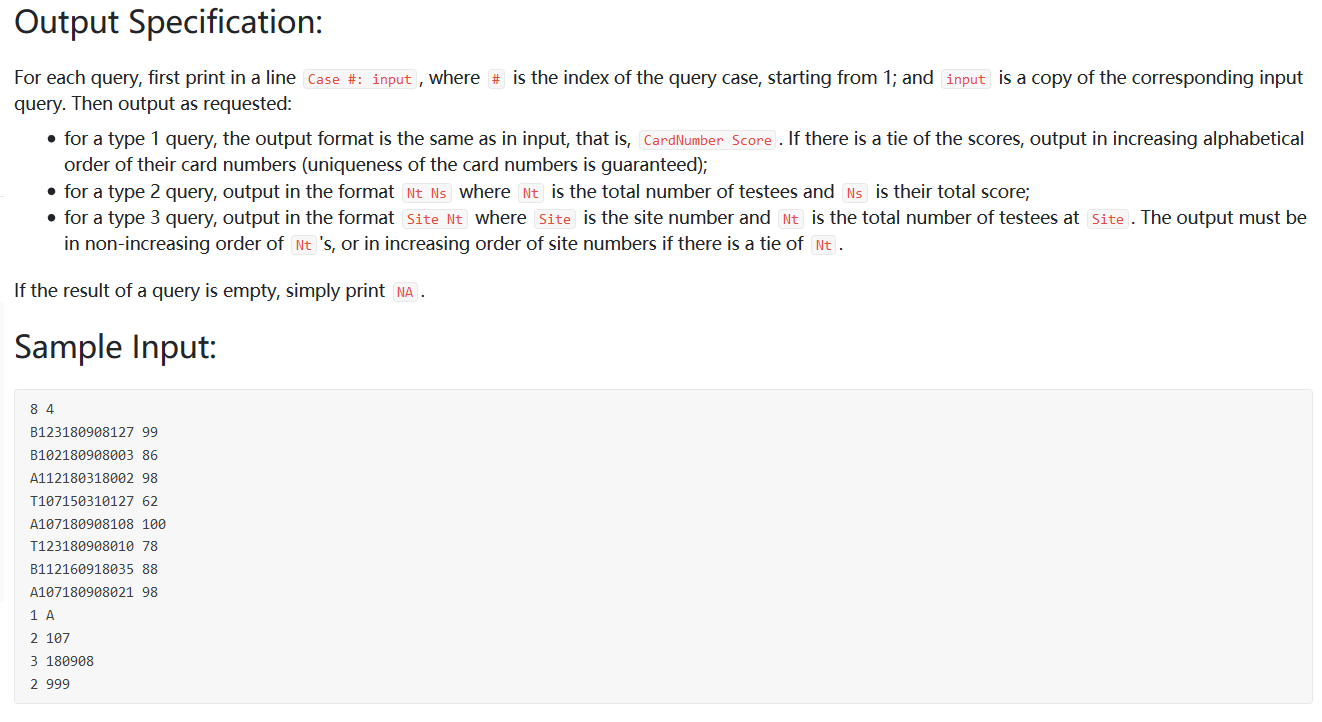
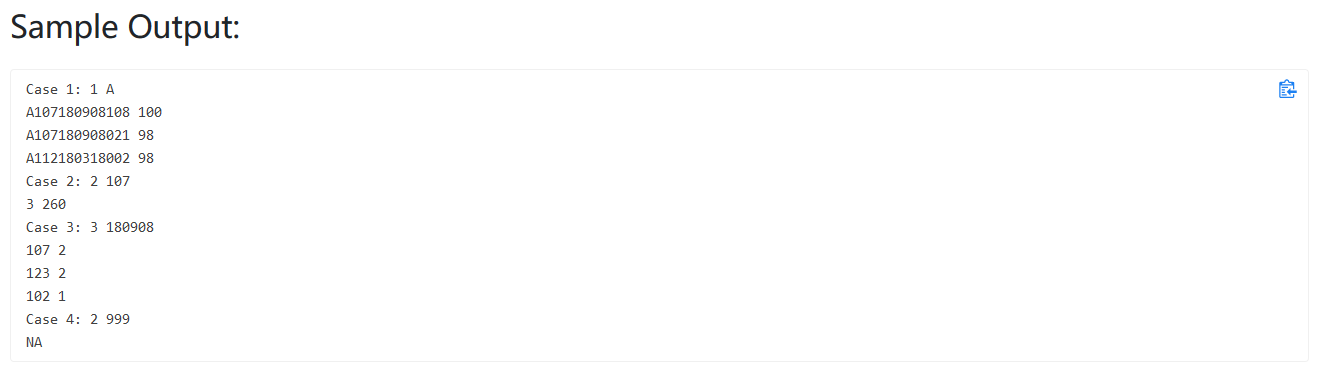
题目大意:给出一组学生的准考证号和成绩,准考证号包含了等级(乙甲顶),考场号,日期,和个人编号信息,并有三种查询方式修改前的代码 :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef struct patinfo { char type; string total; string site; string testdate; string testee_num; int score; }patinfo; bool cmp1 (patinfo A,patinfo B) if (A.score==B.score){ return A.total<B.total; } return A.score>B.score; } bool flag_2 (pair<string,int > o1,pair<string,int > o2) return o1.second>o2.second; } vector<patinfo> PatList; int main () freopen ("a.txt" , "r" , stdin); int N,M; cin>>N>>M; for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++){ string aa; cin>>aa; int score; cin>>score; patinfo patexample; patexample.total = aa; patexample.type = aa[0 ]; patexample.site = aa.substr (1 ,3 ); patexample.testdate = aa.substr (4 ,6 ); patexample.testee_num = aa.substr (10 ,3 ); patexample.score = score; PatList.push_back (patexample); } for (int i=0 ;i<M;i++){ int query; cin>>query; if (query==1 ){ char T; cin>>T; vector<patinfo> p1; for (int j=0 ;j<PatList.size ();j++){ if (PatList[j].type==T){ p1.push_back (PatList[j]); } } sort (p1.begin (),p1.end (),cmp1); cout<<"Case " <<i+1 <<": 1 " <<T<<endl; if (p1.size ()==0 ) cout<<"NA" ; for (int j=0 ;j<p1.size ();j++){ cout<<p1[j].total<<" " <<p1[j].score; if (j<p1.size ()-1 ) cout<<endl; } }else if (query==2 ){ string aa; cin>>aa; int number = 0 ; int total = 0 ; for (int j=0 ;j<PatList.size ();j++){ if (PatList[j].site==aa){ number++; total+=PatList[j].score; } } cout<<"Case " <<i+1 <<": 2 " <<aa<<endl; if (number==0 ) cout<<"NA" ; else { cout<<number<<" " <<total; } }else if (query==3 ){ string aa; cin>>aa; unordered_map<string,int > M; for (int j=0 ;j<PatList.size ();j++){ if (PatList[j].testdate==aa){ string cc = PatList[j].site; if (M.find (cc)==M.end ()){ M[cc] = 1 ; }else { M[cc] += 1 ; } } } vector<pair<string,int >> dic1 (M.begin (),M.end ()); sort (dic1.begin (),dic1.end (),flag_2); cout<<"Case " <<i+1 <<": 3 " <<aa<<endl; if (dic1.size ()==0 ) cout<<"NA" ; for (int j=0 ;j<dic1.size ();j++){ cout<<dic1[j].first<<" " <<dic1[j].second; if (j<dic1.size ()-1 ) cout<<endl; } } if (i<N-1 ) cout<<endl; } }
改后发现格式不需要那么复杂
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef struct patinfo { char type; string total; string site; string testdate; string testee_num; int score; }patinfo; bool cmp1 (patinfo A,patinfo B) if (A.score==B.score){ return A.total<B.total; } return A.score>B.score; } bool flag_2 (pair<string,int > o1,pair<string,int > o2) if (o1.second==o2.second){ return o1.first<o2.first; } return o1.second>o2.second; } vector<patinfo> PatList; int main () freopen ("a.txt" , "r" , stdin); int N,M; cin>>N>>M; for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++){ string aa; cin>>aa; int score; cin>>score; patinfo patexample; patexample.total = aa; patexample.type = aa[0 ]; patexample.site = aa.substr (1 ,3 ); patexample.testdate = aa.substr (4 ,6 ); patexample.testee_num = aa.substr (10 ,3 ); patexample.score = score; PatList.push_back (patexample); } for (int i=0 ;i<M;i++){ int query; cin>>query; if (query==1 ){ char T; cin>>T; vector<patinfo> p1; for (int j=0 ;j<PatList.size ();j++){ if (PatList[j].type==T){ p1.push_back (PatList[j]); } } sort (p1.begin (),p1.end (),cmp1); cout<<"Case " <<i+1 <<": 1 " <<T<<endl; if (p1.size ()==0 ) cout<<"NA" <<endl; for (int j=0 ;j<p1.size ();j++){ cout<<p1[j].total<<" " <<p1[j].score<<endl; } }else if (query==2 ){ string aa; cin>>aa; int number = 0 ; int total = 0 ; for (int j=0 ;j<PatList.size ();j++){ if (PatList[j].site==aa){ number++; total+=PatList[j].score; } } cout<<"Case " <<i+1 <<": 2 " <<aa<<endl; if (number==0 ) cout<<"NA" <<endl; else { cout<<number<<" " <<total<<endl; } }else if (query==3 ){ string aa; cin>>aa; unordered_map<string,int > M; for (int j=0 ;j<PatList.size ();j++){ if (PatList[j].testdate==aa){ string cc = PatList[j].site; M[cc] += 1 ; } } vector<pair<string,int >> dic1; for (auto it : M) dic1.push_back (make_pair (it.first, it.second)); cout<<"Case " <<i+1 <<": 3 " <<aa<<endl; if (dic1.size ()==0 ) cout<<"NA" <<endl; sort (dic1.begin (),dic1.end (),flag_2); for (int j=0 ;j<dic1.size ();j++){ cout<<dic1[j].first<<" " <<dic1[j].second<<endl; } } } }
最后一格多一个换行也没关系
修改后的AC代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef struct testees { string id; int score; }testees; vector<testees> t; int N,M,type;bool cmp (testees a,testees b) if (a.score==b.score) return a.id<b.id; else return a.score>b.score; } bool cmp1 (pair<string,int > a,pair<string,int > b) if (a.second==b.second) return a.first<b.first; else return a.second>b.second; } void deal (string s) unordered_map<string,int > mp; bool flag = false ; if (type==1 ){ sort (t.begin (),t.end (),cmp); for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++){ if (s==t[i].id.substr (0 ,1 )){ printf ("%s %d\n" ,t[i].id.c_str (),t[i].score); flag = true ; } } } else if (type==2 ){ int sum = 0 ,count = 0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++){ if (s==t[i].id.substr (1 ,3 )){ sum += t[i].score; flag = true ; count++; } } if (flag) printf ("%d %d\n" ,count,sum); } else if (type==3 ){ for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++){ if (s==t[i].id.substr (4 ,6 )){ mp[t[i].id.substr (1 ,3 )]++; flag = true ; } } vector<pair<string,int >> vec_mp (mp.begin (),mp.end ()); sort (vec_mp.begin (),vec_mp.end (),cmp1); for (int i=0 ;i<vec_mp.size ();i++){ printf ("%s %d\n" ,vec_mp[i].first.c_str (),vec_mp[i].second); } } if (!flag) printf ("NA\n" ); } int main () string s; cin>>N>>M; for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++){ testees ta; cin>>ta.id>>ta.score; t.push_back (ta); } for (int i=1 ;i<=M;i++){ cin>>type>>s; printf ("Case %d: %d %s\n" ,i,type,s.c_str ()); deal (s); } }
PAT 1154
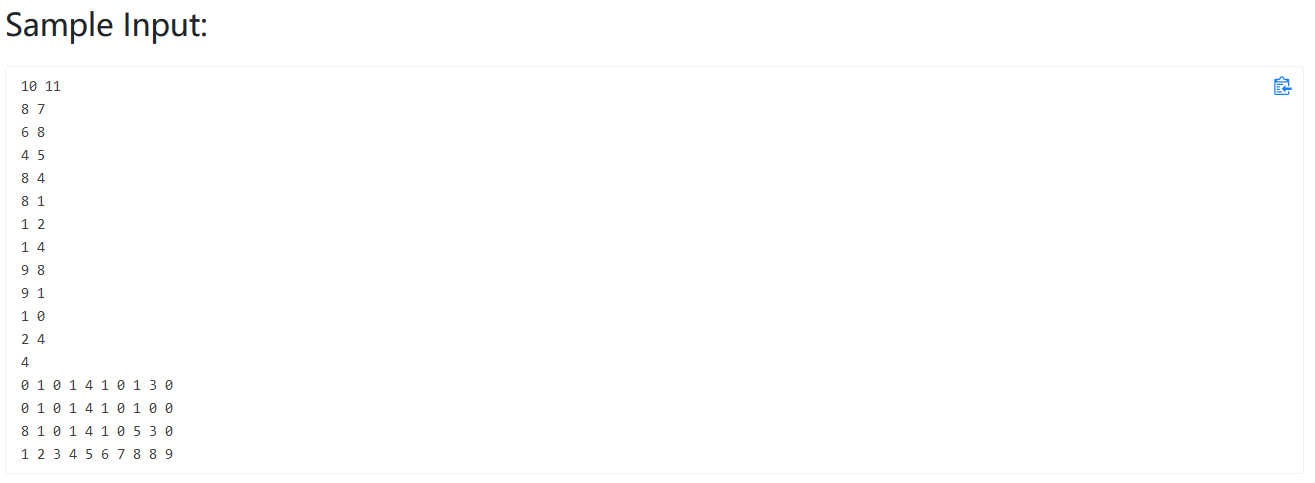
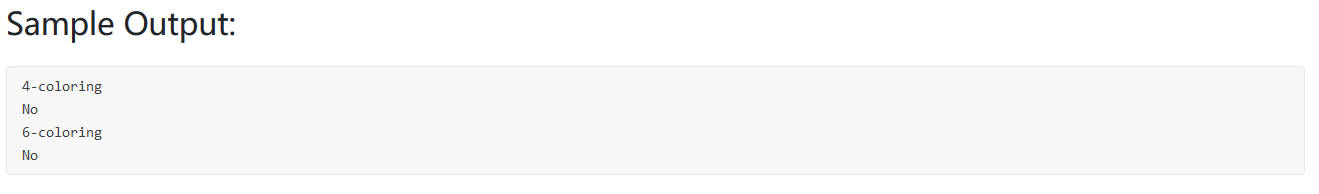
题目大意:
相邻的两边不能同色,不用邻接矩阵,直接用边进行判断即可
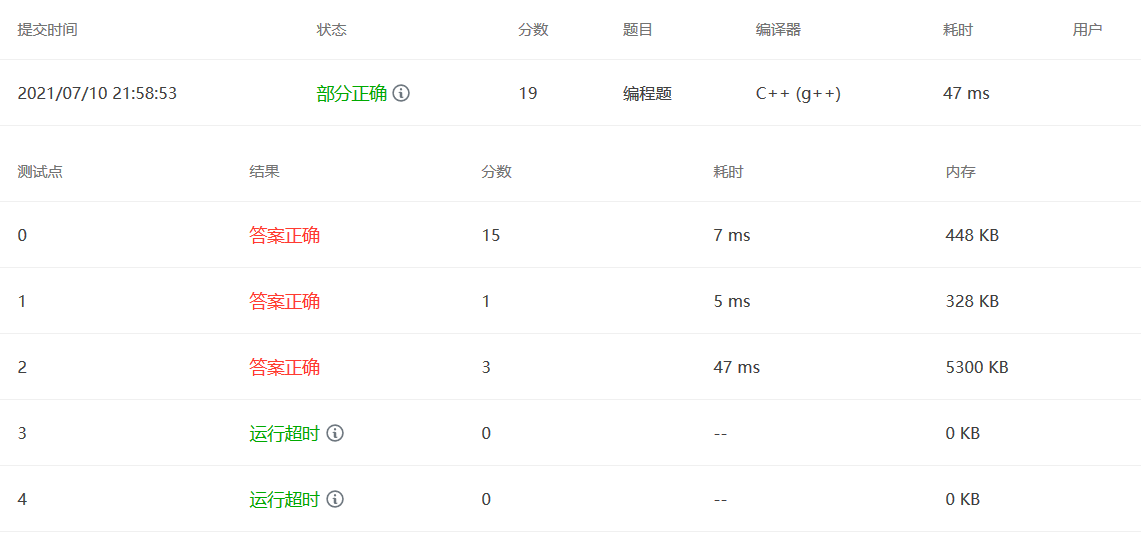
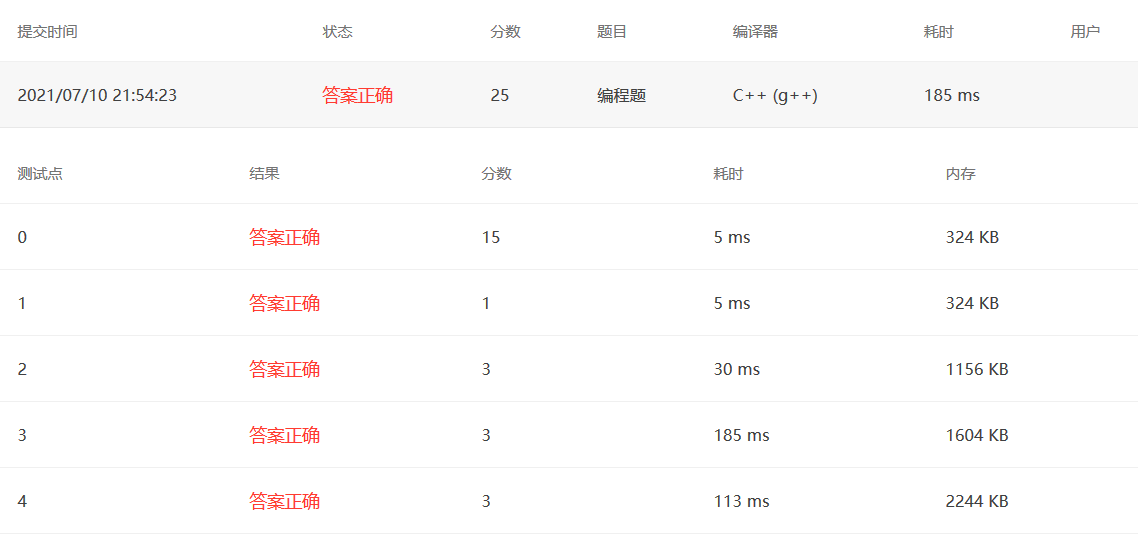
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main () int V,E; cin>>V>>E; vector<int > Graph (V,0 ) ; vector<pair<int ,int >> Edge; for (int i=0 ;i<E;i++){ int a,b; cin>>a>>b; Edge.push_back (make_pair (a,b)); } int query; cin>>query; for (int i=0 ;i<query;i++){ bool flag = true ; unordered_map<int ,int > M; for (int i=0 ;i<V;i++){ int a; cin>>a; Graph[i] = a; M[a]++; } for (int i=0 ;i<E;i++){ if (Graph[Edge[i].first] == Graph[Edge[i].second]){ flag = false ; } } if (flag==false ) cout<<"No" <<endl; else cout<<M.size ()<<"-coloring" <<endl; } }
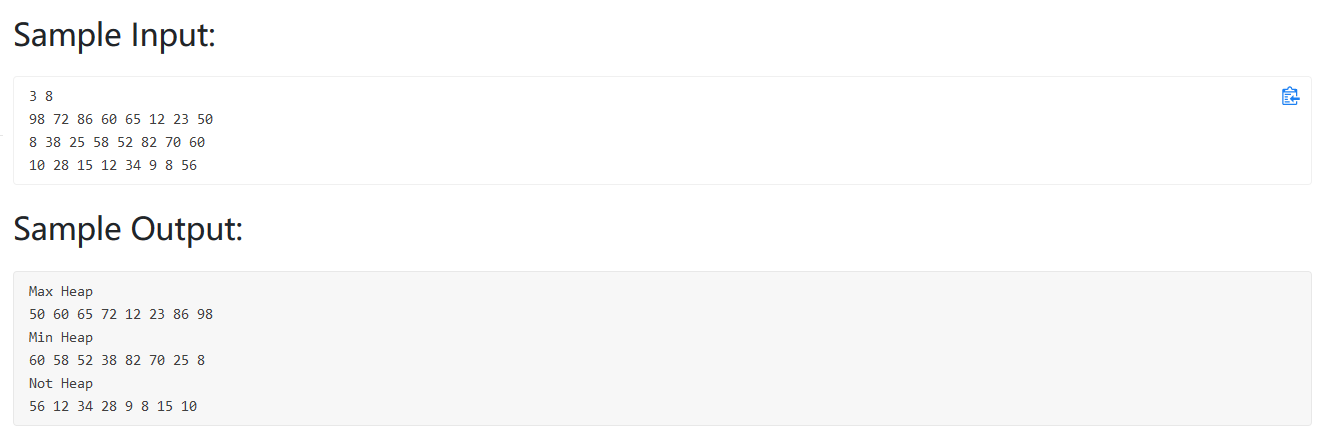
PAT 1155(回溯)
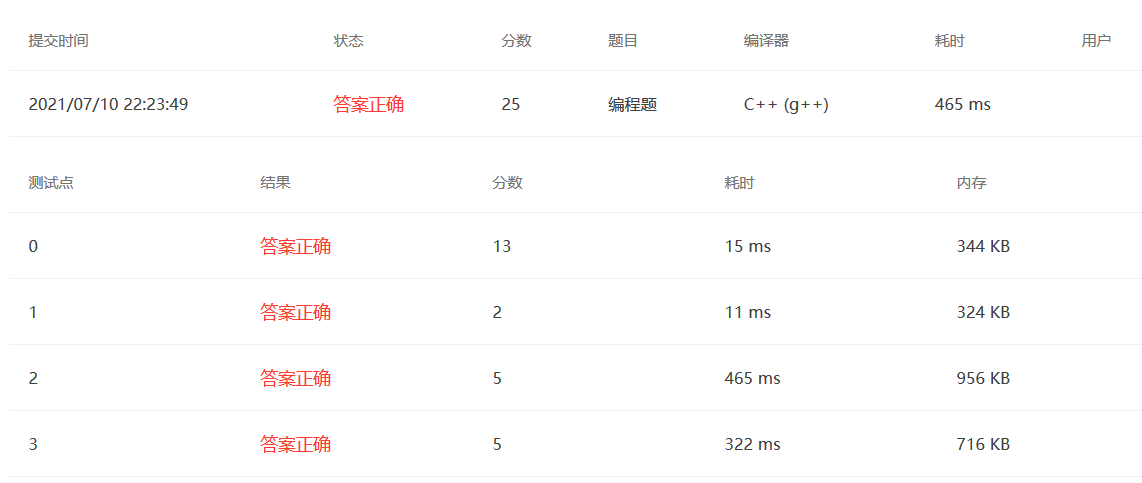
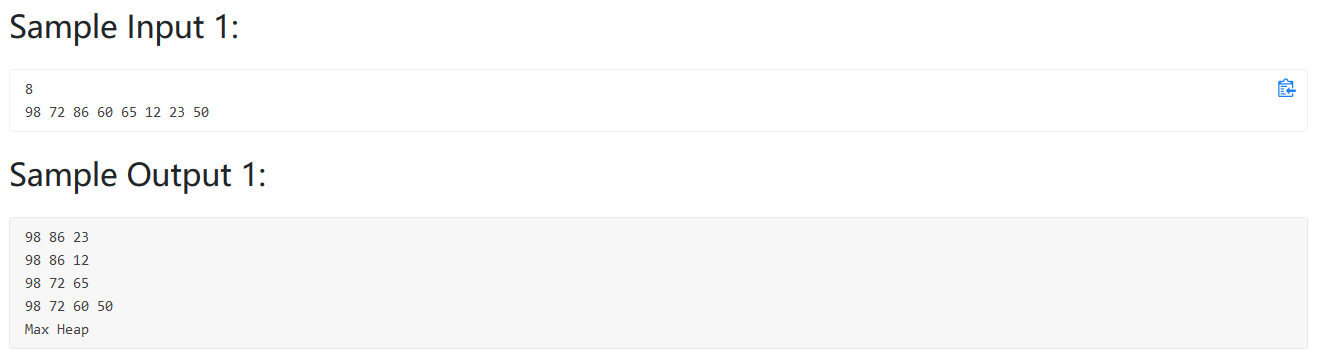
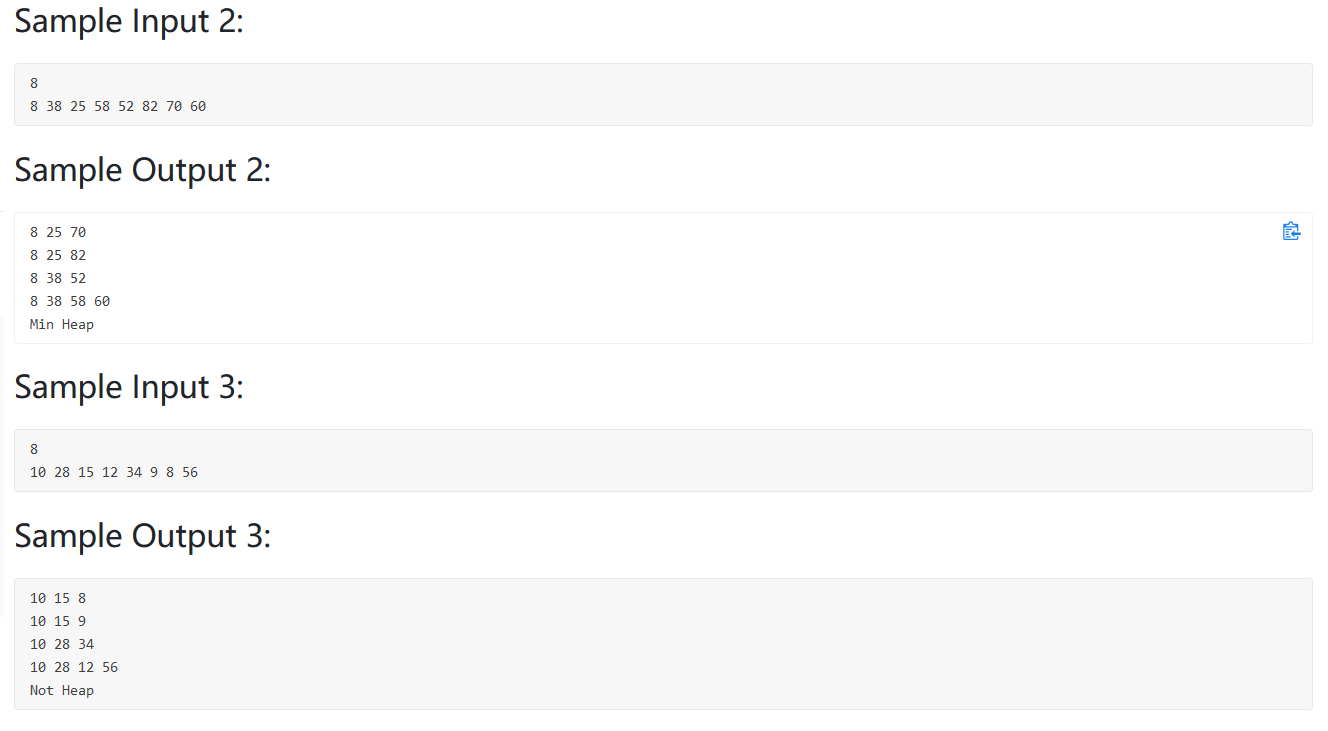
题目大意:给定一个二叉树,判断是不是大顶堆或小顶堆,并且输出路径,从右到左输出,可以利用回溯法解决。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int MAX_OR_MIN;bool flag = true ;int N;vector<int > V; vector<int > path; vector<vector<int >> res; void backtrace (int node) if (2 *node>N){ res.push_back (path); } if (2 *node<=N){ if (MAX_OR_MIN==1 ){ if (V[2 *node]>V[node]){ flag = false ; } }else { if (V[2 *node]<V[node]){ flag = false ; } } path.push_back (V[2 *node]); backtrace (2 *node); path.pop_back (); } if (2 *node+1 <=N){ if (MAX_OR_MIN==1 ){ if (V[2 *node+1 ]>V[node]){ flag = false ; } }else { if (V[2 *node+1 ]<V[node]){ flag = false ; } } path.push_back (V[2 *node+1 ]); backtrace (2 *node+1 ); path.pop_back (); } } int main () cin>>N; V.resize (N+1 ); for (int i=1 ;i<=N;i++){ cin>>V[i]; } for (int i=2 ;i<=N;i++){ if (V[1 ]>V[i]){ MAX_OR_MIN = 1 ; break ; } if (V[1 ]<V[i]){ MAX_OR_MIN = 0 ; break ; } } path.push_back (V[1 ]); backtrace (1 ); for (int i=res.size ()-1 ;i>=0 ;i--){ for (int j=0 ;j<res[i].size ();j++){ if (j==res[i].size ()-1 ) cout<<res[i][j]; else cout<<res[i][j]<<" " ; } cout<<endl; } if (flag){ if (MAX_OR_MIN) cout<<"Max Heap" <<endl; else cout<<"Min Heap" <<endl; }else { cout<<"Not Heap" <<endl; } }
2021.7.17 PAT 1148
题目大意:狼人杀,给出N个人,其中只有两个是狼人,找出狼人,其中所有人中有两个人说谎,说谎的人里包含一个狼人。
本来是想通过假设说谎的人数 i,j 来找到狼人,后来发现通过假定狼人i,j来验证是否成立来得更加方便。整了一个半小时了都。
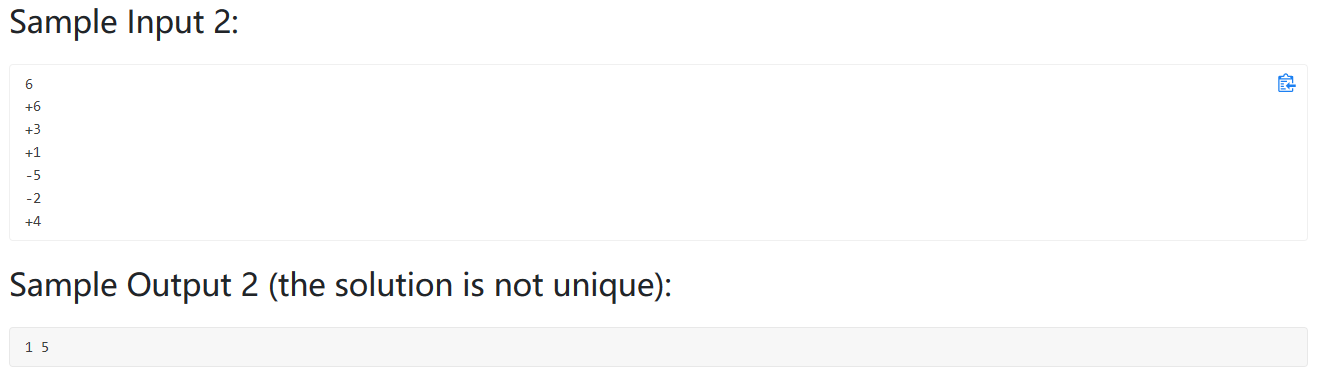
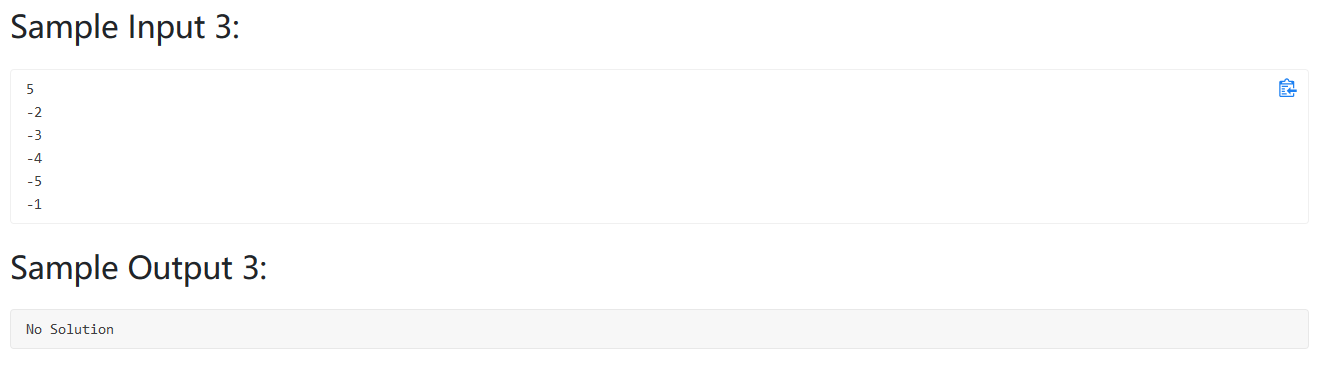
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main () int N; cin>>N; vector<pair<int ,int >> res; vector<int > Data (N+1 ) ; for (int i=1 ;i<=N;i++){ cin>>Data[i]; } int i,j; bool istrue = false ; for (i=1 ;i<N;i++){ for (j=i+1 ;j<=N;j++){ vector<int > output (N+1 ,-1 ) ; for (int k=1 ;k<=N;k++) { if (k==i || k==j) output[k] = -1 ; else output[k] = 1 ; } int fa = 0 ; int wefa = 0 ; for (int k=1 ;k<=N;k++){ if (Data[k] * output[abs (Data[k])]<0 ) { fa++; if (k==i || k==j) wefa++; } } if (fa==2 && wefa==1 ){ cout<<i<<' ' <<j; return 0 ; } } } cout<<"No Solution" ; }
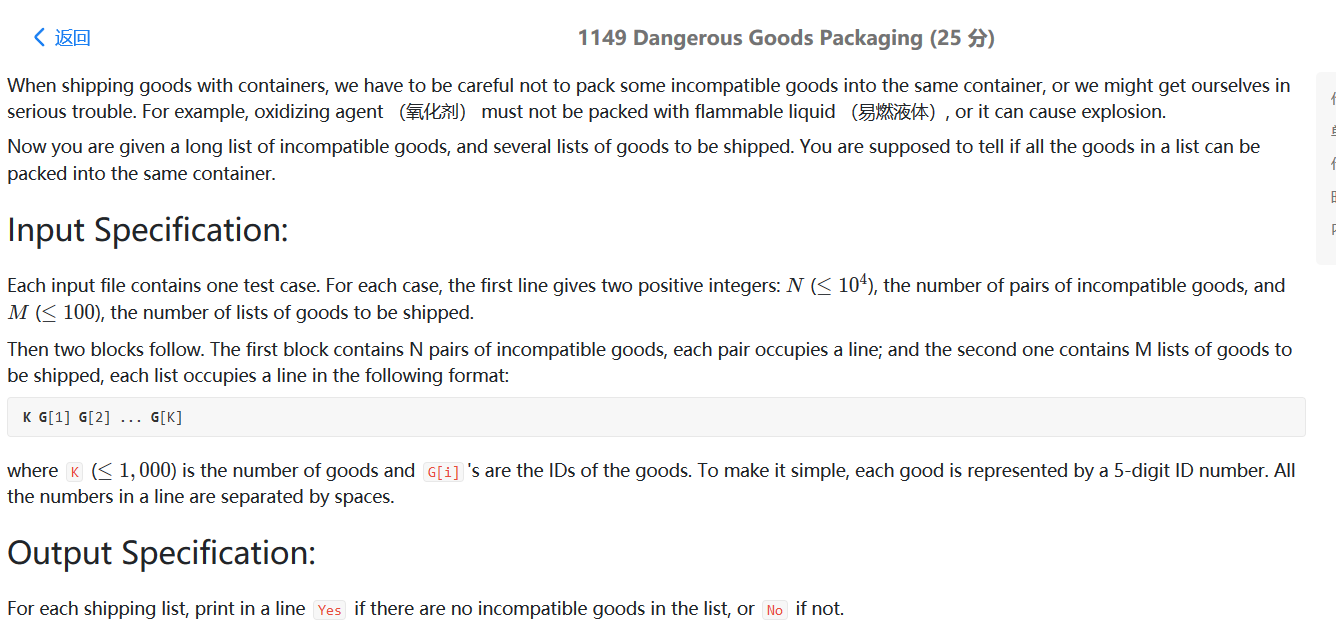
PAT 1149
题目大意:集装箱运输货物时,我们必须特别小心,不能把不相容的货物装在一只箱子里。比如氧化剂绝对不能跟易燃液体同箱,否则很容易造成爆炸。给定一张不相容物品的清单,需要你检查每一张集装箱货品清单,判断它们是否能装在同一只箱子里。对每箱货物清单,判断是否可以安全运输。如果没有不相容物品,则在一行中输出 Yes,否则输出 No~
分析:用map存储每一个货物的所有不兼容货物~在判断给出的一堆货物是否是相容的时候,判断任一货物的不兼容货物是否在这堆货物中~如果存在不兼容的货物,则这堆货物不能相容~如果遍历完所有的货物,都找不到不兼容的两个货物,则这堆货物就是兼容的~
用map存储每一个货物的所有不相容货物,然后逐一进行比较
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main () int M,N; cin>>M>>N; map<string,vector<string>> Map; for (int i=0 ;i<M;i++){ string a,b; cin>>a>>b; if (Map.find (a)==Map.end ()){ vector<string> ss; ss.push_back (b); Map[a] = ss; }else { Map[a].push_back (b); } if (Map.find (b)==Map.end ()){ vector<string> ss; ss.push_back (a); Map[b] = ss; }else { Map[b].push_back (a); } } for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++){ int Q; cin>>Q; vector<string> res (Q) ; for (int k=0 ;k<Q;k++){ cin>>res[k]; } bool flag = true ; for (int ii=0 ;ii<res.size ();ii++){ for (int jj=0 ;jj<res.size ();jj++){ if (ii==jj) continue ; if (Map.find (res[ii])== Map.end ()) continue ; else { vector<string> temp = Map[res[ii]]; for (int zz=0 ;zz<temp.size ();zz++){ if (temp[zz]==res[jj]){ flag = false ; break ; } } } if (flag==false ) break ; } if (flag==false ) break ; } if (flag==true ) cout<<"Yes" <<endl; else cout<<"No" <<endl; } }
修改后,在查找是否兼容这一部分,需要通过map定位到该值所在的结点,然后往节点后的链表顺序查找,这样可能比较浪费时间。
牺牲空间的方法,首先开辟一个大空间res,存放所有可能的物品,每遍历一个物品,就往res中添入不可兼容的物品,之后再查找时,如果在res中,则不可兼容
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main () int M,N; cin>>M>>N; map<int ,vector<int >> Map; for (int i=0 ;i<M;i++){ int a,b; cin>>a>>b; Map[a].push_back (b); Map[b].push_back (a); } for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++){ bool flag = true ; int Q; cin>>Q; vector<int > res (100000 ,0 ) ; int x; while (Q--){ cin>>x; if (res[x]==1 ) flag = false ; res[x] = 1 ; for (int j=0 ;j<Map[x].size ();j++) res[Map[x][j]] = 1 ; } if (flag==true ) cout<<"Yes" <<endl; else cout<<"No" <<endl; } }
PAT 1150
题目大意:旅行商问题,给定一个图,并给定路径,判断该路径是否满足一下条件:
Ts a simple cycle 每个城市只访问一次,并且回到远点
Not a TS cycle 没有访问到每个城市,或者没有回到原点
NA not a TS cycle 路径不可达
TS cycle 多次访问每个城市
然后求距离最短的路径。
思路:构建邻接矩阵,一个visited数组判断是否访问过,按照路径一次模拟一遍即可,水题。
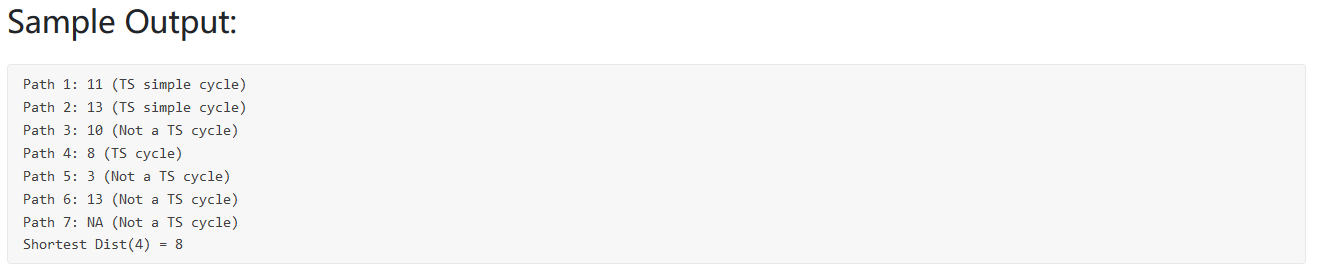
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main () int N,M; cin>>N>>M; int shortest = INT_MAX; int shortestindex = -1 ; vector<vector<int >> Graph (N+1 ,vector <int >(N+1 ,0 )); for (int i=0 ;i<M;i++){ int d1,d2,dist; cin>>d1>>d2>>dist; Graph[d1][d2] = dist; Graph[d2][d1] = dist; } int T; cin>>T; for (int kk=1 ;kk<=T;kk++){ int flag[3 ] = {0 }; vector<int > visited (N+1 ,0 ) ; int total_cost = 0 ; int C; cin>>C; vector<int > path (C+1 ) ; for (int i=1 ;i<=C;i++){ cin>>path[i]; } for (int i=1 ;i<C;i++){ if (Graph[path[i]][path[i+1 ]]==0 ) { flag[0 ] = 1 ; break ; }else { total_cost += Graph[path[i]][path[i+1 ]]; visited[path[i]] ++; } } for (int i=1 ;i<visited.size ();i++){ if (visited[i]==0 ) flag[1 ] = 1 ; if (visited[i]>1 ) flag[2 ] = 1 ; } if (!flag[0 ] && !flag[1 ] && !flag[2 ] && path[1 ]==path[C]){ printf ("Path %d: %d (TS simple cycle)\n" ,kk,total_cost); if (total_cost<shortest){ shortest = total_cost; shortestindex = kk; } }else if (flag[0 ]){ printf ("Path %d: NA (Not a TS cycle)\n" ,kk); }else if (flag[1 ] || path[1 ]!=path[C]){ printf ("Path %d: %d (Not a TS cycle)\n" ,kk,total_cost); }else if (flag[2 ]){ printf ("Path %d: %d (TS cycle)\n" ,kk,total_cost); if (total_cost<shortest){ shortest = total_cost; shortestindex = kk; } } } printf ("Shortest Dist(%d) = %d" ,shortestindex,shortest); }
PAT 1151
题目大意:给出中序序列和先序序列,再给出两个点,求这两个点的最近公共祖先~
柳神题解:不用建树~已知某个树的根结点,若a和b在根结点的左边,则a和b的最近公共祖先在当前子树根结点的左子树寻找,如果a和b在当前子树根结点的两边,在当前子树的根结点就是a和b的最近公共祖先,如果a和b在当前子树根结点的右边,则a和b的最近公共祖先就在当前子树的右子树寻找。中序加先序可以唯一确定一棵树,在不构建树的情况下,在每一层的递归中,可以得到树的根结点,在此时并入lca算法可以确定两个结点的公共祖先~
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;unordered_map<int ,int > Inordered_Map; void search_ancestor (vector<int > preorder,vector<int > inorder,int node1, int node2,int pre_left,int pre_right,int in_left,int in_right) int in_position = Inordered_Map[preorder[pre_left]]; int n1_position = Inordered_Map[node1]; int n2_position = Inordered_Map[node2]; int mid_position = pre_left+in_position-in_left; if ((n1_position-in_position)*(n2_position-in_position)<0 ){ printf ("LCA of %d and %d is %d.\n" ,node1,node2,inorder[in_position]); return ; }else if ((n1_position-in_position)*(n2_position-in_position)==0 ){ if (n1_position==in_position){ printf ("%d is an ancestor of %d.\n" ,inorder[in_position],node2); }else if (n2_position==in_position){ printf ("%d is an ancestor of %d.\n" ,inorder[in_position],node1); } return ; }else if (n1_position<in_position && n2_position<in_position){ search_ancestor (preorder,inorder,node1,node2,pre_left+1 ,mid_position,in_left,in_position-1 ); }else if (n1_position>in_position && n2_position>in_position){ search_ancestor (preorder,inorder,node1,node2,mid_position+1 ,pre_right,in_position+1 ,in_right); } } int main () int M,N; cin>>M>>N; vector<int > preorder (N) ; vector<int > inorder (N) ; for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++) cin>>inorder[i]; for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++) cin>>preorder[i]; for (int i=0 ;i<inorder.size ();i++){ Inordered_Map[inorder[i]] = i; } for (int i=0 ;i<M;i++){ int node1,node2; cin>>node1>>node2; if (Inordered_Map.find (node1)==Inordered_Map.end () && Inordered_Map.find (node2)==Inordered_Map.end ()){ printf ("ERROR: %d and %d are not found.\n" ,node1,node2); }else if (Inordered_Map.find (node1)==Inordered_Map.end ()){ printf ("ERROR: %d is not found.\n" ,node1); }else if (Inordered_Map.find (node2)==Inordered_Map.end ()){ printf ("ERROR: %d is not found.\n" ,node2); }else { int n = preorder.size ()-1 ; search_ancestor (preorder,inorder,node1,node2,0 ,n,0 ,n); } } }
问题出在递归过程中变量设置太多,导致递归栈溢出
1 2 void search_ancestor(vector<int> preorder,vector<int> inorder,int node1, int node2,int pre_left,int pre_right,int in_left,int in_right)
改成,将preorder,inorder设置成全局变量。
1 void search_ancestor(int node1,int node2,int pre_left,int in_left,int in_right)
修改后的代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;unordered_map<int ,int > Inordered_Map; vector<int > preorder,inorder; void search_ancestor (int node1,int node2,int pre_left,int in_left,int in_right) int in_position = Inordered_Map[preorder[pre_left]]; int n1_position = Inordered_Map[node1]; int n2_position = Inordered_Map[node2]; int mid_position = pre_left+in_position-in_left; if ((n1_position-in_position)*(n2_position-in_position)<0 ){ printf ("LCA of %d and %d is %d.\n" ,node1,node2,inorder[in_position]); return ; }else if ((n1_position-in_position)*(n2_position-in_position)==0 ){ if (n1_position==in_position){ printf ("%d is an ancestor of %d.\n" ,inorder[in_position],node2); }else if (n2_position==in_position){ printf ("%d is an ancestor of %d.\n" ,inorder[in_position],node1); } return ; }else if (n1_position<in_position && n2_position<in_position){ search_ancestor (node1,node2,pre_left+1 ,in_left,in_position-1 ); }else if (n1_position>in_position && n2_position>in_position){ search_ancestor (node1,node2,mid_position+1 ,in_position+1 ,in_right); } } int main () int M,N; cin>>M>>N; preorder.resize (N); inorder.resize (N); for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++) cin>>inorder[i]; for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++) cin>>preorder[i]; for (int i=0 ;i<inorder.size ();i++){ Inordered_Map[inorder[i]] = i; } for (int i=0 ;i<M;i++){ int node1,node2; cin>>node1>>node2; if (Inordered_Map.find (node1)==Inordered_Map.end () && Inordered_Map.find (node2)==Inordered_Map.end ()){ printf ("ERROR: %d and %d are not found.\n" ,node1,node2); }else if (Inordered_Map.find (node1)==Inordered_Map.end ()){ printf ("ERROR: %d is not found.\n" ,node1); }else if (Inordered_Map.find (node2)==Inordered_Map.end ()){ printf ("ERROR: %d is not found.\n" ,node2); }else { int n = preorder.size ()-1 ; search_ancestor (node1,node2,0 ,0 ,n); } } }
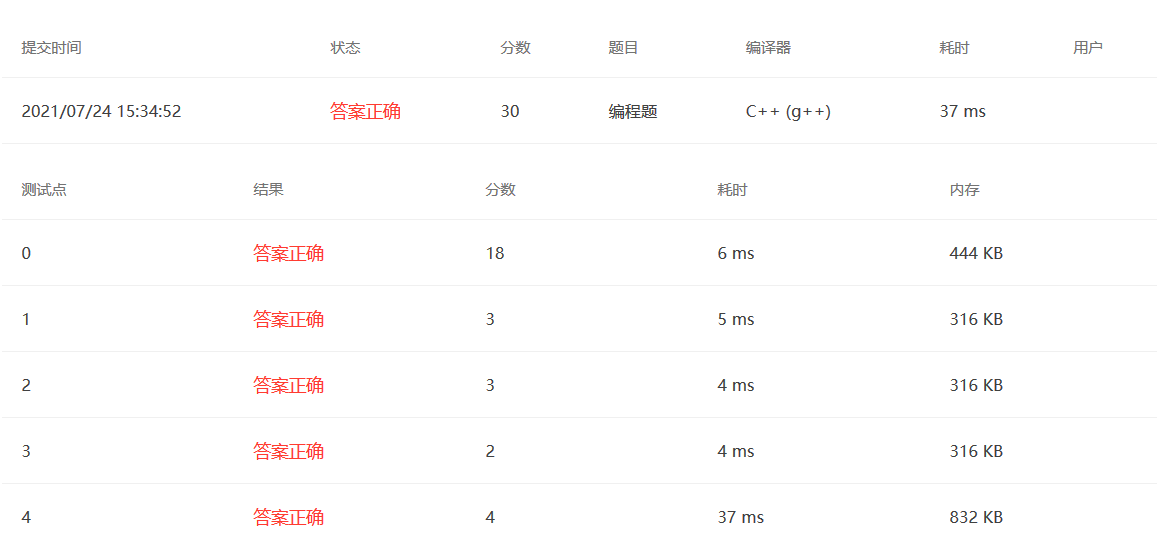
2021.7.24 PAT 1144
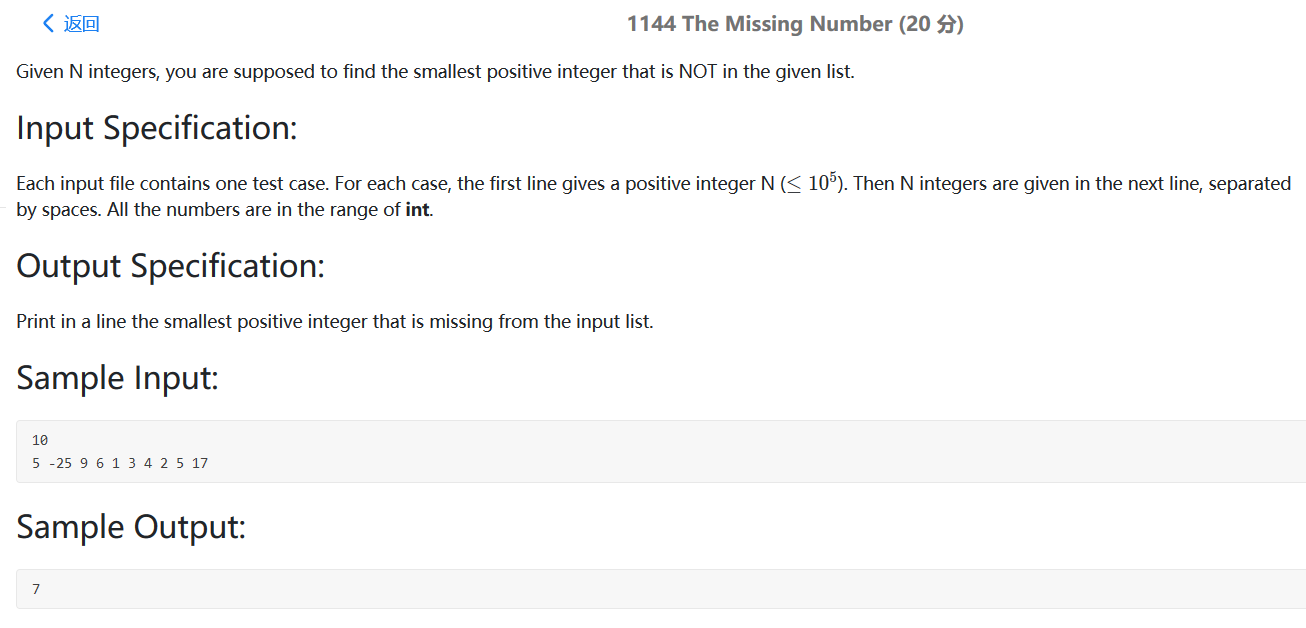
题目大意:给一个数串,找到数串中没有出现的最小正整数
思路:用一个长度为N的哈希表就可以了,因为最小整数不可能超过N,符合条件就放入,不符合条件就跳过,最后从1开始遍历。
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main () int N; cin>>N; vector<int > L (N) ; vector<int > M (N+2 ,0 ) ; for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++){ cin>>L[i]; if (L[i]>=1 && L[i]<=N) M[L[i]]++; } for (int i=1 ;i<N+2 ;i++){ if (M[i]==0 ){ cout<<i; return 0 ; } } }
PAT 1145
题目大意:
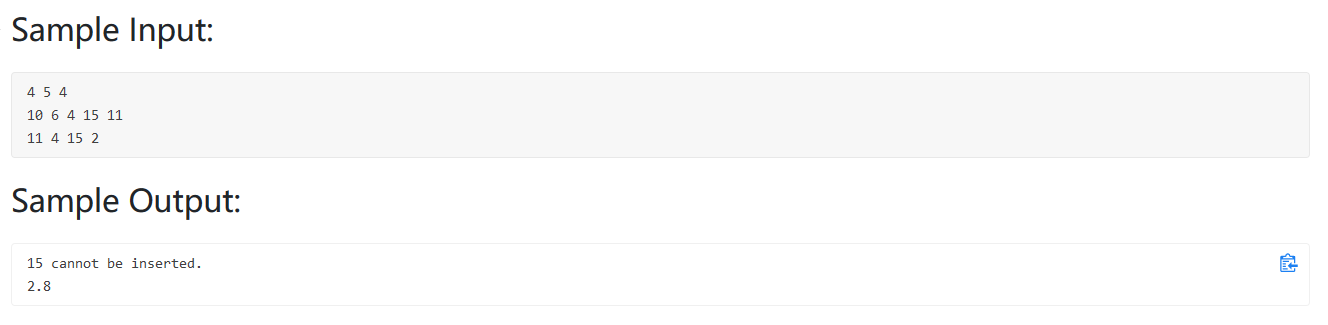
(quadratic:平方的)
给定一个序列,用平方探测法(只用正数)解决哈希冲突,然后给出m个数字(皆为正数),如果这个数字不能够被插入就输出”X cannot be inserted.”,然后输出这m个数字的平均查找次数
思路:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;bool isprime (int x) if (x==2 ) return true ; for (int i=2 ;i<=sqrt (x);i++){ if (x%i==0 ) return false ; } return true ; } int Msize,N,M;int main () cin>>Msize>>N>>M; while (!isprime (Msize)) Msize++; vector<int > Hash (Msize,0 ) ; for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++) { int a; cin>>a; int j; for (j=0 ;j<Msize;j++){ if (Hash[(a+j*j)%Msize]==0 ){ Hash[(a+j*j)%Msize] = a; break ; } } if (j==Msize) printf ("%d cannot be inserted.\n" ,a); } double sum = 0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<M;i++){ int b; cin>>b; int time = 1 ; for (int j=0 ;j<Msize;j++){ int t = (b+j*j)%Msize; if (Hash[t]==b || Hash[t]==0 ){ break ; } time++; } sum += time; } printf ("%.1f" ,sum/M); }
PAT 1146
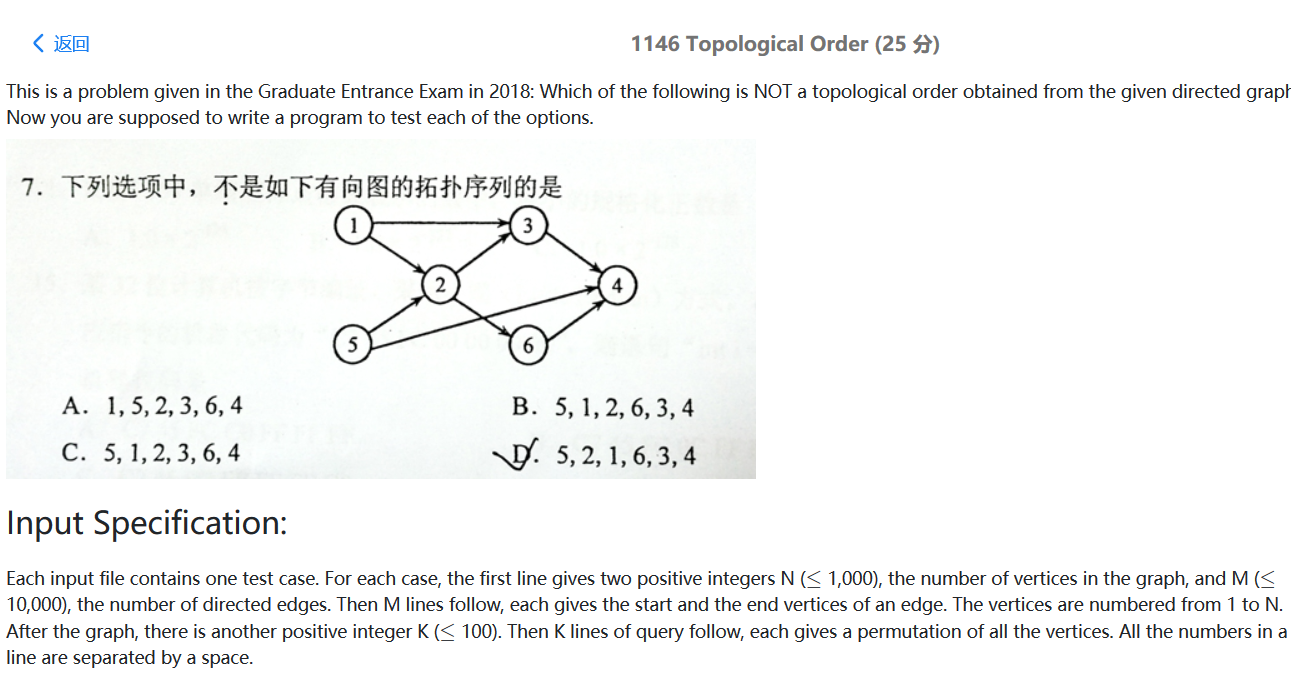
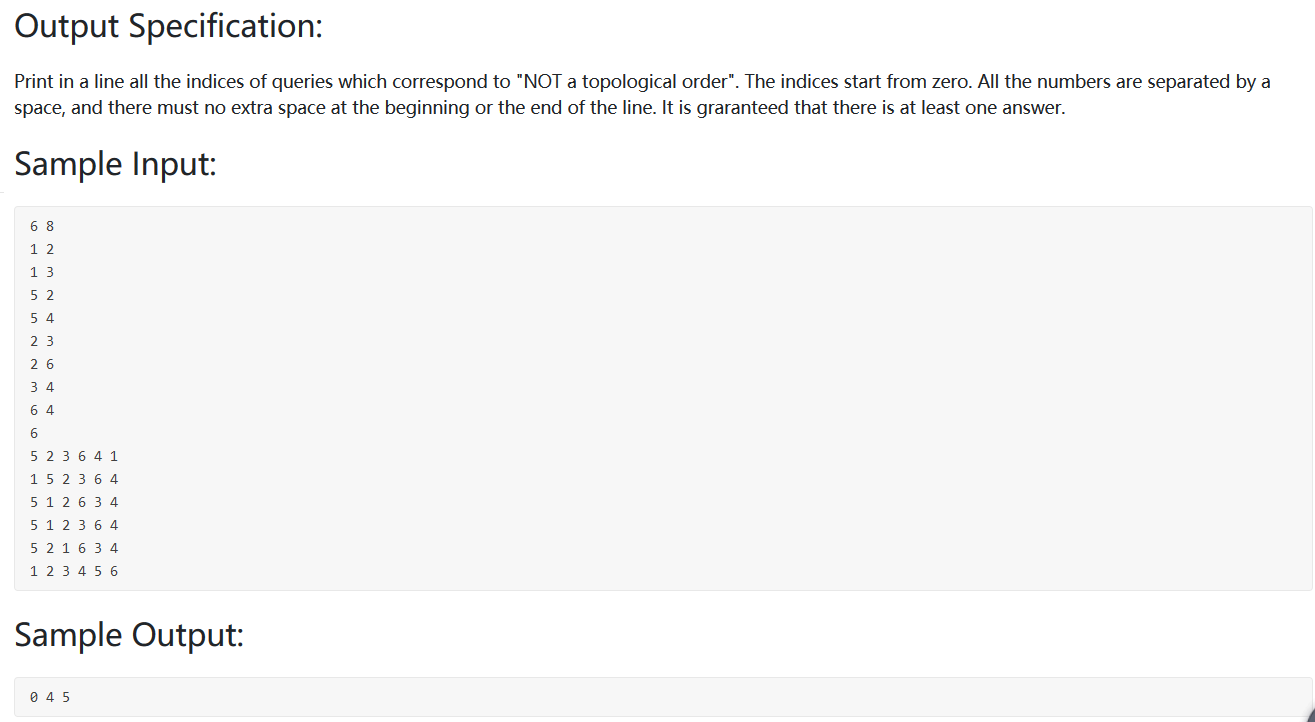
题目大意:判断一个序列是不是拓扑序列。
思路:构建邻接矩阵,计算入度,根据给出序列判断入度是否为0,然后将以该顶点为起点的边的终点的入度—1,依次判断下一个。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main () int N,M; cin>>N>>M; vector<vector<int >> Graph (N+1 ,vector <int >(N+1 ,0 )); for (int i=0 ;i<M;i++){ int a,b; cin>>a>>b; Graph[a][b] = 1 ; } vector<int > indegree (N+1 ) ; for (int i=1 ;i<=N;i++){ int in = 0 ; for (int j=1 ;j<=N;j++){ if (Graph[j][i]==1 ) in++; } indegree[i] = in; } int T; cin>>T; vector<int > res; for (int i=0 ;i<T;i++){ vector<int > seq (N) ; for (int j=1 ;j<=N;j++){ cin>>seq[j-1 ]; } vector<int > indegree1 (indegree) ; for (int j=0 ;j<N;j++){ if (indegree1[seq[j]]==0 ){ for (int k=1 ;k<=N;k++){ if (Graph[seq[j]][k]==1 ){ indegree1[k]--; } } }else { res.push_back (i); break ; } } } for (int i=0 ;i<res.size ();i++){ if (i==res.size ()-1 ) cout<<res[i]; else cout<<res[i]<<" " ; } }
PAT 1147
题目大意:给定一个完全二叉树,要求判断是否是大顶堆或小顶堆,并给出该二叉树的后序遍历。
判断大顶堆或小顶堆只需要遍历整个序列,判断seq[i] 和 seq[2i] 和 seq[2 i+1]的关系即可。
后序遍历采用栈进行模拟,
如果有左节点且左节点没被访问过,左节点入栈,
如果左节点被访问过且右节点没被访问过,右节点入栈
如果是叶子节点,且左右节点都被访问过,则出栈,visited设1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;#define MAX 1 #define MIN 0 #define NOTHEAP -1 void postorder (vector<int > seq) int size = seq.size ()-1 ; vector<int > visited (size+1 ,0 ) ; vector<int > res; stack<int > S; S.push (1 ); while (!S.empty ()){ int node = S.top (); if (node*2 <=size && !visited[node*2 ]) S.push (node*2 ); else if (node*2 +1 <=size && !visited[node*2 +1 ]) S.push (node*2 +1 ); else if (node*2 >size || (node*2 +1 <=size && visited[node*2 +1 ]) || (node*2 +1 >size && node*2 <=size && visited[node*2 ])){ S.pop (); visited[node] = 1 ; res.push_back (seq[node]); } } for (int i=0 ;i<res.size ();i++){ if (i==res.size ()-1 ) cout<<res[i]; else cout<<res[i]<<" " ; } cout<<endl; } int main () int M,N; cin>>N>>M; while (N--) { vector<int > seq (M+1 ) ; int max_or_min; for (int i=1 ;i<=M;i++){ cin>>seq[i]; } if (seq[1 ]>seq[M]) max_or_min = MAX; else max_or_min = MIN; for (int i=1 ;i<=M;i++){ if (max_or_min==MAX){ if (2 *i<=M && seq[2 *i]>seq[i]) {max_or_min = NOTHEAP;break ;} if (2 *i+1 <=M && seq[2 *i+1 ]>seq[i]){ max_or_min = NOTHEAP;break ;} }else if (max_or_min==MIN){ if (2 *i<=M && seq[2 *i]<seq[i]) {max_or_min = NOTHEAP;break ;} if (2 *i+1 <=M && seq[2 *i+1 ]<seq[i]){ max_or_min = NOTHEAP;break ;} } } if (max_or_min==MAX) cout<<"Max Heap" <<endl; else if (max_or_min==MIN) cout<<"Min Heap" <<endl; else if (max_or_min==NOTHEAP) cout<<"Not Heap" <<endl; postorder (seq); } }
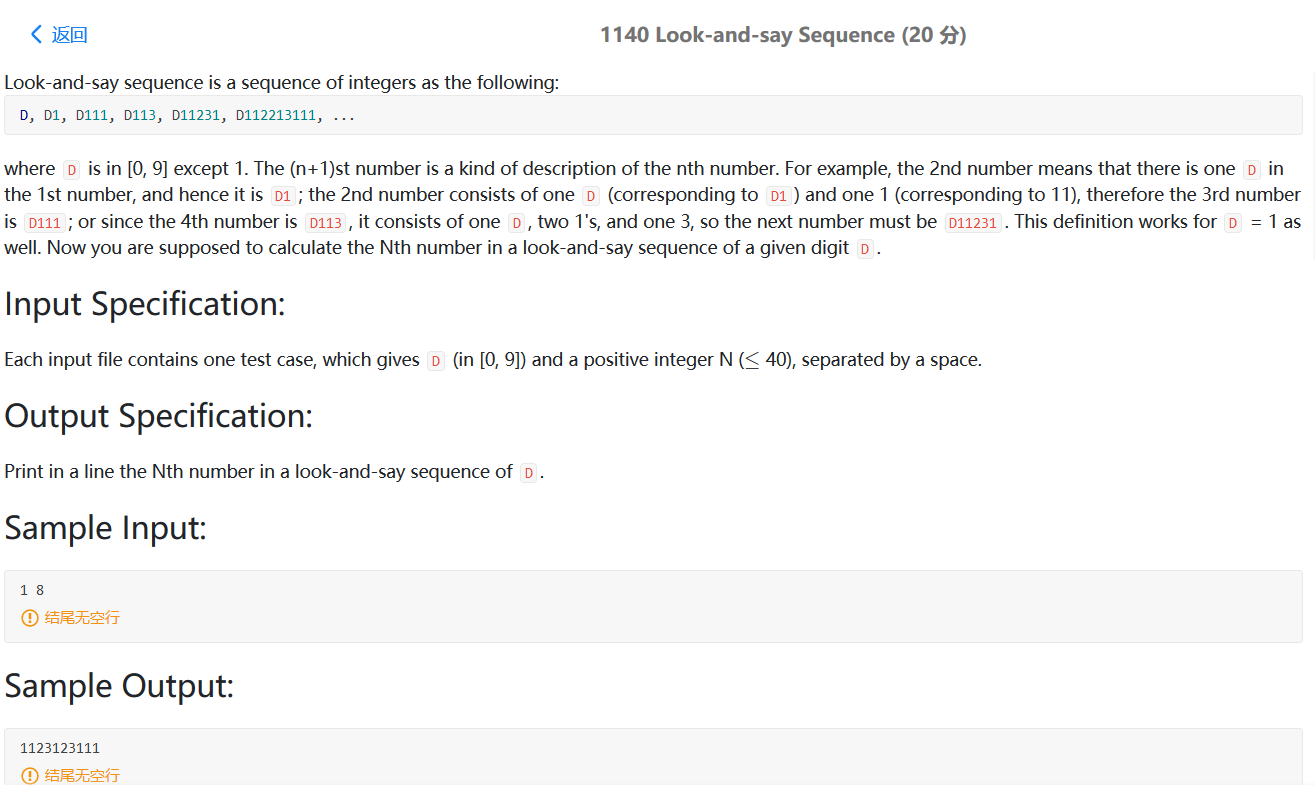
2021.7.31 PAT 1140
题目大意:
题意:后面一个数是前面一个数的描述,一般第一个数是d,代表0-9的任意一个数,第二 数是第一个数的描述,就是将d+d的个数。同样,第三个数是第二个数的描述,依次,例如:1 11(前一个1是第一个数,后一个1是第一个中1的个数) 12(代表前一个数中有2个1) 1121(前面一个数中有1个1,1个2,数放前,个数放后) 122111 112213 12221131 1123123111 。
思路:采用模拟的方法,c表示当前字符,如果遍历到的字符不是c,则输出到temp中,如果是c,则c的个数size++.
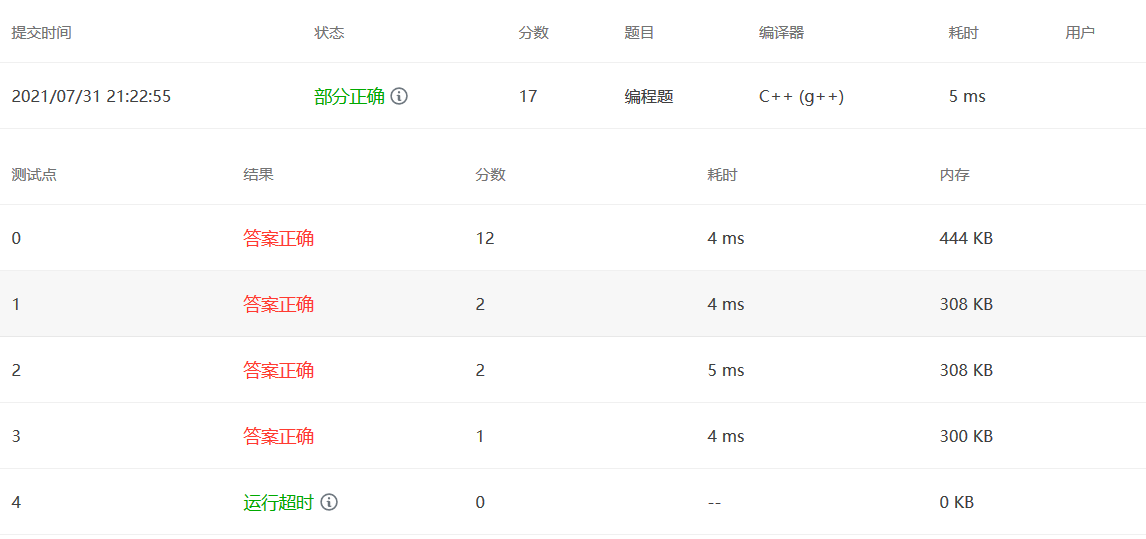
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main () int D,index; cin>>D>>index; string s = to_string (D); for (int i=2 ;i<=index;i++){ string temp = "" ; int size = 1 ; char c = s[0 ]; for (int j=1 ;j<s.length ();j++){ if (s[j]==c){ size++; }else { temp = temp + c + to_string (size); c = s[j]; size = 1 ; } } temp = temp + c + to_string (size); s = temp; } cout<<s; }
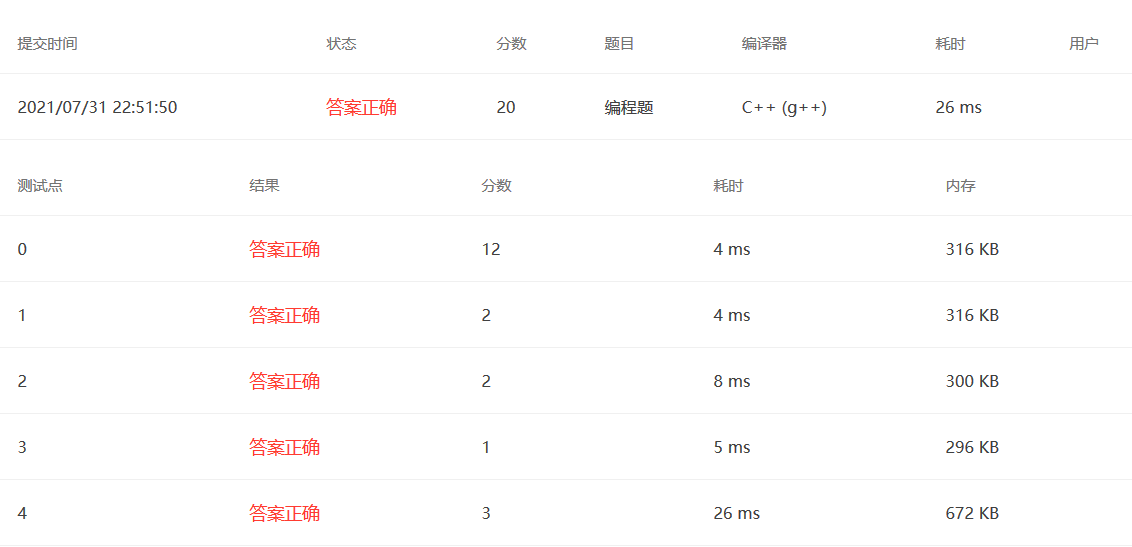
原因在于
使用=是深拷贝,需将temp重新拷贝一份再赋值给temp
使用+= 是直接在后面append。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main () int D,index; cin>>D>>index; string s = to_string (D); for (int i=2 ;i<=index;i++){ string temp = "" ; int size = 1 ; char c = s[0 ]; for (int j=1 ;j<s.length ();j++){ if (s[j]==c){ size++; }else { temp += c + to_string (size); c = s[j]; size = 1 ; } } temp += c + to_string (size); s = temp; } cout<<s; }
PAT 1141
问题描述:给定每个考生的成绩和学校,统计该学校的总成绩并排序。
思路:用一个Map用于查找学校信息,便于统计学校总成绩,然后扔到vector进行排序。
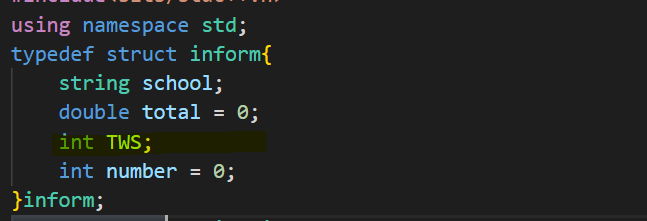
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef struct inform { string school; double total = 0 ; int number = 0 ; }inform; unordered_map<string,inform> Map; vector<inform> StuList; bool cmp (inform a,inform b) if (a.total==b.total && a.number==b.number){ return a.school<b.school; }else if (a.total==b.total){ return a.number<b.number; }else { return a.total>b.total; } } int main () int N; cin>>N; while (N--){ string id; int score; string school; cin>>id>>score>>school; transform (school.begin (),school.end (),school.begin (),::tolower); Map[school].school = school; if (id[0 ]=='B' ){ Map[school].total += double (score)/1.5 ; }else if (id[0 ]=='A' ){ Map[school].total += score; }else if (id[0 ]=='T' ){ Map[school].total += double (score)*1.5 ; } Map[school].number++; } unordered_map<string,inform>::iterator iter; for (iter=Map.begin ();iter!=Map.end ();iter++){ StuList.push_back (iter->second); } sort (StuList.begin (),StuList.end (),cmp); int len = StuList.size (); int rank = 1 ; cout<<StuList.size ()<<endl; for (int i=1 ;i<=len;i++){ if (i-2 >=0 && (int )StuList[i-1 ].total==(int )StuList[i-2 ].total){} else rank = i; printf ("%d %s %d %d" ,rank,StuList[i-1 ].school.c_str (),(int )(StuList[i-1 ].total),StuList[i-1 ].number); if (i!=len) cout<<endl; } return 0 ; }
sort的使用,测试点五是一个坑,因为每个学校的分数相当于一个加权的成绩,在前期处理的时候就应该按照浮点数处理,只有在排序的时候将其转换为整数即可。
正确代码:
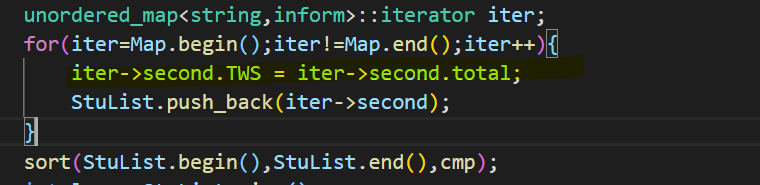
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef struct inform { string school; double total = 0 ; int TWS; int number = 0 ; }inform; unordered_map<string,inform> Map; vector<inform> StuList; bool cmp (inform a,inform b) if (a.TWS==b.TWS && a.number==b.number){ return a.school<b.school; }else if (a.TWS==b.TWS){ return a.number<b.number; }else { return a.TWS>b.TWS; } } int main () int N; cin>>N; while (N--){ string id; int score; string school; cin>>id>>score>>school; transform (school.begin (),school.end (),school.begin (),::tolower); Map[school].school = school; if (id[0 ]=='B' ){ Map[school].total += double (score)/1.5 ; }else if (id[0 ]=='A' ){ Map[school].total += score; }else if (id[0 ]=='T' ){ Map[school].total += double (score)*1.5 ; } Map[school].number++; } unordered_map<string,inform>::iterator iter; for (iter=Map.begin ();iter!=Map.end ();iter++){ iter->second.TWS = iter->second.total; StuList.push_back (iter->second); } sort (StuList.begin (),StuList.end (),cmp); int len = StuList.size (); int rank = 1 ; cout<<StuList.size ()<<endl; for (int i=1 ;i<=len;i++){ if (i-2 >=0 && (int )StuList[i-1 ].total==(int )StuList[i-2 ].total){} else rank = i; printf ("%d %s %d %d" ,rank,StuList[i-1 ].school.c_str (),(int )(StuList[i-1 ].TWS),StuList[i-1 ].number); if (i!=len) cout<<endl; } return 0 ; }
PAT 1142
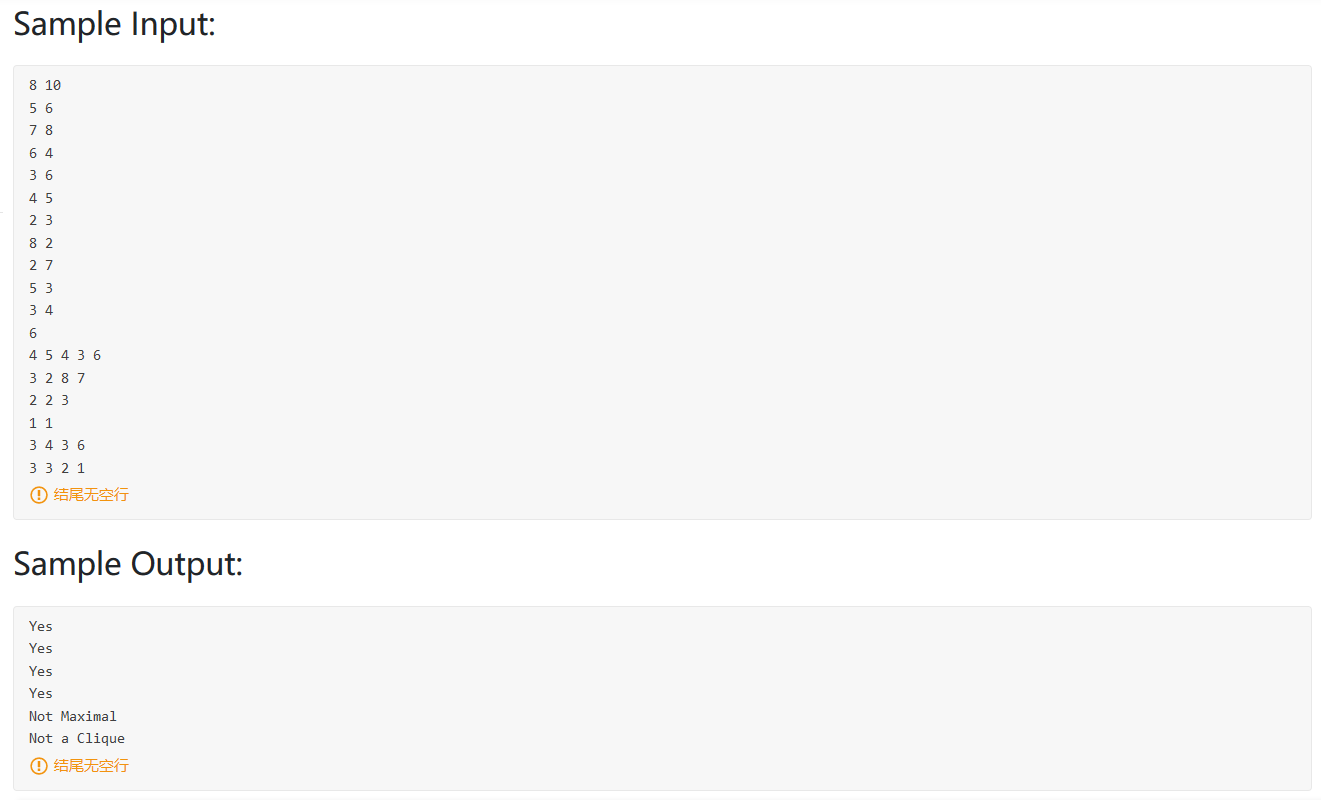
题目大意:问题描述:给定一个无向图,和一些顶点,判断这些顶点是否组成了集合(每两个顶点都相连)
Yes 是一个团,每两个顶点都相邻
Not Maximal 是一个团,但是可以再加入一个顶点,使得每两个顶点相连
Not a Clique 不是每两个顶点都相连。
思路:构造邻接矩阵,对给定序列依次判断是否是一个团,然后再尝试加入其他顶点,判断是否是最大团。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef struct inform { string school; double total = 0 ; int TWS; int number = 0 ; }inform; unordered_map<string,inform> Map; vector<inform> StuList; bool cmp (inform a,inform b) if (a.TWS==b.TWS && a.number==b.number){ return a.school<b.school; }else if (a.TWS==b.TWS){ return a.number<b.number; }else { return a.TWS>b.TWS; } } int main () int N; cin>>N; while (N--){ string id; int score; string school; cin>>id>>score>>school; transform (school.begin (),school.end (),school.begin (),::tolower); Map[school].school = school; if (id[0 ]=='B' ){ Map[school].total += double (score)/1.5 ; }else if (id[0 ]=='A' ){ Map[school].total += score; }else if (id[0 ]=='T' ){ Map[school].total += double (score)*1.5 ; } Map[school].number++; } unordered_map<string,inform>::iterator iter; for (iter=Map.begin ();iter!=Map.end ();iter++){ iter->second.TWS = iter->second.total; StuList.push_back (iter->second); } sort (StuList.begin (),StuList.end (),cmp); int len = StuList.size (); int rank = 1 ; cout<<StuList.size ()<<endl; for (int i=1 ;i<=len;i++){ if (i-2 >=0 && (int )StuList[i-1 ].total==(int )StuList[i-2 ].total){} else rank = i; printf ("%d %s %d %d" ,rank,StuList[i-1 ].school.c_str (),(int )(StuList[i-1 ].TWS),StuList[i-1 ].number); if (i!=len) cout<<endl; } return 0 ; }
PAT 1143
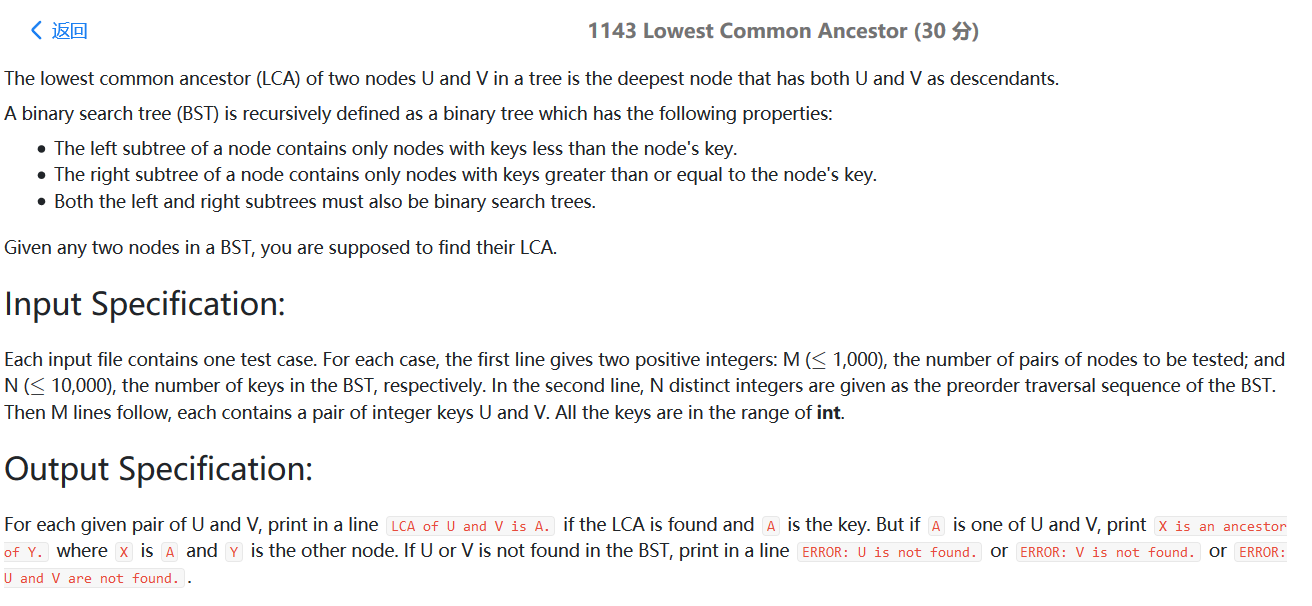
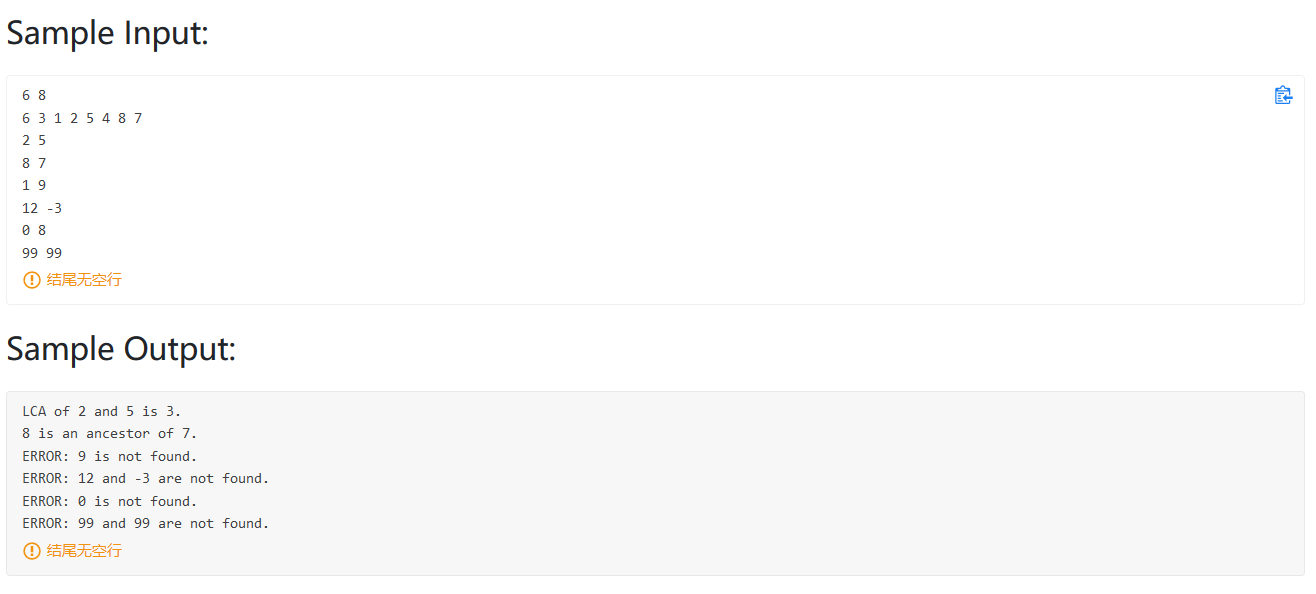
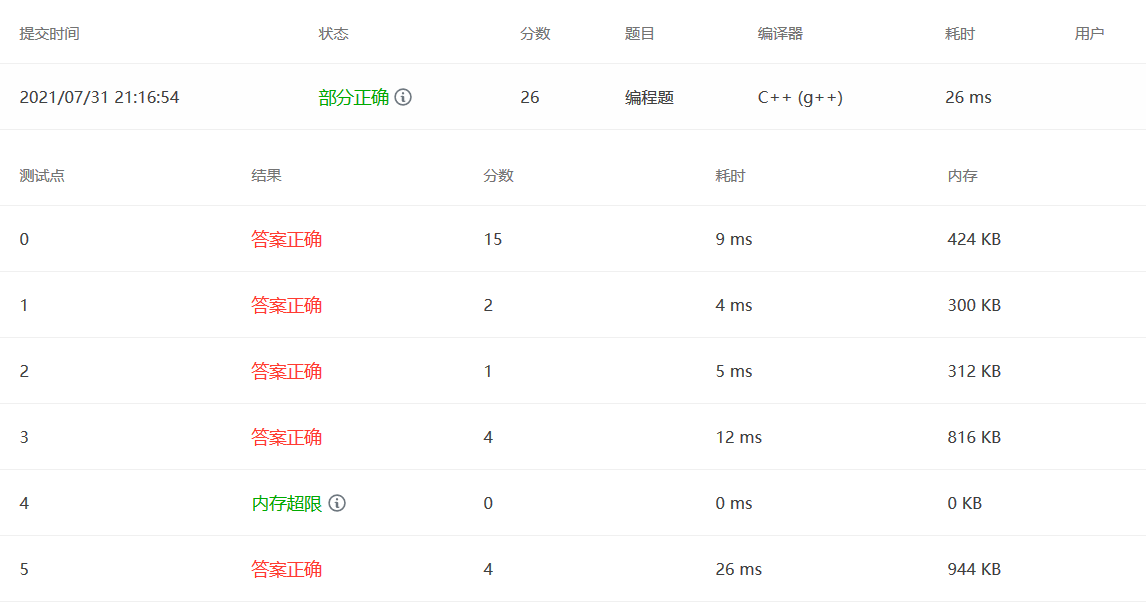
题目大意:用先序遍历的方式给出一棵排序二叉树。让你回答n个询问。
用TreeMap存树的每个结点,第一步判断是否存在 否则not found
第二部查找最近的公共祖孙,这里利用二叉排序树的特点,如果n1 和 n2 一个大于根节点 一个小于根节点,则根节点必定是公共祖先,否则递归进行查找。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int searchLCA (vector<int > Tree,int left,int right,int n1,int n2) int t = Tree[left]; if ((n1<t && n2>t) || (n1>t && n2<t) || (n1==t||n2==t)) return t; else { int i = left+1 ; while (Tree[i]<t) i++; if (n1<t && n2<t) return searchLCA (Tree,left+1 ,i-1 ,n1,n2); else return searchLCA (Tree,i,right,n1,n2); } } int main () int M,N; cin>>M>>N; vector<int > Tree (N) ; unordered_map<int ,int > TreeMap; for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++) { cin>>Tree[i]; TreeMap[Tree[i]]++; } for (int i=0 ;i<M;i++){ int n1,n2; cin>>n1>>n2; if (TreeMap.find (n1)==TreeMap.end () && TreeMap.find (n2)==TreeMap.end ()){ printf ("ERROR: %d and %d are not found." ,n1,n2); }else if (TreeMap.find (n1)==TreeMap.end ()){ printf ("ERROR: %d is not found." ,n1); }else if (TreeMap.find (n2)==TreeMap.end ()){ printf ("ERROR: %d is not found." ,n2); }else { int lca = searchLCA (Tree,0 ,N-1 ,n1,n2); if (lca==n1){ printf ("%d is an ancestor of %d." ,n1,n2); }else if (lca==n2){ printf ("%d is an ancestor of %d." ,n2,n1); }else { printf ("LCA of %d and %d is %d." ,n1,n2,lca); } } if (i!=M-1 ) cout<<endl; } return 0 ; }
佬们的代码:他是直接利用先序遍历的特点,按顺序判断是否是祖先
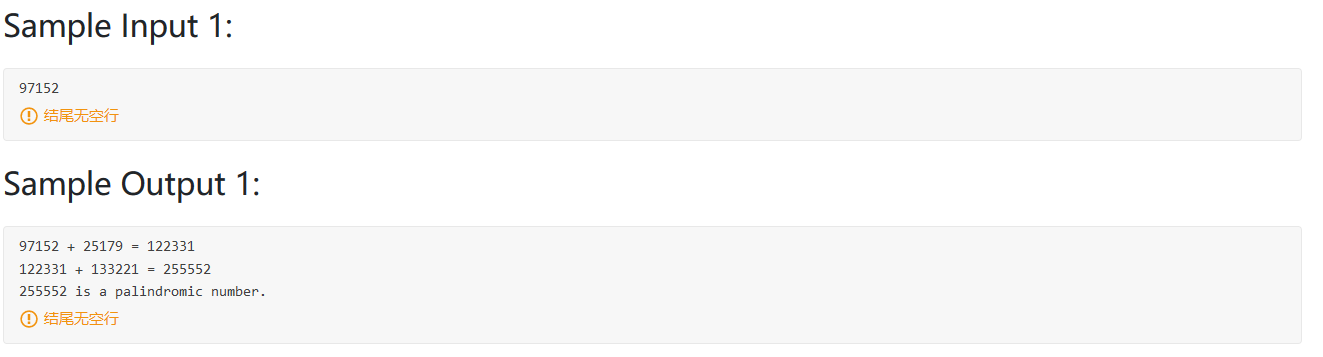
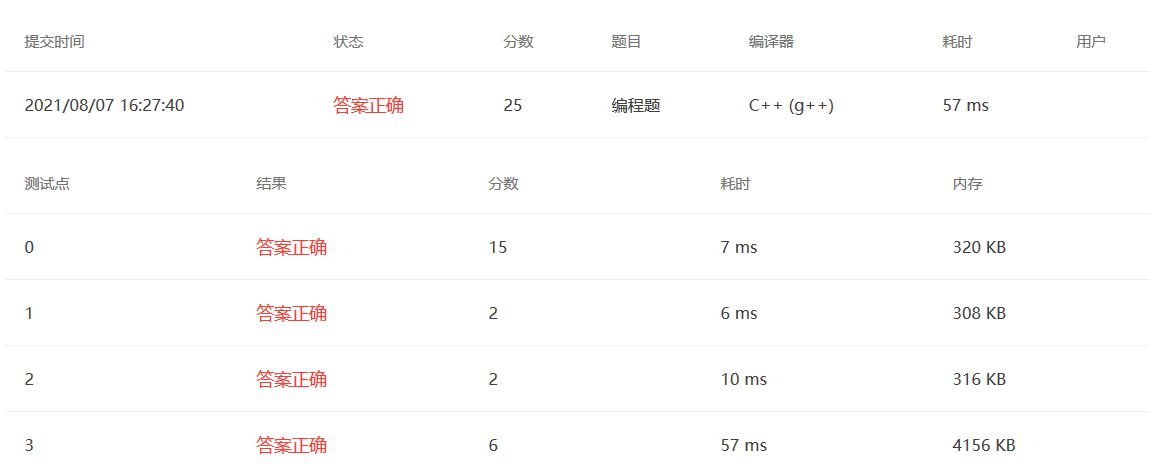
2021.8.7 PAT 1136
题目大意:一个数加它的翻转能否在10次内得到一个回文数
思路:模拟大数加法,并且模拟反转过程。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;string add (string a,string b) string res; int len = a.length (); int jinwei = 0 ; int benwei = 0 ; for (int i=len-1 ;i>=0 ;i--){ int c = a[i]-'0' + b[i]-'0' + jinwei; benwei = c%10 ; res = to_string (benwei) + res; jinwei = c/10 ; } if (jinwei!=0 ) res = to_string (jinwei) + res; return res; } bool ispalindromic (string a) int i=0 ,j=a.length ()-1 ; while (i<=j){ if (a[i] != a[j]) return false ; i++; j--; } return true ; } int main () string a = "" ; cin>>a; int i = 1 ; while (!ispalindromic (a) && i<=10 ){ printf ("%s + " ,a.c_str ()); string c = a; reverse (a.begin (),a.end ()); printf ("%s = " ,a.c_str ()); a = add (a,c); printf ("%s\n" ,a.c_str ()); i++; } if (i>10 ) printf ("Not found in 10 iterations." ); else printf ("%s is a palindromic number." ,a.c_str ()); }
PAT 1137
题目大意:
判断一个学生是否有资格获得整数的条件有2个:1.学生是否能编程>=200题 2.学生的总评成绩是否>=60
由于题目是分开给出各项成绩,而且Id唯一,所以我们可以使用Map方便查找。最后进行判断,判断完后排序。
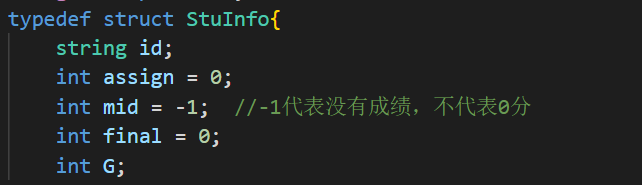
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef struct StuInfo { string id; int assign = 0 ; int mid = 0 ; int final = 0 ; int G; }StuInfo; bool cmp (StuInfo a,StuInfo b) if (a.G==b.G) return a.id<b.id; else return a.G>b.G; } unordered_map<string,StuInfo> Map; int main () int P,M,N; cin>>P>>M>>N; for (int i = 0 ; i < P; i++){ StuInfo stu; cin>>stu.id>>stu.assign; Map[stu.id] = stu; } for (int i = 0 ;i < M; i++){ StuInfo stu; cin>>stu.id>>stu.mid; if (Map.find (stu.id)!=Map.end ()){ Map[stu.id].mid = stu.mid; }else { Map[stu.id] = stu; } } for (int i = 0 ;i < N; i++){ StuInfo stu; cin>>stu.id>>stu.final ; if (Map.find (stu.id)!=Map.end ()){ Map[stu.id].final = stu.final ; }else { Map[stu.id] = stu; } } vector<StuInfo> StuList; unordered_map<string,StuInfo>::iterator iter; for (iter=Map.begin ();iter!=Map.end ();iter++){ StuInfo stu = iter->second; if (stu.assign<200 ) continue ; if (stu.mid>stu.final ) stu.G = (int )((float )stu.mid*0.4 + (float )stu.final *0.6 + 0.5 ); else stu.G = stu.final ; if (stu.G<60 ) continue ; StuList.push_back (stu); } sort (StuList.begin (),StuList.end (),cmp); for (int i=0 ;i<StuList.size ();i++){ string name = StuList[i].id; int assign = StuList[i].assign; int mid = StuList[i].mid>0 ? StuList[i].mid : -1 ; int fin = StuList[i].final >0 ? StuList[i].final : -1 ; int G = StuList[i].G; printf ("%s %d %d %d %d\n" ,name.c_str (),assign,mid,fin,G); } return 0 ; }
大坑 :
题目中的-1的意思表示的是没有学生的某一项没有分数(而非分数为0!没有分数代表没来考试,而分数为0代表考试考了0分!)
所以mid的初值应该设为-1 而不应该设为0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef struct StuInfo { string id; int assign = 0 ; int mid = -1 ; int final = 0 ; int G; }StuInfo; bool cmp (StuInfo a,StuInfo b) if (a.G==b.G) return a.id<b.id; else return a.G>b.G; } unordered_map<string,StuInfo> Map; int main () int P,M,N; cin>>P>>M>>N; for (int i = 0 ; i < P; i++){ StuInfo stu; cin>>stu.id>>stu.assign; Map[stu.id] = stu; } for (int i = 0 ;i < M; i++){ StuInfo stu; cin>>stu.id>>stu.mid; if (Map.find (stu.id)!=Map.end ()){ Map[stu.id].mid = stu.mid; }else { Map[stu.id] = stu; } } for (int i = 0 ;i < N; i++){ StuInfo stu; cin>>stu.id>>stu.final ; if (Map.find (stu.id)!=Map.end ()){ Map[stu.id].final = stu.final ; }else { Map[stu.id] = stu; } } vector<StuInfo> StuList; unordered_map<string,StuInfo>::iterator iter; for (iter=Map.begin ();iter!=Map.end ();iter++){ StuInfo stu = iter->second; if (stu.assign<200 ) continue ; if (stu.mid>stu.final ) stu.G = (int )((float )stu.mid*0.4 + (float )stu.final *0.6 + 0.5 ); else stu.G = stu.final ; if (stu.G<60 ) continue ; StuList.push_back (stu); } sort (StuList.begin (),StuList.end (),cmp); for (int i=0 ;i<StuList.size ();i++){ string name = StuList[i].id; int assign = StuList[i].assign; int mid = StuList[i].mid>=0 ? StuList[i].mid : -1 ; int fin = StuList[i].final >0 ? StuList[i].final : -1 ; int G = StuList[i].G; printf ("%s %d %d %d %d\n" ,name.c_str (),assign,mid,fin,G); } return 0 ; }
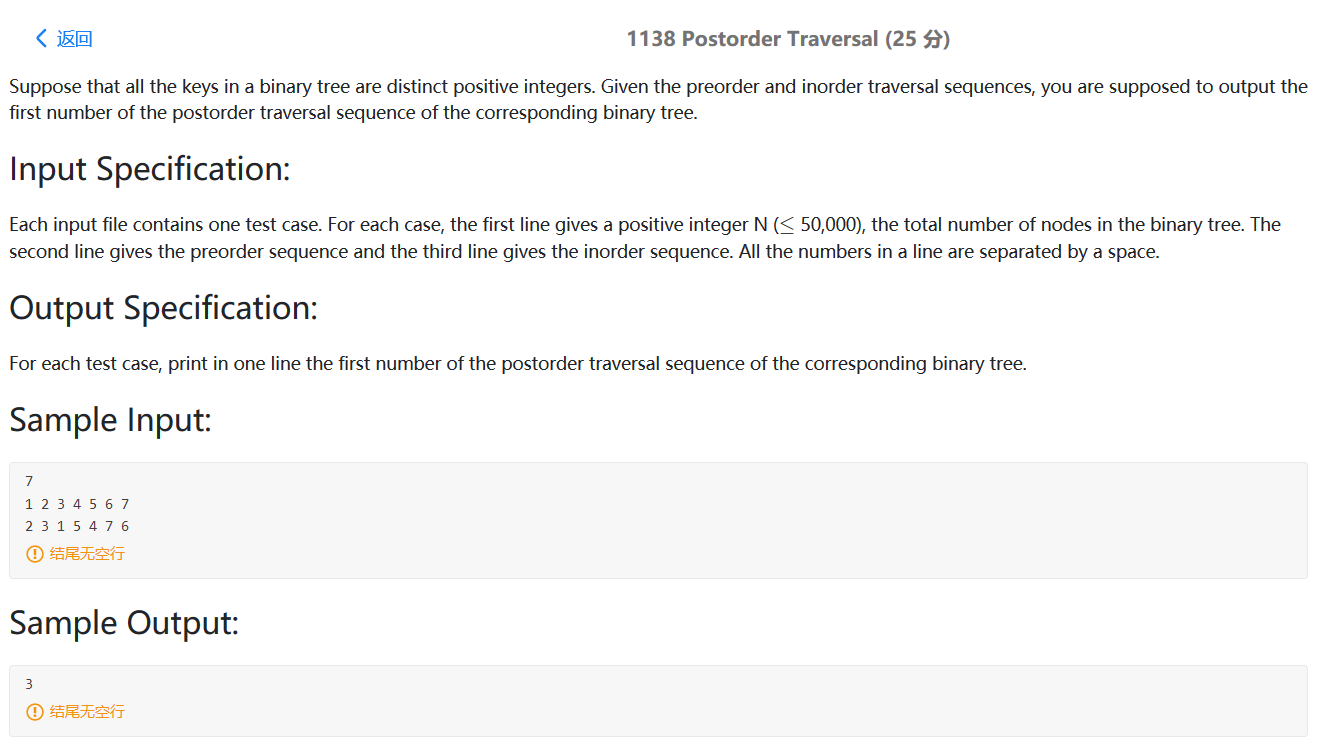
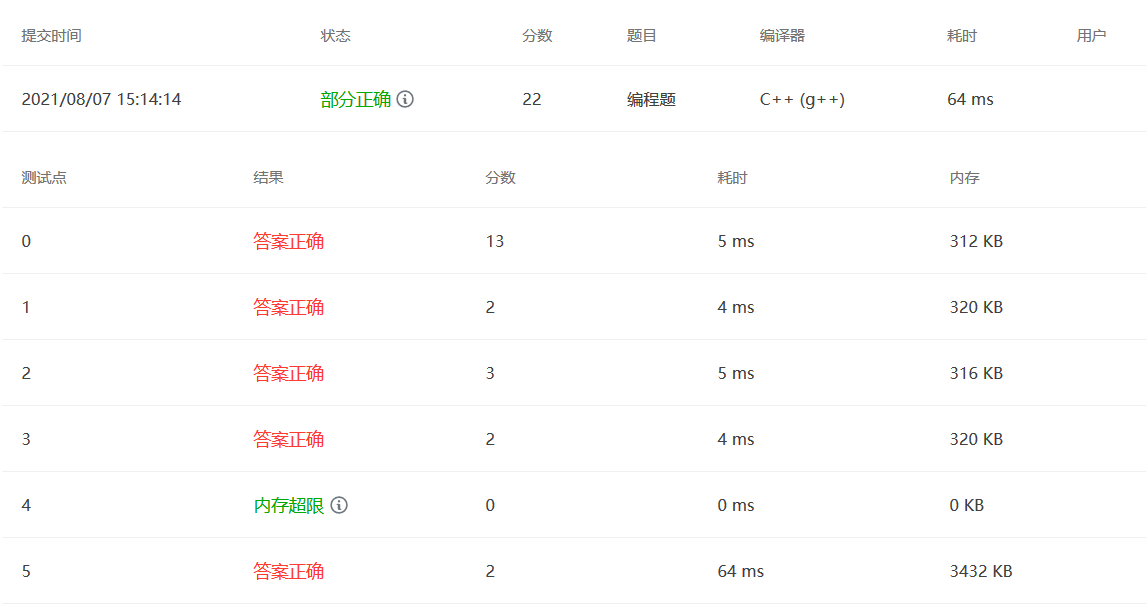
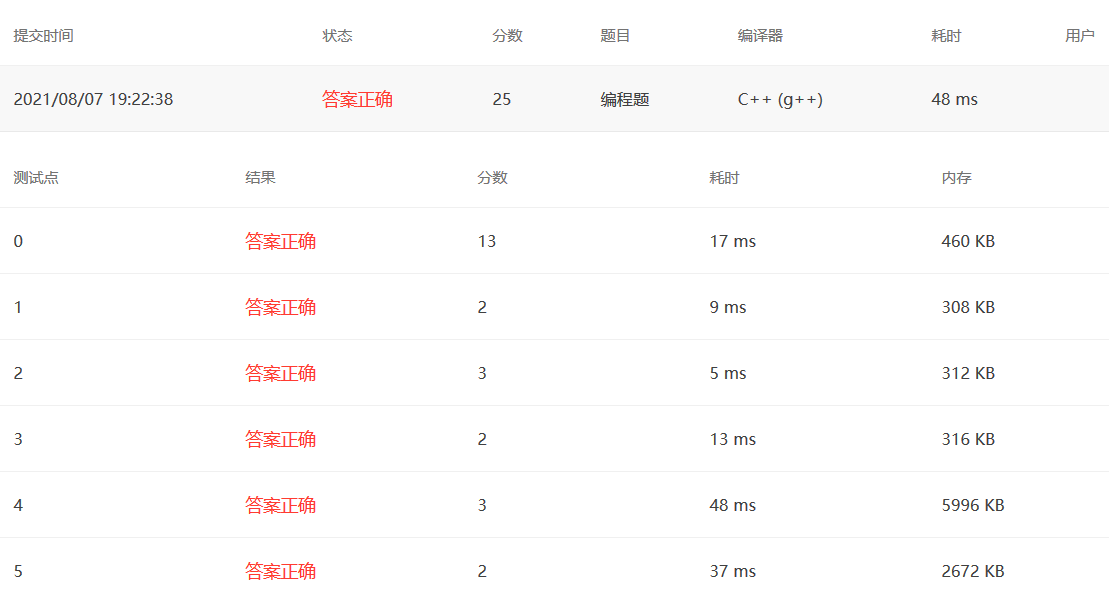
PAT 1138
题目大意:给出数的前序、中序,求后序输出的第一个值
思路:按照前序、中序序列构造树的方法,采用递归,中间需要用到Map来查找中序序列的位置。
如果有左子树,后序遍历的第一个序列在左子树中寻找,否则在右子树中寻找。只有一个节点,则Return;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;unordered_map<int ,int > Map; int TreeBuild (vector<int > preorder,vector<int > inorder, int pl,int pr,int il,int ir) if (pl==pr) return preorder[pl]; int cur = preorder[pl]; int mid_cur = Map[cur]; if (mid_cur==il){ return TreeBuild (preorder,inorder,pl+1 ,pr,il+1 ,ir); }else { return TreeBuild (preorder,inorder,pl+1 ,pl+mid_cur-il,il,mid_cur-1 ); } } int main () int N; cin>>N; vector<int > preorder (N,0 ) ; vector<int > inorder (N,0 ) ; for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++) cin>>preorder[i]; for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++) { cin>>inorder[i]; Map[inorder[i]]=i; } cout<<TreeBuild (preorder,inorder,0 ,N-1 ,0 ,N-1 ); return 0 ; }
改进方法:函数传值的时候尽量不要把整个vector都传进去,否则会出现爆内存的情况。需要把vector设置成全局变量
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;unordered_map<int ,int > Map; vector<int > preorder,inorder; int TreeBuild (int pl,int pr,int il,int ir) if (pl==pr) return preorder[pl]; int cur = preorder[pl]; int mid_cur = Map[cur]; if (mid_cur==il){ return TreeBuild (pl+1 ,pr,il+1 ,ir); }else { return TreeBuild (pl+1 ,pl+mid_cur-il,il,mid_cur-1 ); } } int main () int N; cin>>N; preorder.resize (N,0 ); inorder.resize (N,0 ); for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++) cin>>preorder[i]; for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++) { cin>>inorder[i]; Map[inorder[i]]=i; } cout<<TreeBuild (0 ,N-1 ,0 ,N-1 ); return 0 ; }
PAT 1139
题意 :如果一个男孩子A对一个女孩子B有好感,那么他需要跟他的好哥们C说,然后C再去找B的闺蜜,让闺蜜给B带话。
思路就是从A的同性朋友中找出C,再从B的同性朋友中找出D,然后C,D是好朋友的话,这个话就带到了。
但是输出那里规定A,B可以是同性,
If they are of the same gender, then both friends must be in the same gender as theirs.
emmmmmmm,这道题gay里gay气的。
思路 :Person结构体存储自己的Id,还有男朋友,女朋友(其实也可以一起存储),然后用一个Map<id,Person>方便使用Id找到相对应的朋友。
然后给定两个朋友A,朋友B,根据Map找到对应的A的男朋友或女朋友,and 找到B的男朋友或女朋友,最后写一个函数判断这两人之间是否存在关系,然后将存在关系的朋友排好序,输出。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef struct Person { int id; vector<int > boyfriend; vector<int > girlfriend; }Person; unordered_map<int ,Person> Map; bool cmp (pair<int ,int > a,pair<int ,int > b) if (a.first==b.first) return a.second<b.second; else return a.first<b.first; } bool isfriend (int id,int q) Person p = Map[id]; if (q>0 ){ for (int i=0 ;i<p.boyfriend.size ();i++){ if (q==p.boyfriend[i]) return true ; } return false ; }else { for (int i=0 ;i<p.girlfriend.size ();i++){ if (q==p.girlfriend[i]) return true ; } return false ; } } int main () int N,M; cin>>N>>M; for (int i=0 ;i<M;i++){ int id1,id2; cin>>id1>>id2; if (Map.find (id1)==Map.end ()){ Person p; p.id = id1; Map[id1] = p; } if (Map.find (id2)==Map.end ()){ Person p; p.id = id2; Map[id2] = p; } if (id2>0 ) Map[id1].boyfriend.push_back (id2); else Map[id1].girlfriend.push_back (id2); if (id1>0 ) Map[id2].boyfriend.push_back (id1); else Map[id2].girlfriend.push_back (id1); } int K; cin>>K; for (int k=0 ;k<K;k++){ int id1,id2; cin>>id1>>id2; vector<pair<int ,int >> res; if (id1>0 && id2>0 ){ vector<int > id1friend; vector<int > id2friend; Person p = Map[id1]; for (int i=0 ;i<p.boyfriend.size ();i++){ id1friend.push_back (p.boyfriend[i]); } Person q = Map[id2]; for (int i=0 ;i<q.boyfriend.size ();i++){ id2friend.push_back (q.boyfriend[i]); } for (int i=0 ;i<id1friend.size ();i++) for (int j=0 ;j<id2friend.size ();j++){ if (isfriend (id1friend[i],id2friend[j])){ res.push_back (make_pair (abs (id1friend[i]),abs (id2friend[j]))); } } }else if (id1<0 && id2<0 ){ vector<int > id1friend; vector<int > id2friend; Person p = Map[id1]; for (int i=0 ;i<p.girlfriend.size ();i++){ id1friend.push_back (p.girlfriend[i]); } Person q = Map[id2]; for (int i=0 ;i<q.girlfriend.size ();i++){ id2friend.push_back (q.girlfriend[i]); } for (int i=0 ;i<id1friend.size ();i++) for (int j=0 ;j<id2friend.size ();j++){ if (isfriend (id1friend[i],id2friend[j])){ res.push_back (make_pair (abs (id1friend[i]),abs (id2friend[j]))); } } }else if (id1>0 && id2<0 ){ vector<int > id1friend; vector<int > id2friend; Person p = Map[id1]; for (int i=0 ;i<p.boyfriend.size ();i++){ id1friend.push_back (p.boyfriend[i]); } Person q = Map[id2]; for (int i=0 ;i<q.girlfriend.size ();i++){ id2friend.push_back (q.girlfriend[i]); } for (int i=0 ;i<id1friend.size ();i++) for (int j=0 ;j<id2friend.size ();j++){ if (isfriend (id1friend[i],id2friend[j])){ res.push_back (make_pair (abs (id1friend[i]),abs (id2friend[j]))); } } }else if (id1<0 && id2>0 ){ vector<int > id1friend; vector<int > id2friend; Person p = Map[id1]; for (int i=0 ;i<p.girlfriend.size ();i++){ id1friend.push_back (p.girlfriend[i]); } Person q = Map[id2]; for (int i=0 ;i<q.boyfriend.size ();i++){ id2friend.push_back (q.boyfriend[i]); } for (int i=0 ;i<id1friend.size ();i++) for (int j=0 ;j<id2friend.size ();j++){ if (isfriend (id1friend[i],id2friend[j])){ res.push_back (make_pair (abs (id1friend[i]),abs (id2friend[j]))); } } } sort (res.begin (),res.end (),cmp); cout<<res.size ()<<endl; for (int i=0 ;i<res.size ();i++){ printf ("%d %d\n" ,res[i].first,res[i].second); } } }
参考了以下柳神的代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;unordered_map<int ,bool > arr; struct node { int a,b; }; bool cmp (node x,node y) return x.a != y.a ? x.a < y.a : x.b < y.b; } int main () int n,m,k; scanf ("%d%d" ,&n,&m); vector<int > v[10000 ]; for (int i=0 ;i<m;i++){ string a,b; cin>>a>>b; int asa = abs (stoi (a)),asb = abs (stoi (b)); if (a.length () == b.length ()) { v[asa].push_back (asb); v[asb].push_back (asa); } arr[asa * 10000 + asb] = arr[asb * 10000 + asa] = true ; } scanf ("%d" , &k); for (int i = 0 ; i < k; i++) { int c, d; cin >> c >> d; vector<node> ans; for (int j = 0 ; j < v[abs (c)].size (); j++) { for (int k = 0 ; k < v[abs (d)].size (); k++) { if (v[abs (c)][j] == abs (d) || abs (c) == v[abs (d)][k]) continue ; if (arr[v[abs (c)][j] * 10000 + v[abs (d)][k]] == true ) ans.push_back (node{v[abs (c)][j], v[abs (d)][k]}); } } sort (ans.begin (), ans.end (), cmp); printf ("%d\n" , int (ans.size ())); for (int j = 0 ; j < ans.size (); j++) printf ("%04d %04d\n" , ans[j].a, ans[j].b); } return 0 ; }
改进后 ,重新捋一下思路 :
重点!!!
题目简化后为A寻找同性伴侣B,D寻找同性伴侣A,然后A和B是朋友,则添加到结果中。
由于数据错综复杂,所以不适合采用邻接矩阵,我们只需要记录他们之间的关系即可,数据结构可以直接采用 map<pair<int,int>,bool>来存储两者间的关系,其中make_pair<int,int>可以使用哈希映射,比如make_pair<a,b>可以等价为 a*10000+b,同时不会导致哈希冲突。
如何寻找同性朋友呢,可以使用结构体Person, Person下有一个vector用于存储同性朋友,为了快速找到 id 对应的结构体Person,我们可以用map将id直接映射到Person中。
如果用Int接收朋友,会出现+0000和-0000的情况,不能判断是否为同性朋友,题目说we use a negative sign to represent girls. 用一个符号代表女性朋友,我们可以先用string接收,然后stoi(s)转成Int形,用s.length是否相同来判断是否为同性朋友。 (对应2、3个测试点)
输出的数据必须从小到大排序
A在寻找同性朋友时应该避免找到他的同性伴侣D,坑点(对应4、5、6测试点)
输出要保留4位小数 %04d 对应(2、3测试点)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef struct Person { int id; vector<int > gayfriend; }Person; unordered_map<int ,Person> Map; unordered_map<int ,bool > isfriend; bool cmp (pair<int ,int > a,pair<int ,int > b) if (a.first==b.first) return a.second<b.second; else return a.first<b.first; } int main () int N,M; cin>>N>>M; for (int i=0 ;i<M;i++){ string sd1,sd2; cin>>sd1>>sd2; int id1 = abs (stoi (sd1)),id2 = abs (stoi (sd2)); if (Map.find (id1)==Map.end ()){ Person p; p.id = id1; Map[id1] = p; } if (Map.find (id2)==Map.end ()){ Person p; p.id = id2; Map[id2] = p; } isfriend[id1*10000 +id2]=true ; isfriend[id2*10000 +id1]=true ; if (sd1.length ()==sd2.length ()){ Map[id1].gayfriend.push_back (id2); Map[id2].gayfriend.push_back (id1); } } int K; cin>>K; for (int k=0 ;k<K;k++){ int id1,id2; cin>>id1>>id2; id1 = abs (id1); id2 = abs (id2); vector<pair<int ,int >> res; Person p1 = Map[id1]; Person p2 = Map[id2]; for (int i=0 ;i<p1.gayfriend.size ();i++) for (int j=0 ;j<p2.gayfriend.size ();j++){ int fri1 = p1.gayfriend[i]; int fri2 = p2.gayfriend[j]; if (fri1==id2 || fri2==id1) continue ; if (isfriend[fri1*10000 +fri2] && fri1!=fri2){ res.push_back (make_pair (fri1,fri2)); } } sort (res.begin (),res.end (),cmp); cout<<res.size ()<<endl; for (int i=0 ;i<res.size ();i++){ printf ("%04d %04d\n" ,res[i].first,res[i].second); } } }
2021.8.14 PAT 1132
题目大意:一个偶数个位的正整数num,把它从中间分成左右两个整数a、b,问num能不能被a和b的乘积整除,能的话输出yes,不能的话输出no
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main () int N; cin>>N; while (N--){ string s; cin>>s; long long c = stoll (s); string s1 = s.substr (0 ,s.length ()/2 ); string s2 = s.substr (s.length ()/2 ,s.length ()/2 ); long long c1 = stoll (s1); long long c2 = stoll (s2); if (c%(c1*c2)==0 ) cout<<"Yes" <<endl; else cout<<"No" <<endl; } }
因为没有判断c1*c2能不能是0,正确的是
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main () int N; cin>>N; while (N--){ string s; cin>>s; long long c = stoll (s); string s1 = s.substr (0 ,s.length ()/2 ); string s2 = s.substr (s.length ()/2 ,s.length ()/2 ); long long c1 = stoll (s1); long long c2 = stoll (s2); if ((c1*c2) &&c%(c1*c2)==0 ) cout<<"Yes" <<endl; else cout<<"No" <<endl; } }
PAT 1133
题目大意:给出一个链表,将链表分为三部分,第一部分小于0的数,第二部分小于=K的数,第三部分,大于K的数。
思路:数据结构,一个结构体,存放地址address,数number,下一跳nextaddress,再采用map使得可以方便地根据address查找结点所在的位置,然后获取下一跳,以此类推。最后通过三次查找把合适的部分取出来放到vector中,这样就排好序了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef struct node { string address; int number; string nextaddress; bool isvisited = false ; }node; unordered_map<string,node> M; vector<node> res; int main () string fadd; cin>>fadd; int N,K; cin>>N>>K; for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++){ node n; cin>>n.address>>n.number>>n.nextaddress; M[n.address] = n; } string nextaddress = fadd; while (nextaddress!="-1" ){ node n = M[nextaddress]; if (!n.isvisited && n.number<0 ) { res.push_back (n); M[nextaddress].isvisited = true ; } nextaddress = n.nextaddress; } nextaddress = fadd; while (nextaddress!="-1" ){ node n = M[nextaddress]; if (!n.isvisited && n.number<=K) { res.push_back (n); M[nextaddress].isvisited = true ; } nextaddress = n.nextaddress; } nextaddress = fadd; while (nextaddress!="-1" ){ node n = M[nextaddress]; if (!n.isvisited) { res.push_back (n); M[nextaddress].isvisited = true ; } nextaddress = n.nextaddress; } for (int i=0 ;i<res.size ();i++){ if (i!=res.size ()-1 ){ printf ("%s %d %s\n" ,res[i].address.c_str (),res[i].number,res[i+1 ].address.c_str ()); }else { printf ("%s %d -1" ,res[i].address.c_str (),res[i].number); } } }
PAT 1134
题目大意:n个顶点和m条边的图,分别给出m条边的两端顶点,然后对其进行k次查询,每次查询输入一个顶点集合,要求判断这个顶点集合是否能完成顶点覆盖,即图中的每一条边都至少有一个顶点在这个集合中。
思路:很简单,将顶点集合用map存,然后遍历边,判断是否有一个顶点在map中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;vector<pair<int ,int >> edgeset; int main () int N,M; cin>>N>>M; for (int i=0 ;i<M;i++){ int e1,e2; cin>>e1>>e2; edgeset.push_back (make_pair (e1,e2)); } int K; cin>>K; for (int i=0 ;i<K;i++){ int n; cin>>n; unordered_map<int ,int > Map; for (int j=0 ;j<n;j++){ int c; cin>>c; Map[c]=1 ; } bool flag = true ; for (int j=0 ;j<edgeset.size ();j++){ int e1 = edgeset[j].first, e2 = edgeset[j].second; if (Map.find (e1)==Map.end () && Map.find (e2)==Map.end ()){ flag = false ; break ; } } if (flag==false ) cout<<"No" <<endl; else cout<<"Yes" <<endl; } }
PAT 1135
题目大意 :给一棵二叉搜索树的前序遍历,判断它是否为红黑树,是输出Yes,否则输出No。
1、非红即黑
2、根结点是否为黑色
3、将NULL看成1个叶子节点,为黑black色
4、如果1个结点是红色,它的孩子节点是否都为黑色
5、从任意结点到叶子结点的路径中,黑色结点的个数是否相同
考场错误思路一 :由于是二叉排序树加上先序序列,可以递归构造二叉树。然后dfs的过程中判断第4个条件,并统计第5个条件(黑色结点个数是否相同)
一开始理解错了,从根节点到叶子结点的路径中,黑色结点个数相同。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef struct TreeNode { int val; TreeNode *left; TreeNode *right; TreeNode (int x) : val (x), left (NULL ), right (NULL ) {} }TreeNode; TreeNode* BuildTree (vector<int > preorder,int le,int ri) { if (le>ri) return nullptr ; int r = preorder[le]; TreeNode* root = new TreeNode (r); int i=le+1 ; while (abs (preorder[i])<abs (r)) i++; TreeNode* left = BuildTree (preorder,le+1 ,i-1 ); TreeNode* right = BuildTree (preorder,i,ri); root->left = left; root->right = right; return root; } vector<int > black_num; bool DFS (TreeNode* root,int black) if (root->val<0 ){ if (root->left && root->left->val<0 ) return false ; if (root->right && root->right->val<0 ) return false ; } if (root->val>0 ) black++; if (!root->left && !root->right){ black_num.push_back (black); return true ; } if (root->left && root->right) return DFS (root->left,black)&&DFS (root->right,black); else if (root->left) return DFS (root->left,black); else if (root->right) return DFS (root->right,black); } bool is_red_or_black (TreeNode* root) black_num.clear (); if (root==nullptr || root->val<0 ) return false ; bool dfs = DFS (root,0 ); if (dfs==false ) return false ; else { for (int i=0 ;i<black_num.size ()-1 ;i++){ if (black_num[i]!=black_num[i+1 ]) return false ; } } return true ; } int main () int N; cin>>N; while (N--) { int total; cin>>total; vector<int > preorder (total,0 ) ; for (int i=0 ;i<total;i++){ cin>>preorder[i]; } TreeNode* tree = BuildTree (preorder,0 ,total-1 ); bool flag = is_red_or_black (tree); if (flag) cout<<"Yes" <<endl; else cout<<"No" <<endl; } }
第3个结点段错误,建树过程中存在一些问题。
考场错误思路二 :为了使得每一层到叶子结点的黑色结点数相同,我私自认为
//判断是否为红黑树
//1、红黑树一定是一棵平衡二叉树
//2、红黑树一定层次分明,一层黑一层白
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef struct TreeNode { int val; TreeNode *left; TreeNode *right; TreeNode (int x) : val (x), left (NULL ), right (NULL ) {} }TreeNode; TreeNode* BuildTree (vector<int > preorder,int le,int ri) { if (le>ri) return nullptr ; int r = preorder[le]; TreeNode* root = new TreeNode (r); int i=le+1 ; while (i<ri && abs (preorder[i])<abs (r)) i++; TreeNode* left = BuildTree (preorder,le+1 ,i-1 ); TreeNode* right = BuildTree (preorder,i,ri); root->left = left; root->right = right; return root; } int gethigh (TreeNode* root) if (root==nullptr ) return 0 ; int lefthigh = gethigh (root->left); int righhigh = gethigh (root->right); return 1 +max (lefthigh,righhigh); } bool isbalanced (TreeNode* root) if (root==nullptr ) return true ; int lh = gethigh (root->left); int rh = gethigh (root->right); if (lh-rh>1 || rh-lh>1 ) return false ; return isbalanced (root->left) && isbalanced (root->right); } bool levelsearch (TreeNode* root) int black = 1 ; queue<TreeNode*> Q; Q.push (root); while (!Q.empty ()){ int lsize = Q.size (); for (int i=0 ;i<lsize;i++){ TreeNode* p = Q.front (); Q.pop (); if (p->val*black<0 ) return false ; if (p->left) Q.push (p->left); if (p->right) Q.push (p->right); } black*=-1 ; } return true ; } bool is_red_or_black (TreeNode* root) if (root==nullptr || root->val<0 ) return false ; if (!isbalanced (root)) return false ; if (!levelsearch (root)) return false ; return true ; } int main () int N; cin>>N; while (N--) { int total; cin>>total; vector<int > preorder (total,0 ) ; for (int i=0 ;i<total;i++){ cin>>preorder[i]; } TreeNode* tree = BuildTree (preorder,0 ,total-1 ); bool flag = is_red_or_black (tree); if (flag) cout<<"Yes" <<endl; else cout<<"No" <<endl; } }
当然是错误的,所以红黑树不是平衡二叉树
正确思路 :
这里是判断平衡二叉树的变体,算高度时只统计黑色结点的个数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef struct TreeNode { int val; TreeNode *left; TreeNode *right; TreeNode (int x) : val (x), left (NULL ), right (NULL ) {} }TreeNode; TreeNode* BuildTree (vector<int > preorder,int le,int ri) { if (le>ri) return nullptr ; int r = preorder[le]; TreeNode* root = new TreeNode (r); int i=le+1 ; while (i<ri && abs (preorder[i])<abs (r)) i++; TreeNode* left = BuildTree (preorder,le+1 ,i-1 ); TreeNode* right = BuildTree (preorder,i,ri); root->left = left; root->right = right; return root; } int gethigh (TreeNode* root) if (root==nullptr ) return 0 ; int l = gethigh (root->left); int r = gethigh (root->right); return root->val > 0 ? max (l, r) + 1 : max (l, r); } bool isbalanced (TreeNode* root) if (root==nullptr ) return true ; int lh = gethigh (root->left); int rh = gethigh (root->right); if (lh!=rh) return false ; return isbalanced (root->left) && isbalanced (root->right); } bool DFS (TreeNode* root) if (root->val<0 ){ if (root->left && root->left->val<0 ) return false ; if (root->right && root->right->val<0 ) return false ; } if (!root->left && !root->right){ return true ; } if (root->left && root->right) return DFS (root->left)&&DFS (root->right); else if (root->left) return DFS (root->left); else if (root->right) return DFS (root->right); } bool is_red_or_black (TreeNode* root) if (root==nullptr || root->val<0 ) return false ; if (!isbalanced (root)) return false ; if (!DFS (root)) return false ; return true ; } int main () int N; cin>>N; while (N--) { int total; cin>>total; vector<int > preorder (total,0 ) ; for (int i=0 ;i<total;i++){ cin>>preorder[i]; } TreeNode* tree = BuildTree (preorder,0 ,total-1 ); bool flag = is_red_or_black (tree); if (flag) cout<<"Yes" <<endl; else cout<<"No" <<endl; } }
2021.8.20 PAT 1128
判断同一行同一列对角线上有无N皇后,同一列题目已经保证了,同一行用map保证,对角线判断j-i==abs(row[j]-row[i] ) O(n*n)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main () int K; cin>>K; while (K--){ bool flag = true ; int map[1001 ]={0 }; int N; cin>>N; vector<int > row (N+1 ,-1 ) ; for (int i=1 ;i<=N;i++){ cin>>row[i]; if (map[row[i]]==1 ) flag=false ; else map[row[i]]++; } for (int i=1 ;i<row.size ();i++) for (int j=i+1 ;j<row.size ();j++){ if (j-i==abs (row[j]-row[i])) { flag = false ; break ; } } if (flag) cout<<"YES" <<endl; else cout<<"NO" <<endl; } }
PAT 1129
题目大意 :给定一个序列,求目前出现次数最多的k个数字。如果数字出现次数相同,升序排列。
解题思路 :类似LRU,寻找出现次数最多的三个。
数据结构的设计,一个vector<pair<int,int>> KWindow; 存放出现次数最多的K个数字,pair->first代表数字,pair->second代表出现的次数,每加入一个数字,我们就要判断是否要更新KWindow.采用unordered_map存放这个数字在目前出现了几次。
判断是否需要更新KWindow?
情况一:新加入的数字在KWindow中,直接在KWindow中更新就好了,然后排序。
情况二:新加入的数字不在KWindow中,而且KWindow还没满,直接加入,然后排序。
情况三:新加入的数字不在KWindow中,而且KWindow满了,判断是否需要替换,由于之前已经排好序了,只要和最后一个比较,如果次数<最后一个,或者次数相同,数字小于最后一个,则替换掉最后一个。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;vector<int > input; unordered_map<int ,int > Map; vector<pair<int ,int >> KWindow; bool finda (int target,int fre) for (int i=0 ;i<KWindow.size ();i++){ if (KWindow[i].first==target){ KWindow[i].second = fre; return true ; } } return false ; } bool cmp (pair<int ,int > a,pair<int ,int > b) if (a.second==b.second) return a.first<b.first; return a.second>b.second; } int main () int Min = 0 ; int N,K; cin>>N>>K; for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++){ int temp; cin>>temp; input.push_back (temp); } for (int i=1 ;i<N;i++){ Map[input[i-1 ]]++; if (!finda (input[i-1 ],Map[input[i-1 ]])){ if (KWindow.size ()<K){ KWindow.push_back (make_pair (input[i-1 ],Map[input[i-1 ]])); }else if (Map[input[i-1 ]]>Min && KWindow.size ()==K){ KWindow.pop_back (); KWindow.push_back (make_pair (input[i-1 ],Map[input[i-1 ]])); }else if (Map[input[i-1 ]]==Min && KWindow.size ()==K){ if (KWindow[KWindow.size ()-1 ].first>input[i-1 ]){ KWindow.pop_back (); KWindow.push_back (make_pair (input[i-1 ],Map[input[i-1 ]])); } } } sort (KWindow.begin (),KWindow.end (),cmp); Min = KWindow[KWindow.size ()-1 ].second; printf ("%d: " ,input[i]); for (int i=0 ;i<KWindow.size ();i++){ cout<<KWindow[i].first; if (i!=KWindow.size ()-1 ) cout<<" " ; } cout<<endl; } }
PAT 1130
题目大意 :给一个二叉树,输出中缀表达式,且加上括号表示运算的优先级
解题思路 :给定的输入建树的过程我感觉比较复杂。在输入的第一遍建立TreeNode,然后将string映射到TreeNode中,但这样会有一个问题,就是string的值可能相同,所以我给每个输入结点设置了一个id,第二遍结点全部都创建好了,我们就可以根据左子树所在的行数,和右子树所在的行数 所 映射到的结点建立连接。 最后就是寻找根节点的过程,用set就可以了,把有父节点的加入set,最后不在set的那个就是根节点。
后面就是中序遍历,很简单了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef struct TreeNode { string val; TreeNode* left,*right; TreeNode (string val):val (val),left (nullptr ),right (nullptr ){}; }TreeNode; unordered_set<int > Set; unordered_map<int ,TreeNode*> MM; typedef struct input { string val; int id; int left; int right; }input; vector<input> I; TreeNode* BuildTree () for (int i=1 ;i<I.size ();i++){ TreeNode* r = MM[I[i].id]; if (I[i].left!=-1 ){ TreeNode* left = MM[I[I[i].left].id]; Set.insert (I[I[i].left].id); r->left = left; } if (I[i].right!=-1 ){ TreeNode* right = MM[I[I[i].right].id]; Set.insert (I[I[i].right].id); r->right = right; } } for (int i=1 ;i<I.size ();i++){ if (Set.find (I[i].id)==Set.end ()){ return MM[I[i].id]; } } } void preorder (TreeNode* root) if (root->left){ if (root->left->left || root->left->right) cout<<"(" ; preorder (root->left); if (root->left->left || root->left->right) cout<<")" ; } cout<<root->val; if (root->right){ if (root->right->left || root->right->right) cout<<"(" ; preorder (root->right); if (root->right->left || root->right->right) cout<<")" ; } } int main () I.push_back (input{}); int N; cin>>N; for (int i=1 ;i<=N;i++){ input ii; cin>>ii.val>>ii.left>>ii.right; ii.id=i; I.push_back (ii); TreeNode* r = new TreeNode (ii.val); MM[ii.id] = r; } TreeNode* root = BuildTree (); preorder (root); }
PAT 1131
题目大意 :
给出各地铁线所经过的站点,构成一张地铁交通图。再给出起点和终点,让你找出最快的一条路径,如果路径不唯一就选择中转次数最少的那一条 。
解题思路 :
我没有考虑到这一点,所以2,4测试点没有过。
1、本来想用Floyd算法,但是发线每条边权值都为1,所以用BFS搜索即可。
2、构造邻接矩阵有一个问题,就是要解决0000四位整数映射问题,不然开辟10000*10000个空间未免太大了,我的做法是读入是写到set中,然后遍历set建立string-int的映射,还有int-string的映射。
3、建图,采用邻接矩阵,这里存储的是无向图,因此根据线路构造的时候要存储两次,邻接矩阵存储的边值代表线路(几号线)而不是代价。
4、BFS寻找最短路径,用path来存储路径,path[i] = j表示,从j->i,方便往回寻找
5、找到后需要输出路径,顺着path往回寻找,将结果放到path_中。
6、最后在把path带入到Graph中构造出所要的线路结果。
代码 :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;vector<vector<string>> input; unordered_set<string> Set; unordered_map<string,int > MapStoI; unordered_map<int ,string> MapItoS; vector<vector<int >> Graph; int kkk=0 ; void BFS (string start,string destination) int begin = MapStoI[start]; int end = MapStoI[destination]; vector<bool > visited (kkk,false ) ; vector<int > path (kkk,0 ) ; queue<int > Q; Q.push (begin); while (!Q.empty ()) { int t = Q.front (); Q.pop (); if (t==end) break ; for (int i=0 ;i<kkk;i++){ if (visited[i]==false && Graph[t][i]){ Q.push (i); visited[i] = true ; path[i] = t; } } } int p = end; vector<int > path_; path_.push_back (p); while (p!=begin){ int temp = path[p]; path_.push_back (temp); p = temp; } cout<<path_.size ()-1 <<endl; reverse (path_.begin (),path_.end ()); int bbbb = path_[0 ]; int eeee = path_[0 ]; int xianlu = Graph[path_[0 ]][path_[1 ]]; for (int i=1 ;i<path_.size ();i++){ if (Graph[path_[i]][path_[i-1 ]]==xianlu) eeee = path_[i]; else { printf ("Take Line#%d from %s to %s.\n" ,xianlu,MapItoS[bbbb].c_str (),MapItoS[eeee].c_str ()); xianlu = Graph[path_[i]][path_[i-1 ]]; bbbb = eeee; eeee = i; } } printf ("Take Line#%d from %s to %s.\n" ,xianlu,MapItoS[bbbb].c_str (),MapItoS[end].c_str ()); } void BuildGraph () Graph.resize (kkk,vector <int >(kkk,0 )); for (int i=0 ;i<input.size ();i++){ for (int j=1 ;j<input[i].size ();j++){ Graph[MapStoI[input[i][j-1 ]]][MapStoI[input[i][j]]] = i+1 ; Graph[MapStoI[input[i][j]]][MapStoI[input[i][j-1 ]]] = i+1 ; } } } int main () int M; cin>>M; for (int i=0 ;i<M;i++){ int N; cin>>N; vector<string> C (N) ; for (int j=0 ;j<N;j++){ cin>>C[j]; Set.insert (C[j]); } input.push_back (C); } unordered_set<string>::iterator iter; for (iter=Set.begin ();iter!=Set.end ();iter++){ MapItoS[kkk] = *iter; MapStoI[*iter]=kkk++; } BuildGraph (); int Q; cin>>Q; while (Q--){ string start,end; cin>>start>>end; BFS (start,end); } }
答案正解 :
1、使用邻接表存储 2、使用line的键为a*10000+b,建立边到线路的映射 3、dfs暴力深搜
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int visit[10000 ],minCnt,minTransfer; vector<vector<int >> v (10000 ); vector<int > path,tempPath; int start,end1;unordered_map<int ,int > line; int transferCnt (vector<int > a) int cnt=-1 ,preLine=0 ; for (int i=1 ;i<a.size ();i++){ if (line[a[i-1 ]*10000 +a[i]] != preLine) cnt++; preLine=line[a[i-1 ]*10000 +a[i]]; } return cnt; } void dfs (int node,int cnt) if (node==end1 && (cnt<minCnt || (cnt ==minCnt&&transferCnt (tempPath) <minTransfer))) { minCnt=cnt; minTransfer=transferCnt (tempPath); path=tempPath; } if (node == end1) return ; for (int i=0 ;i<v[node].size ();i++){ if (visit[v[node][i]] == 0 ){ visit[v[node][i]]=1 ; tempPath.push_back (v[node][i]); dfs ( v[node][i] ,cnt+1 ); visit[v[node][i] ]=0 ; tempPath.pop_back (); } } } int main () int n,m,k,pre,temp; scanf ("%d" ,&n); for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++){ scanf ("%d%d" ,&m,&pre); for (int j=1 ;j<m;j++){ scanf ("%d" ,&temp); v[pre].push_back (temp); v[temp].push_back (pre); line[pre*10000 +temp]=line[temp*10000 +pre]=i+1 ; pre=temp; } } scanf ("%d" ,&k); for (int i=0 ;i<k;i++){ scanf ("%d%d" ,&start,&end1); minCnt=99999 ,minTransfer=99999 ; tempPath.clear (); tempPath.push_back (start); visit[start]=1 ; dfs (start,0 ); visit[start]=0 ; printf ("%d\n" ,minCnt); int preLine=0 ,preTransfer=start; for (int j=1 ;j<path.size () ; j++){ if (line[path[j-1 ]*10000 +path[j]] != preLine){ if (preLine != 0 ) printf ("Take Line#%d from %04d to %04d.\n" , preLine,preTransfer,path[j-1 ] ); preLine=line[path[j-1 ]*10000 +path[j]]; preTransfer = path[j-1 ]; } } printf ("Take Line#%d from %04d to %04d.\n" , preLine,preTransfer,end1); } return 0 ; }
2021.8.29 1h40min搞定 98分
PAT 1124
题目大意 :明PAT考了满分,高兴之余决定发起微博转发抽奖活动,从转发的网友中按顺序每隔N个人就发出一个红包。请你编写程序帮助他确定中奖名单。注意:可能有人转发多次,但不能中奖多次。所以如果处于当前中奖位置的网友已经中过奖,则跳过他顺次取下一位。按照输入的顺序输出中奖名单,每个昵称占一行。如果没有人中奖,则输出“Keep going…”
思路 :只要读懂题目,没有任何头脑的题,一个while循环,加一个set判断重复轻松搞定。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int M,N,S;int main () cin>>M>>N>>S; vector<string> L (M+1 ,"" ) ; set<string> Set; vector<string> res; for (int i=1 ;i<=M;i++){ cin>>L[i]; } int cur = S; while (cur<=M){ if (Set.find (L[cur])==Set.end ()){ Set.insert (L[cur]); res.push_back (L[cur]); cur += N; }else { cur += 1 ; } } if (Set.size ()==0 ) cout<<"Keep going..." ; else { for (int i=0 ;i<res.size ();i++){ cout<<res[i]<<endl; } } }
PAT 1125
题目大意: 绳子每次打结长度都会减小到原来的一半,那么打结的顺序会影响到最终的长度。求最终长度不超过的数。
刚开始都没太懂题目的意思…最后想想应该是排序+模拟。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main () int N; cin>>N; vector<int > Input (N,0 ) ; for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++) cin>>Input[i]; sort (Input.begin (),Input.end ()); int possible = 0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++){ possible = double (possible)/2 + double (Input[i])/2 ; } printf ("%d" ,possible); }
注意:只需排序一次,觉得要每次有新绳子就要排序一下,比你小的两个数的平均数肯定也是最小的呀!
测试点1是只有一段绳子,开始的两段绳子要特殊处理,总长度初值应该是最小绳子长度,而不是0
稍加修改
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main () int N; cin>>N; vector<int > Input (N,0 ) ; for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++) cin>>Input[i]; sort (Input.begin (),Input.end ()); int possible = Input[0 ]; for (int i=1 ;i<N;i++){ possible = (possible+Input[i])/2 ; } printf ("%d" ,possible); }
PAT 1126
题目大意:
对于无向图来说:
是欧拉图,连通且所有节点的度为偶数
是半欧拉图,连通且只有两个节点的度为奇数
转化为统计图的度,然后判断几个节点的度是奇数,如果仅仅只是这样简单处理测试点3过不去,后向仔细看题看到了
需要是连通图才可以。
由于懒得构造邻接矩阵再进行遍历,这里使用并查集来判断是不是完全连通图、
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;class UnionFind {public : int *parents; int total; UnionFind (int total){ this ->total = total; parents = new int [total+1 ]; for (int i=1 ;i<=total;i++){ parents[i] = i; } } void Union (int node1,int node2) int p1 = find (node1); int p2 = find (node2); if (p1!=p2){ parents[p1] = p2; } } int find (int node) while (parents[node]!=node){ parents[node] = parents[parents[node]]; node = parents[node]; } return node; } bool isConnected (int node1,int node2) return find (node1)==find (node2); } bool isEurn () for (int i=1 ;i<total;i++){ if (isConnected (i,i+1 )==false ) return false ; } return true ; } }; int main () int N,M; cin>>N>>M; vector<int > degree (N+1 ,0 ) ; UnionFind* uf = new UnionFind (N); for (int i=0 ;i<M;i++){ int n1,n2; cin>>n1>>n2; degree[n1]++; degree[n2]++; uf->Union (n1,n2); } int oddnum = 0 ; for (int i=1 ;i<=N;i++){ if (i==N) printf ("%d\n" ,degree[i]); else printf ("%d " ,degree[i]); if (degree[i]%2 ) oddnum++; } if (uf->isEurn ()==false ) {cout<<"Non-Eulerian" ; return 0 ;} if (oddnum==0 ) cout<<"Eulerian" ; else if (oddnum==2 ) cout<<"Semi-Eulerian" ; else cout<<"Non-Eulerian" ; }
PAT 1127
题目大意 :给定中序和后序序列,建立一棵树,然后对这棵树进行Z型层序遍历。
思路 :就是在层序遍历的时候需要把层数分出来,然后设置一个flag,需要的时候把序列翻转。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef struct TreeNode { int val; TreeNode* left,*right; TreeNode (int val):val (val),left (nullptr ),right (nullptr ){}; }TreeNode; vector<int > inorder; vector<int > postorder; unordered_map<int ,int > M; TreeNode* BuildTree (int inleft,int inright,int postleft,int postright) { if (inleft>inright) return nullptr ; int curnode = postorder[postright]; TreeNode* root = new TreeNode (curnode); int mid = M[curnode]; TreeNode* left = BuildTree (inleft,mid-1 ,postleft,postleft+mid-1 -inleft); TreeNode* right = BuildTree (mid+1 ,inright,postleft+mid-1 -inleft+1 ,postright-1 ); root->left = left; root->right = right; return root; } vector<int > res; void ZigZag (TreeNode* root) int yinzi = -1 ; queue<TreeNode*> q; q.push (root); while (!q.empty ()){ vector<int > temp; int levelsize = q.size (); for (int i=0 ;i<levelsize;i++){ TreeNode* node = q.front (); q.pop (); temp.push_back (node->val); if (node->left) q.push (node->left); if (node->right) q.push (node->right); } if (yinzi==-1 ) reverse (temp.begin (),temp.end ()); yinzi *= -1 ; res.insert (res.end (),temp.begin (),temp.end ()); } } int main () int N; cin>>N; for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++){ int t; cin>>t; inorder.push_back (t); M[t] = i; } for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++){ int t; cin>>t; postorder.push_back (t); } TreeNode* root = BuildTree (0 ,N-1 ,0 ,N-1 ); ZigZag (root); for (int i = 0 ; i < res.size (); i++) { if (i==res.size ()-1 ) printf ("%d" ,res[i]); else printf ("%d " ,res[i]); } }
2021.9.5 PAT 1120
题意:统计数的各位数字之和,并升序输出
用set啥的就行了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;vector<int > res; unordered_map<int ,int > Map; int main () int N; cin>>N; for (int i=0 ;i<N;i++){ string s; cin>>s; int count = 0 ; for (int j=0 ;j<s.length ();j++){ count += s[j]-'0' ; } Map[count]++; } unordered_map<int ,int >::iterator iter; for (iter=Map.begin ();iter!=Map.end ();iter++) { res.push_back (iter->first); } sort (res.begin (),res.end ()); printf ("%d\n" ,res.size ()); for (int i=0 ;i<res.size ();i++){ if (i==res.size ()-1 ) printf ("%d" ,res[i]); else printf ("%d " ,res[i]); } }
PAT 1121
题目大意:给N对夫妻编号,再给M个派对里的参与人的编号,输出单身的人的编号(包括夫妻没全部到场的也算单身)
用map统计夫妻配对的情况,再用一个map[10000]统计到场情况,最后一一排除即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main () vector<int > Map (100000 ,0 ) ; vector<int > input (100000 ,0 ) ; vector<int > in; vector<int > res; int N; cin>>N; while (N--) { int t,b; cin>>t>>b; Map[t]=b; Map[b]=t; } int M; cin>>M; while (M--){ int id; cin>>id; in.push_back (id); input[id]++; } for (int i=0 ;i<in.size ();i++){ if (input[Map[in[i]]]!=0 ) continue ; else res.push_back (in[i]); } sort (res.begin (),res.end ()); printf ("%d\n" ,res.size ()); for (int i=0 ;i<res.size ();i++){ if (i==res.size ()-1 ) printf ("%d" ,res[i]); else printf ("%d " ,res[i]); } }
改用set存储M个人的信息,就可以通过
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main () vector<int > Map (100000 ,0 ) ; vector<int > input (100000 ,0 ) ; vector<int > in; set<int > res; int N; cin>>N; while (N--) { int t,b; cin>>t>>b; Map[t]=b; Map[b]=t; } int M; cin>>M; while (M--){ int id; cin>>id; in.push_back (id); input[id]++; } for (int i=0 ;i<in.size ();i++){ if (input[Map[in[i]]]!=0 ) continue ; else res.insert (in[i]); } printf ("%d\n" ,res.size ()); for (auto it=res.begin ();it!=res.end ();it++) { if (it!=res.begin ())printf (" " ); printf ("%05d" ,*it); } }
PAT 1122
判断是否是哈密顿回路,随便写写就AC了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main () int V,E; cin>>V>>E; vector<vector<int >> graph (V+1 ,vector <int >(V+1 ,0 )); for (int i=0 ;i<E;i++){ int e1,e2; cin>>e1>>e2; graph[e1][e2]=1 ; graph[e2][e1]=1 ; } int Q; cin>>Q; while (Q--){ int n; cin>>n; vector<int > Input (n) ; unordered_set<int > Set; for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++) cin>>Input[i]; if (Input.size ()!=V+1 || Input[0 ]!=Input[V]){ cout<<"NO" <<endl; continue ; } for (int j=0 ;j<V;j++){ if (graph[Input[j]][Input[j+1 ]]==1 ){ Set.insert (Input[j]); } else { break ; } } if (Set.size ()==V) cout<<"YES" <<endl; else cout<<"NO" <<endl; } }
PAT 1123